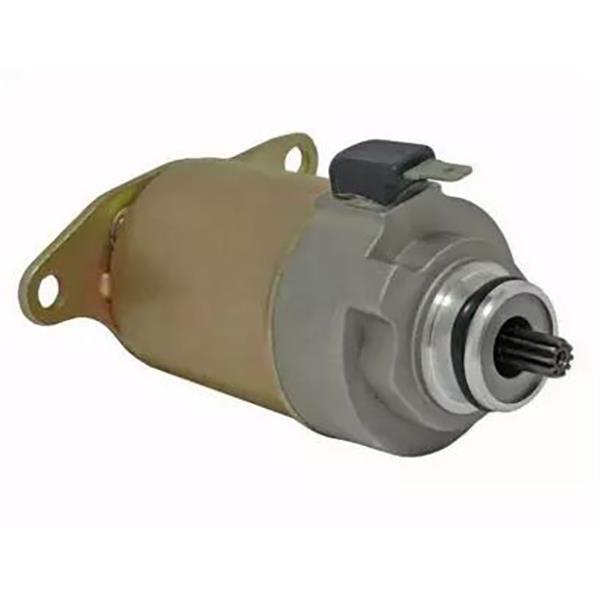
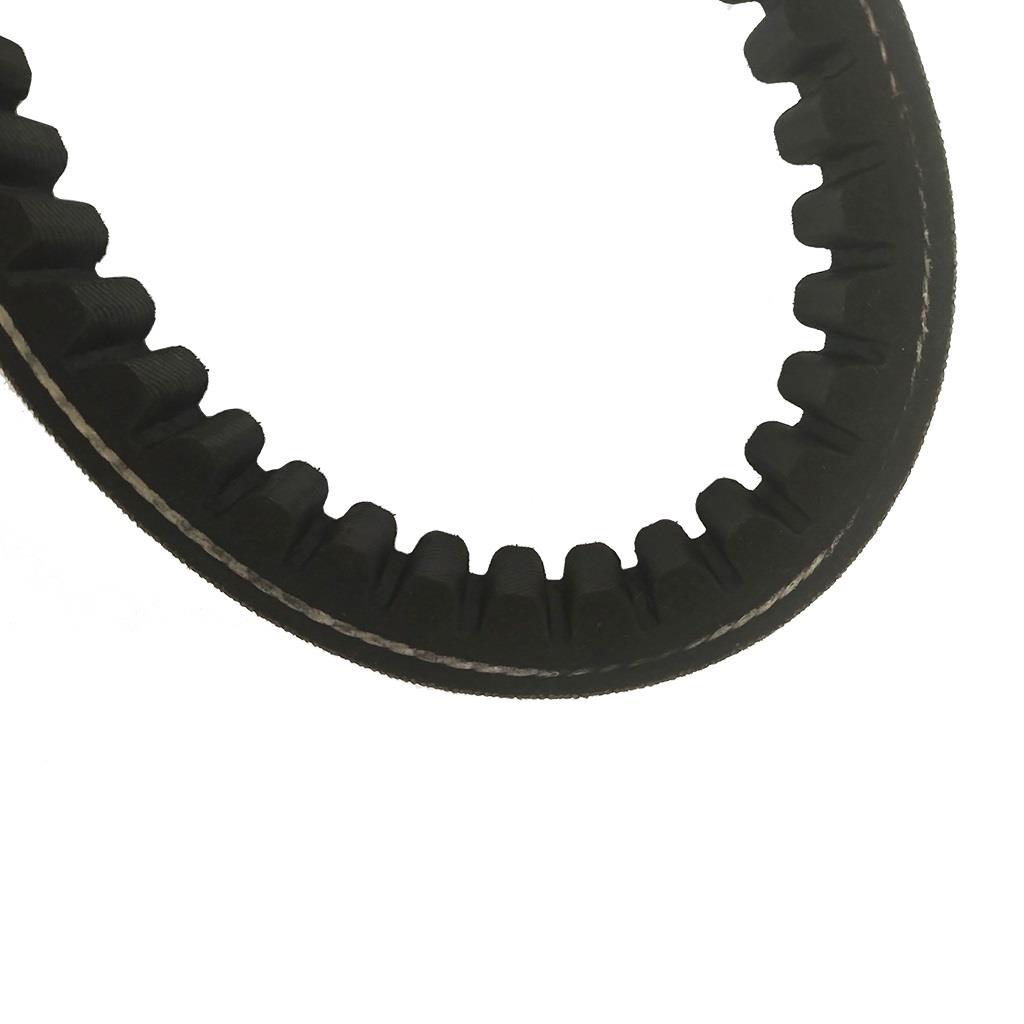
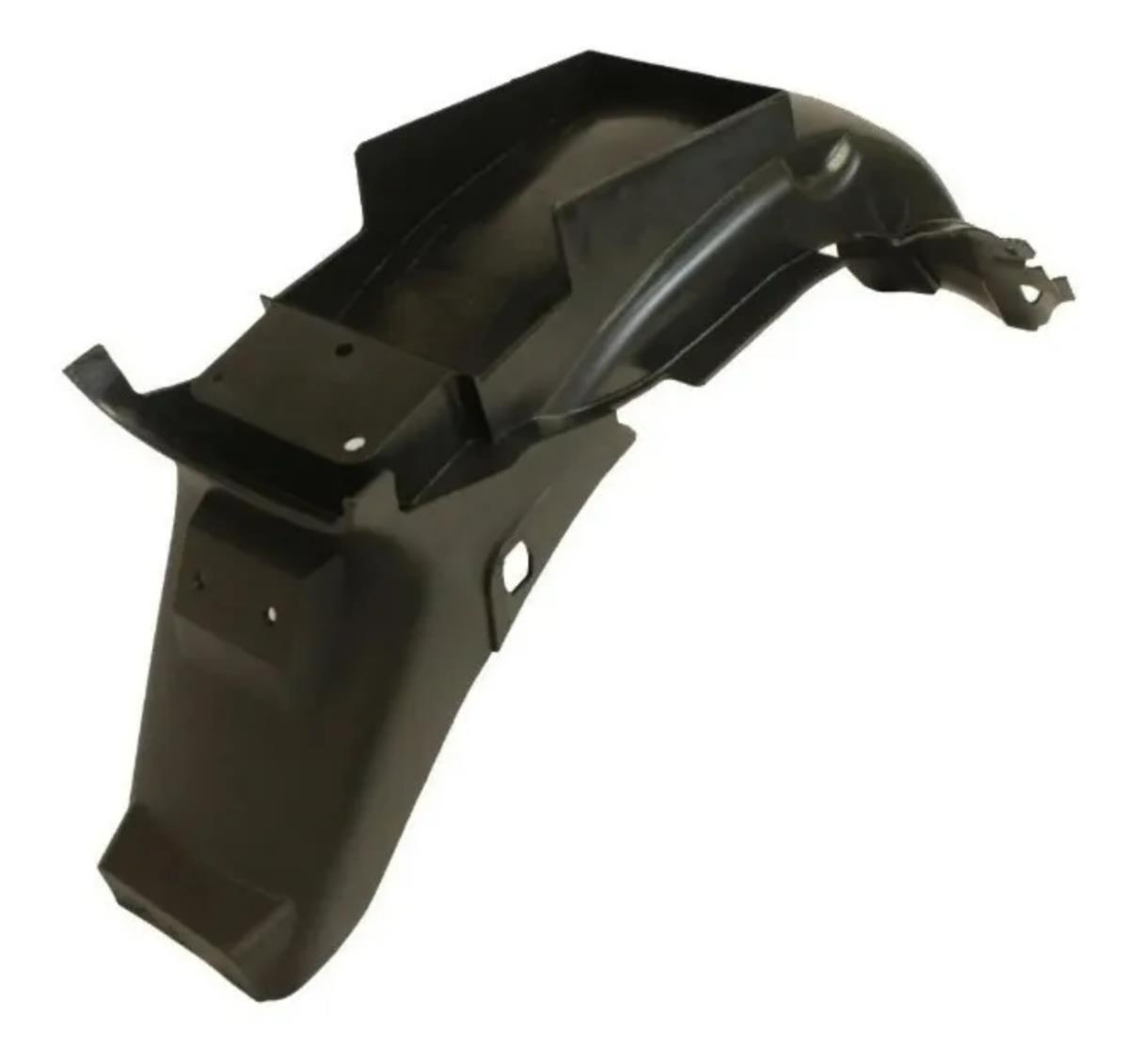
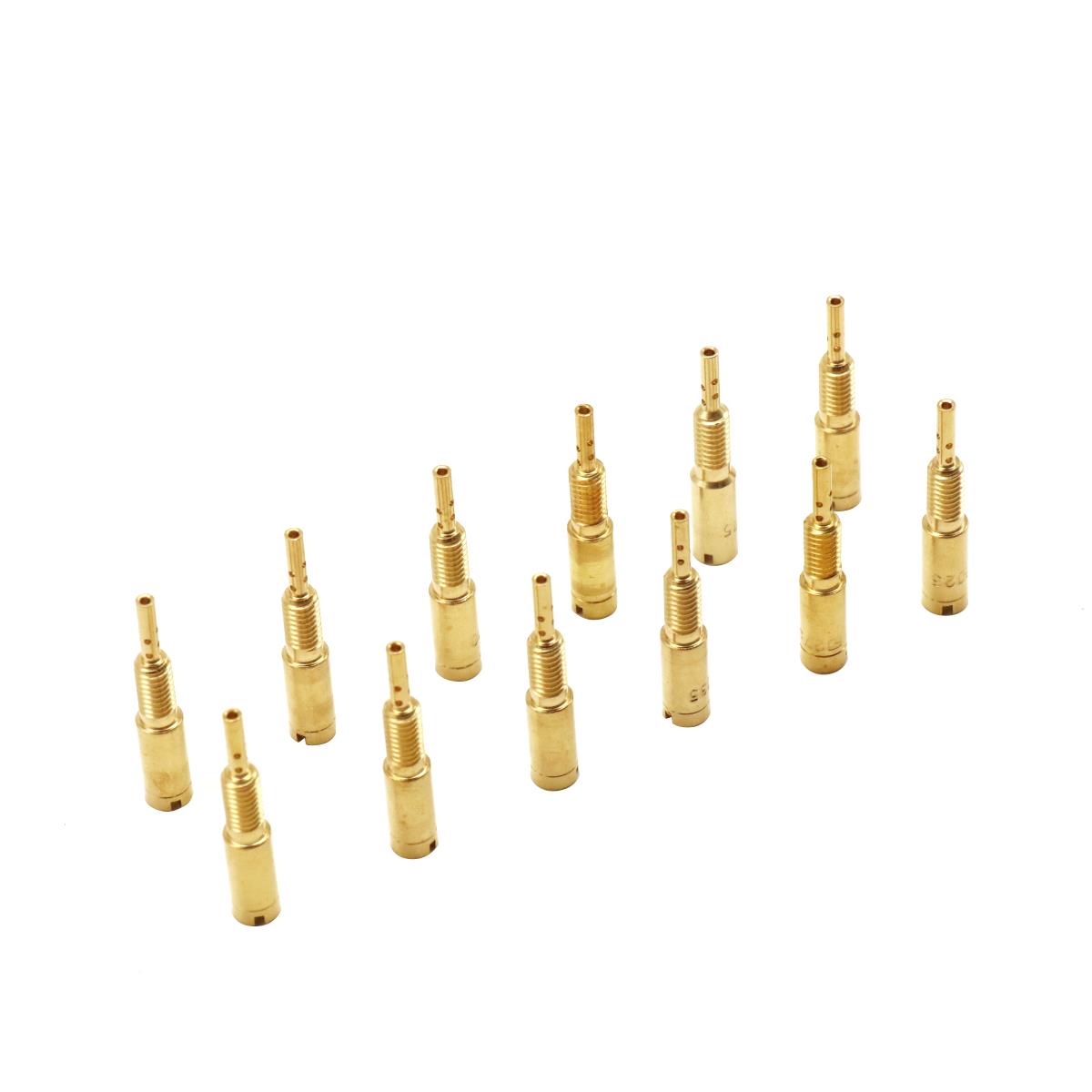
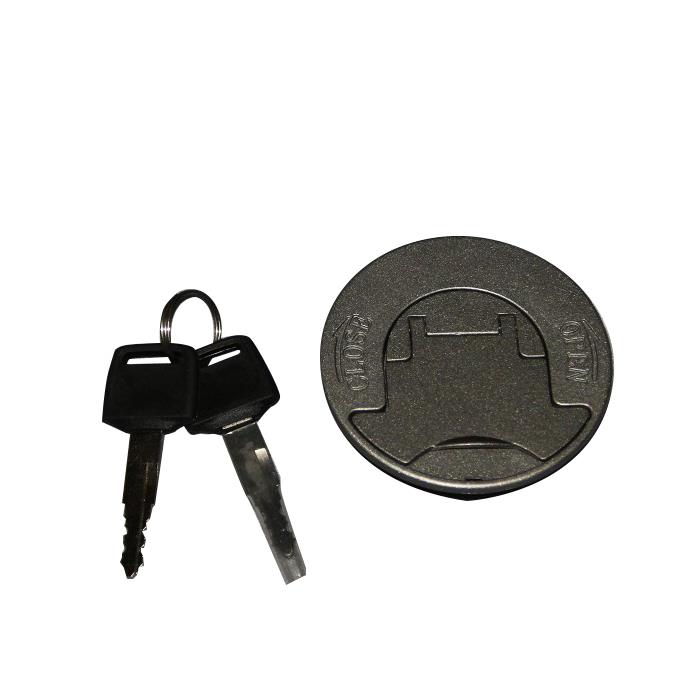
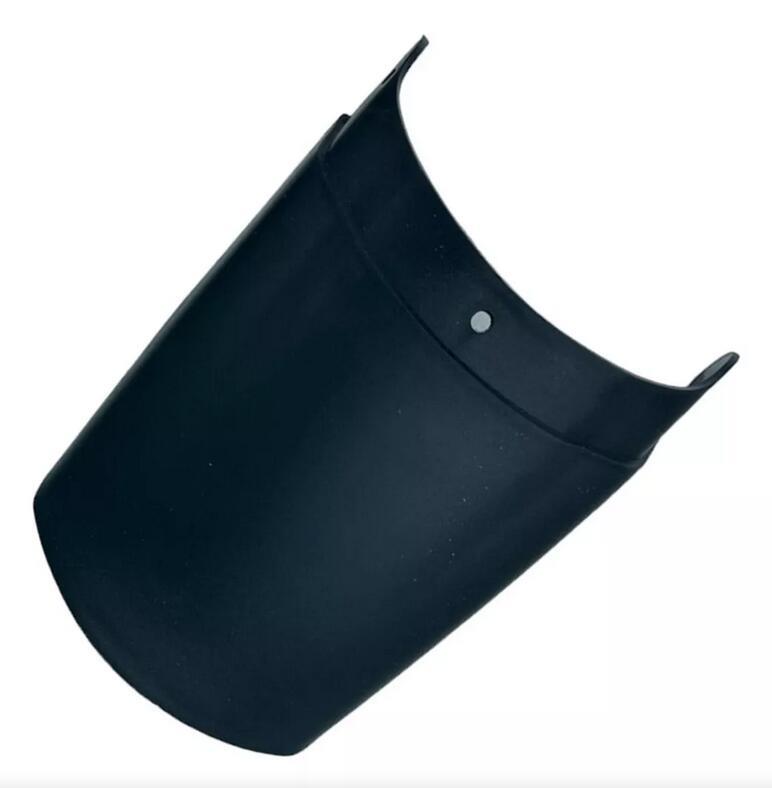
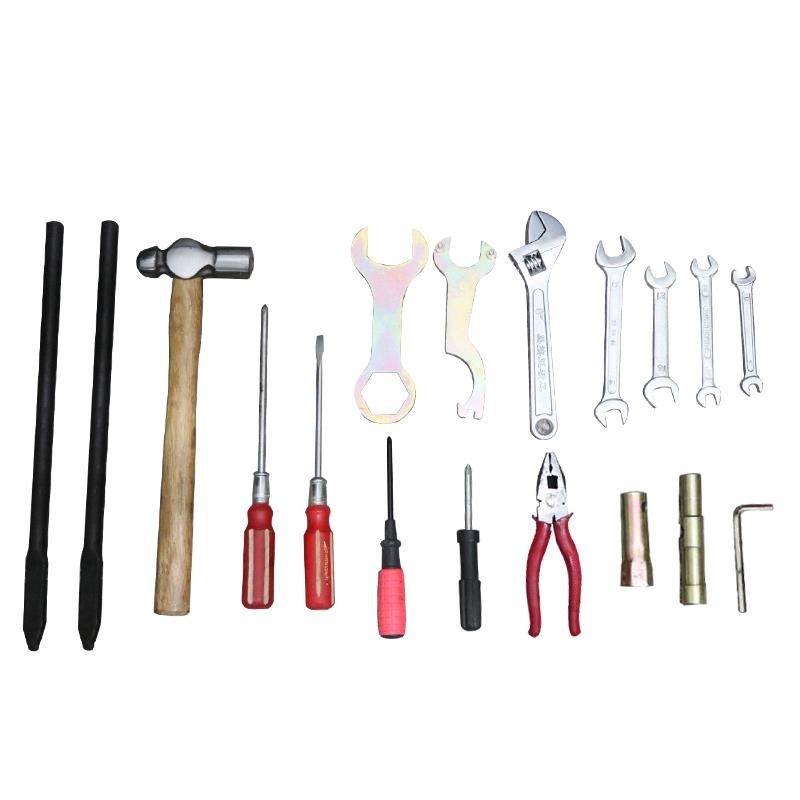
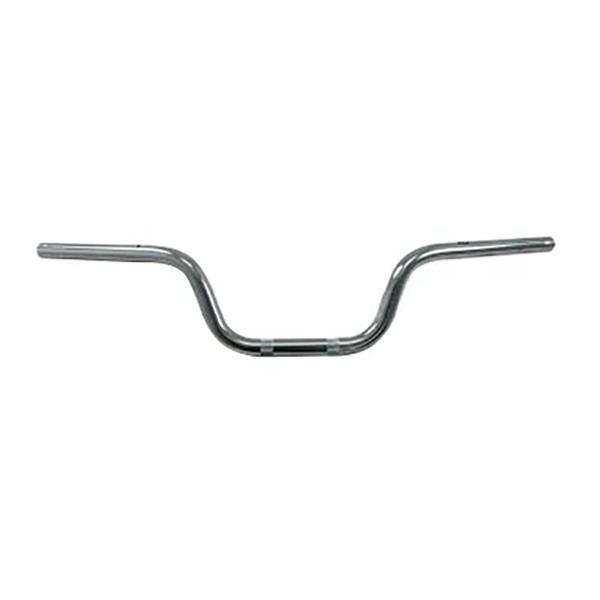
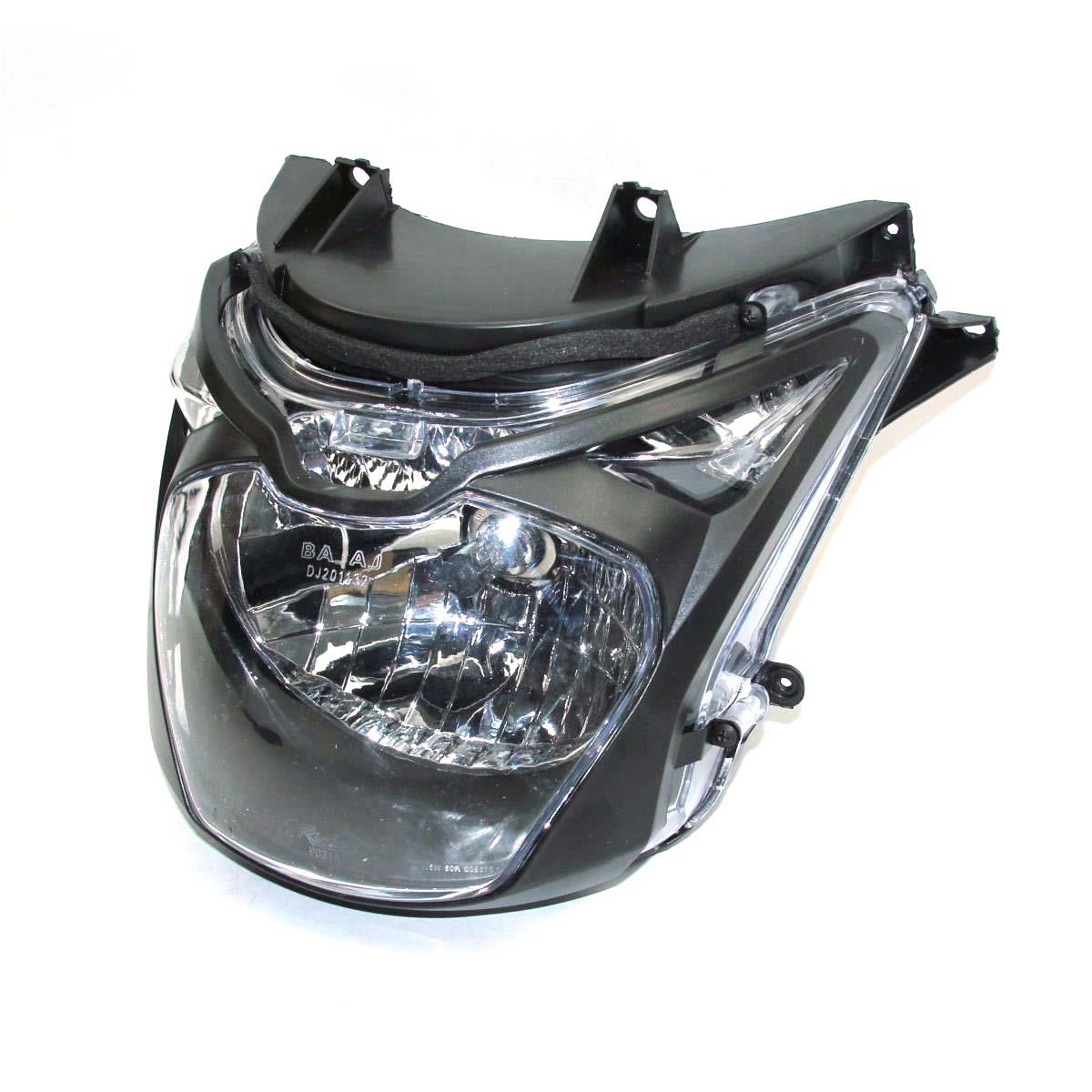
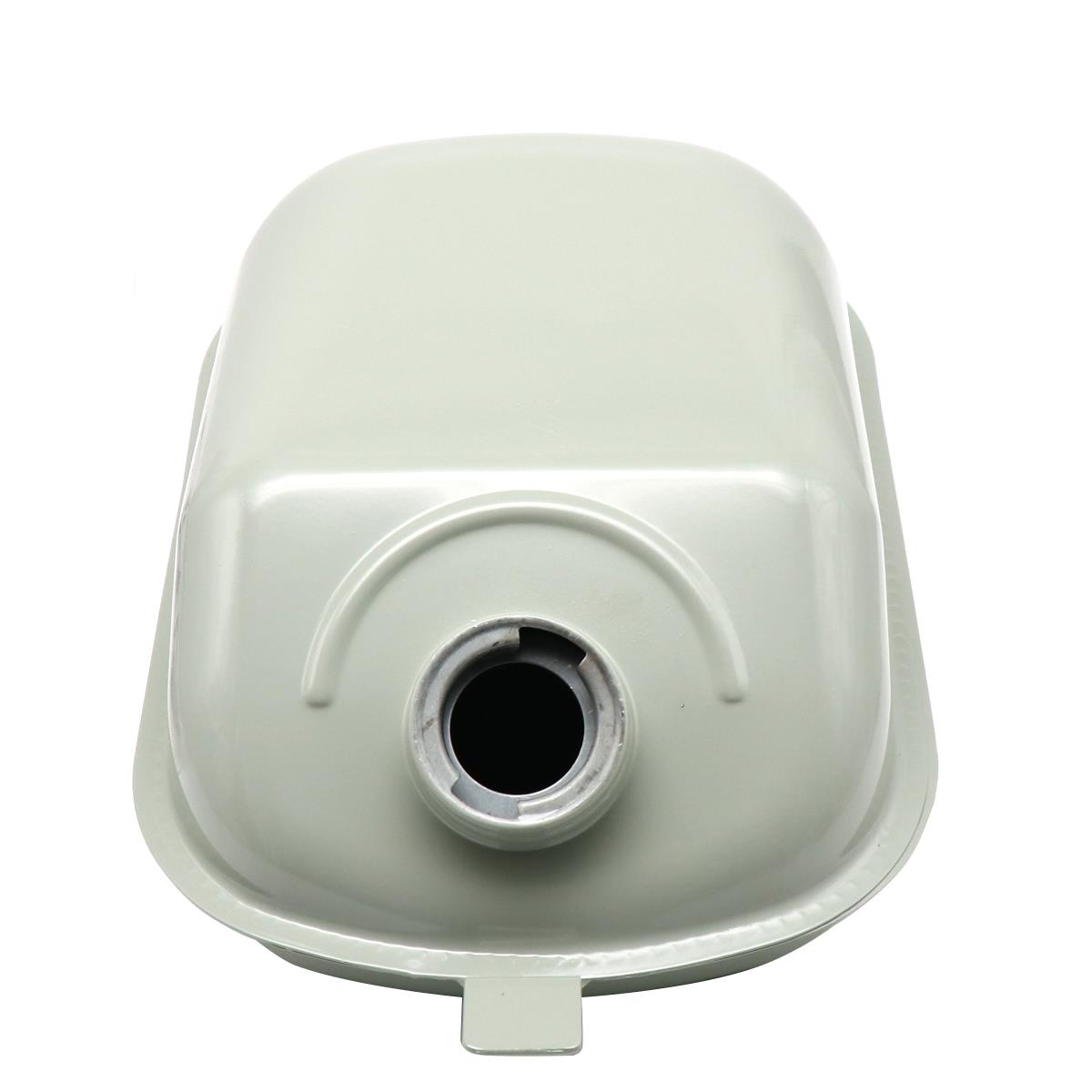
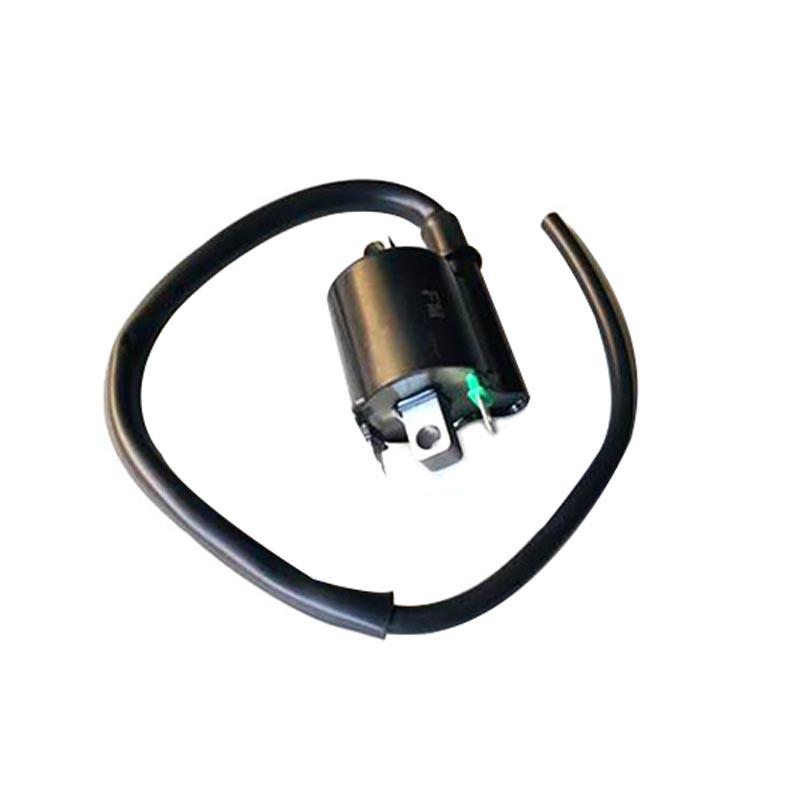
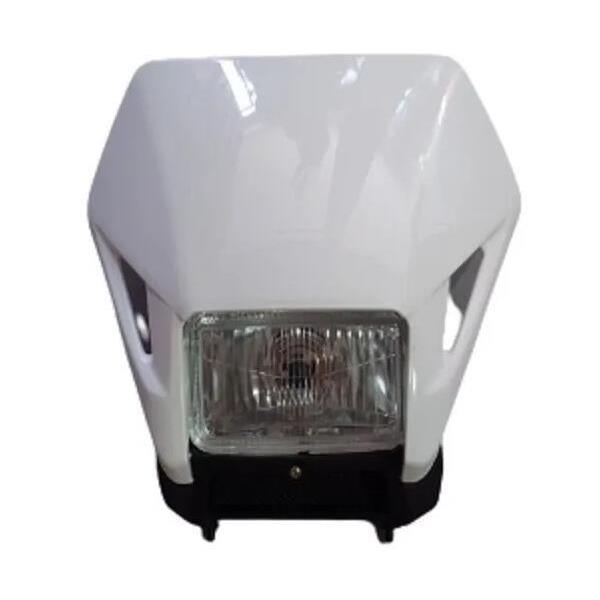
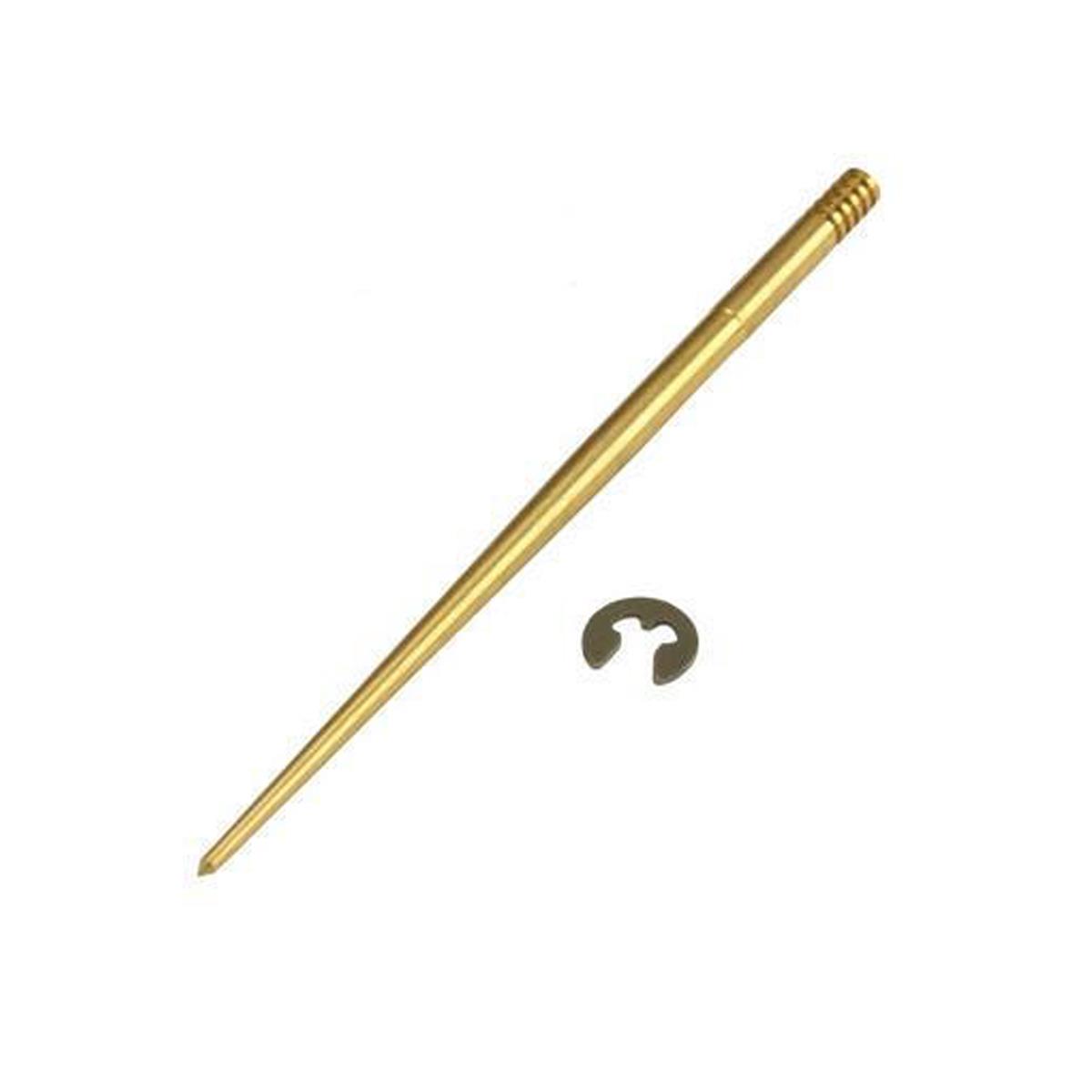
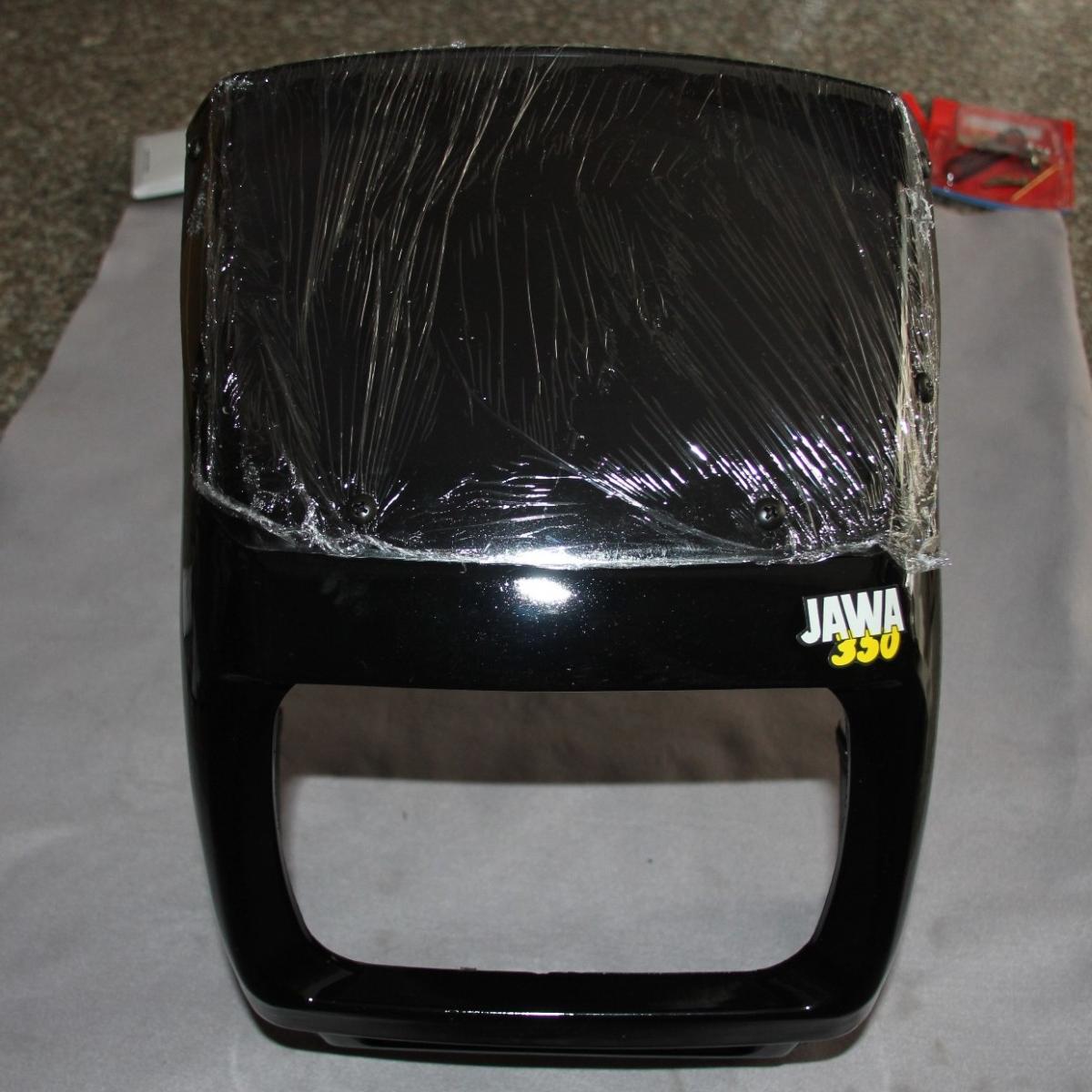
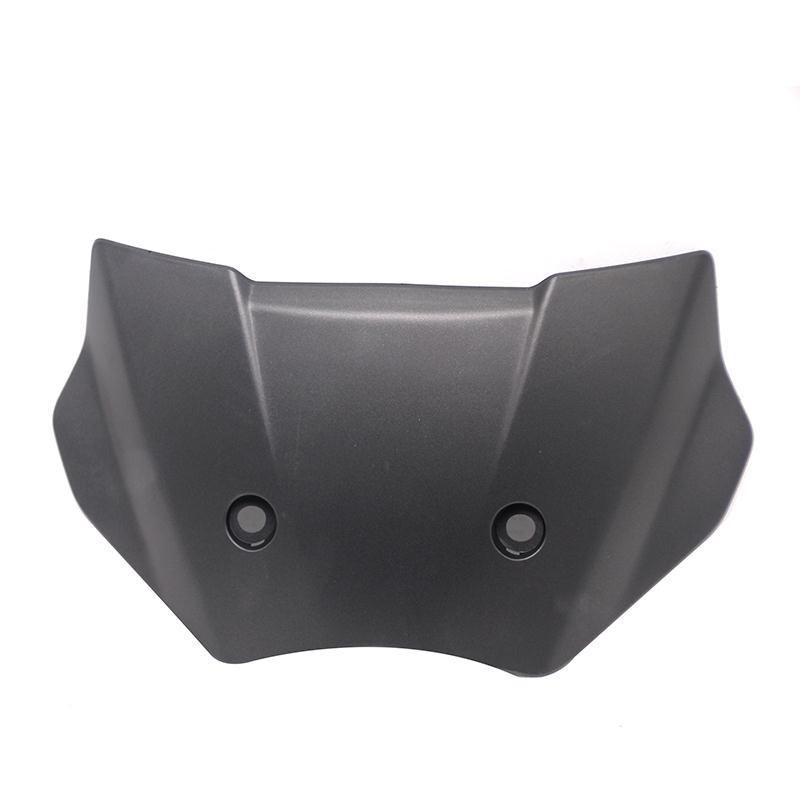
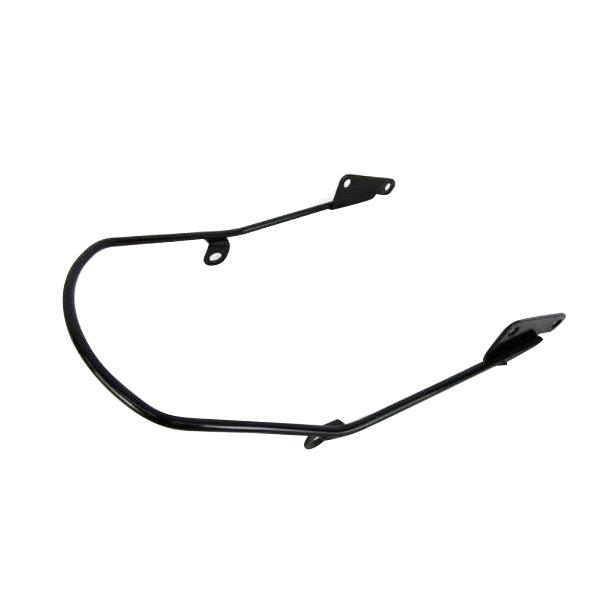
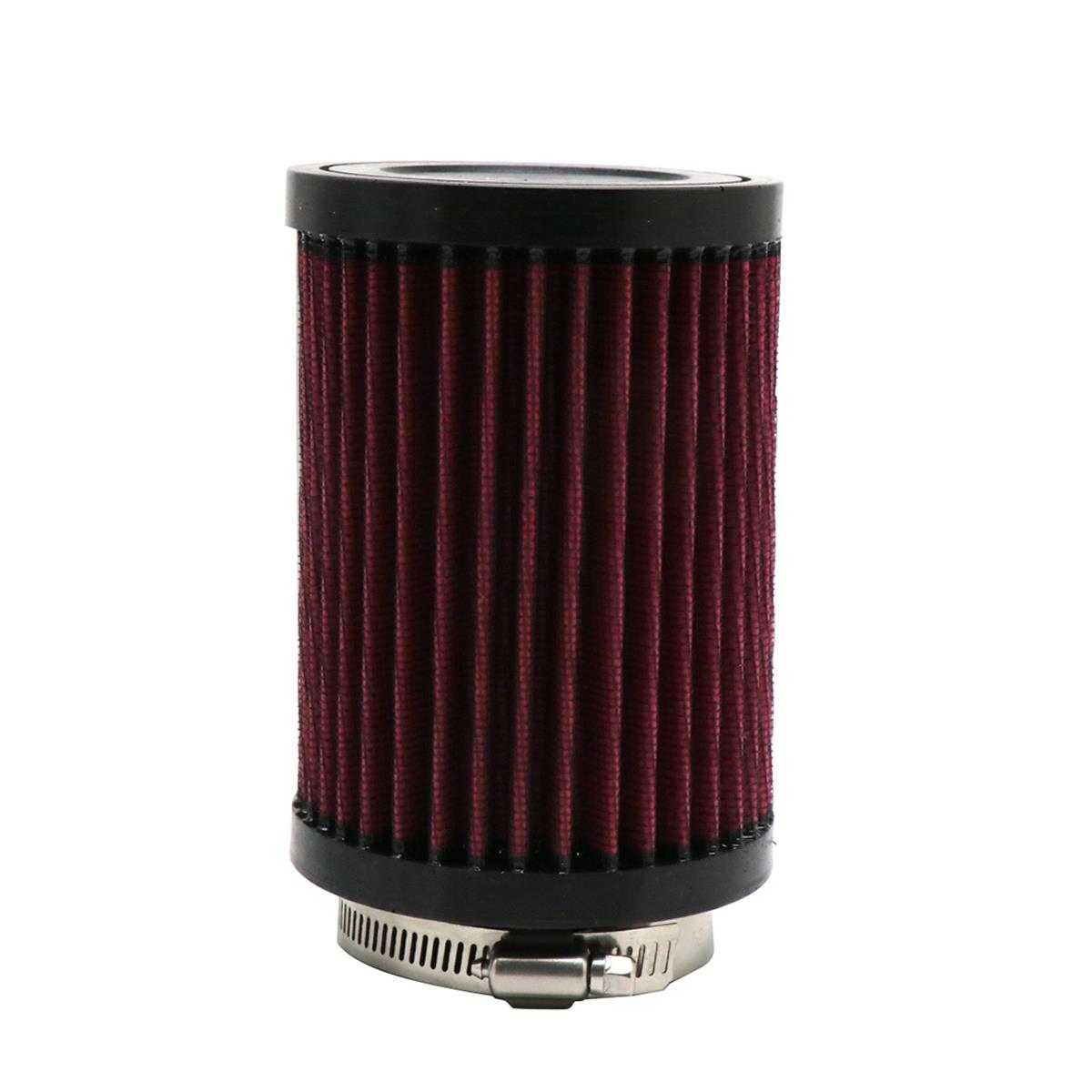
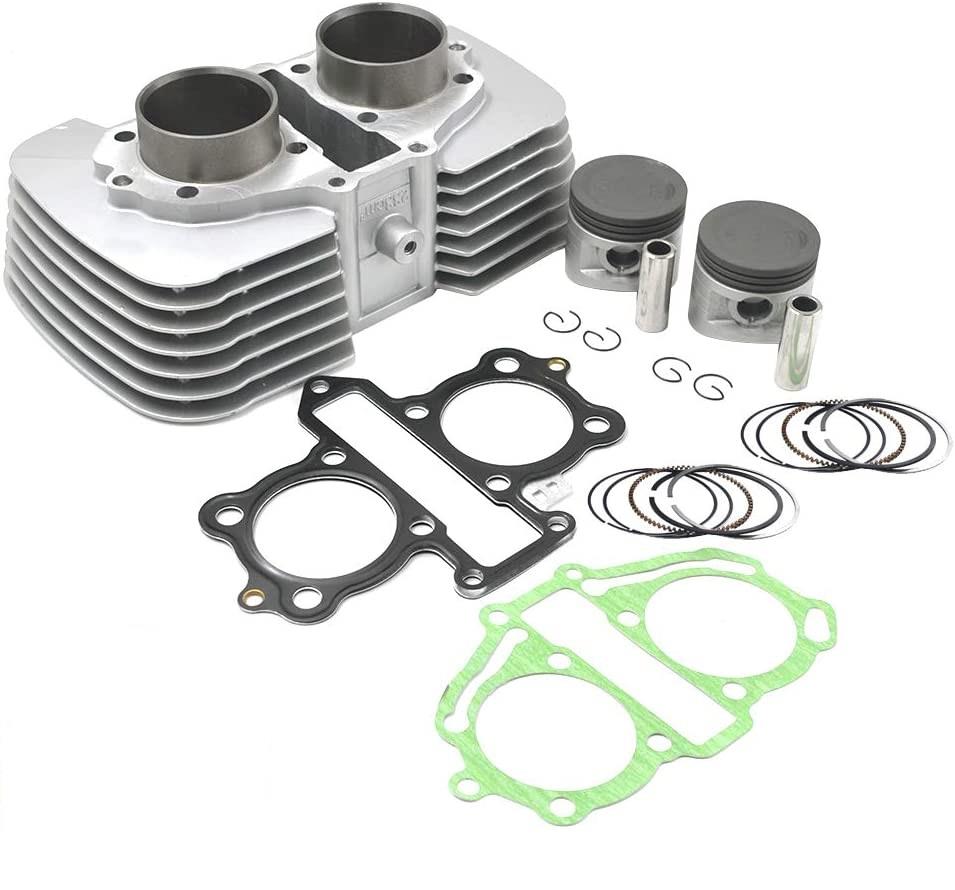
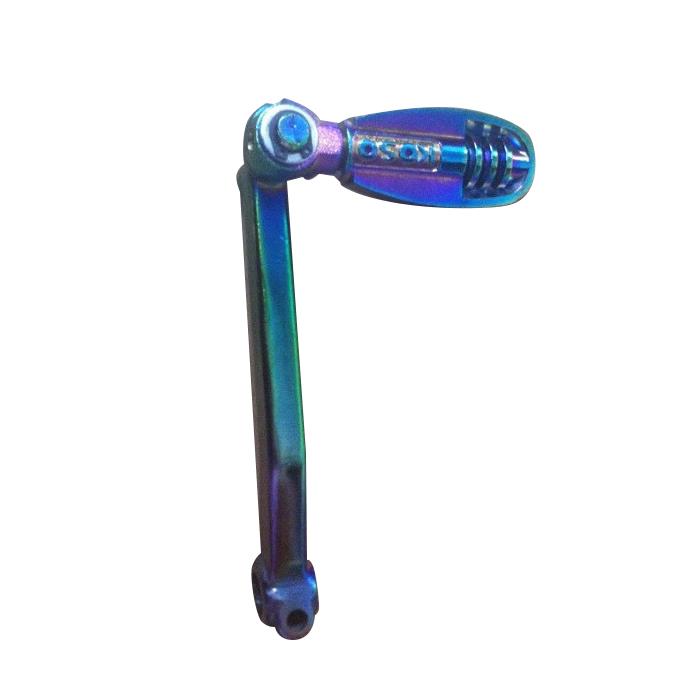
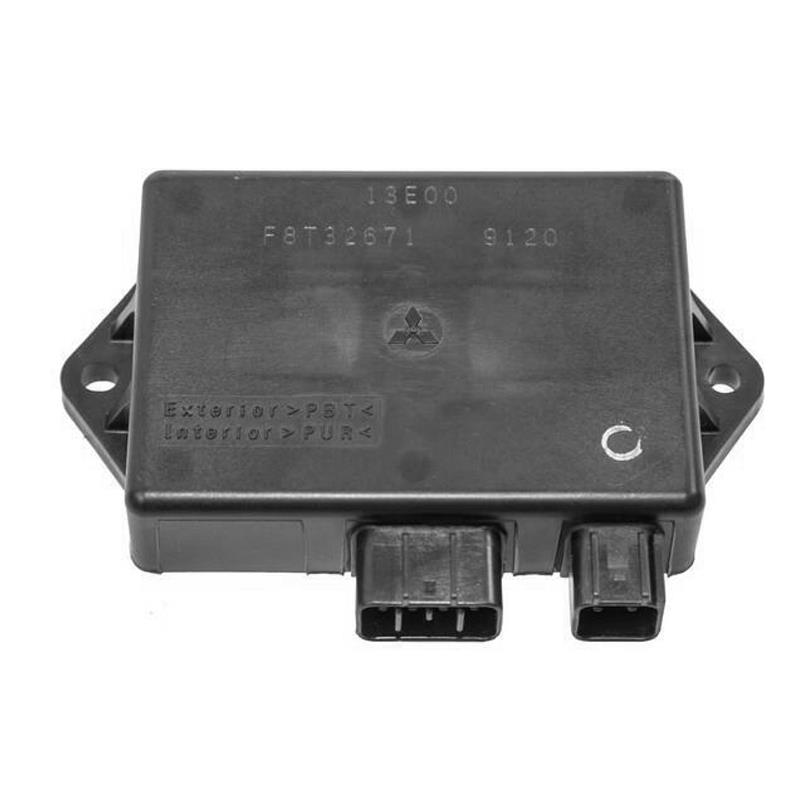
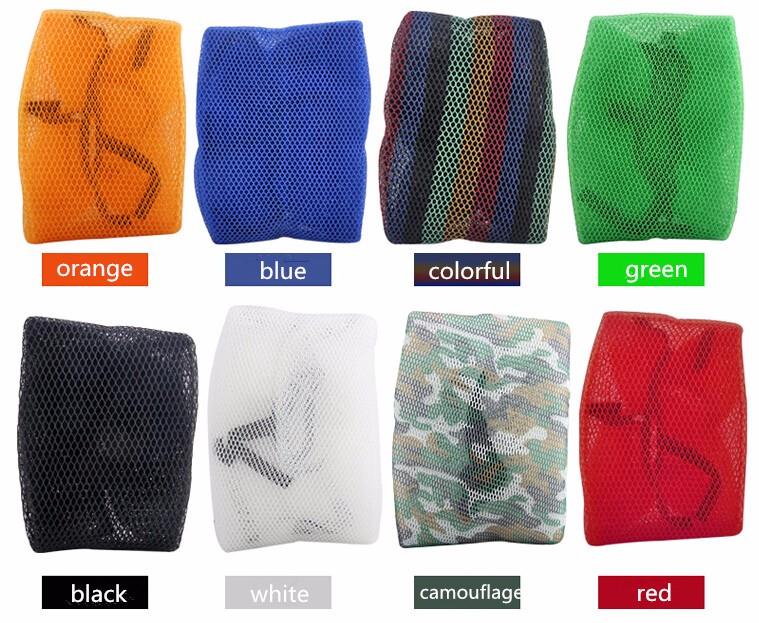
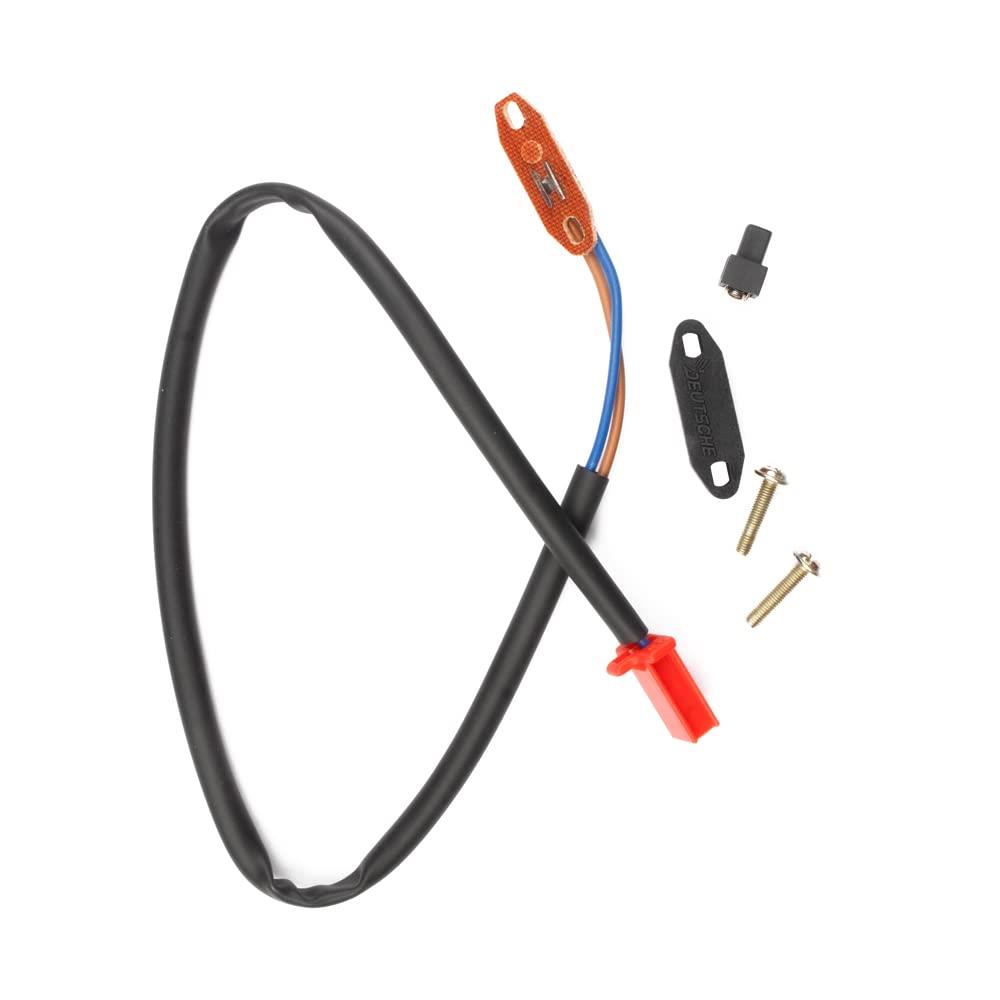
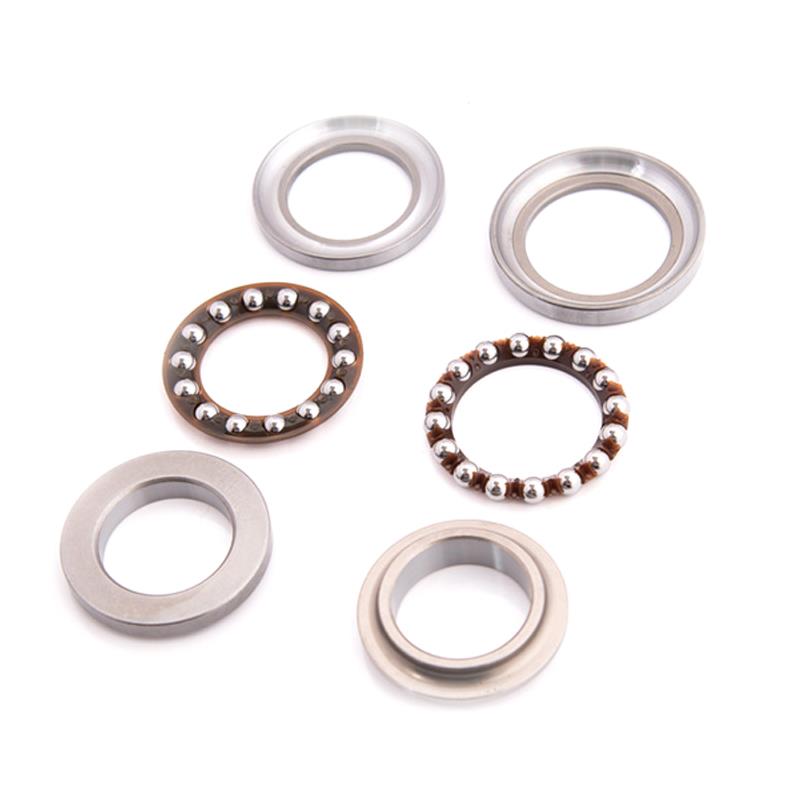
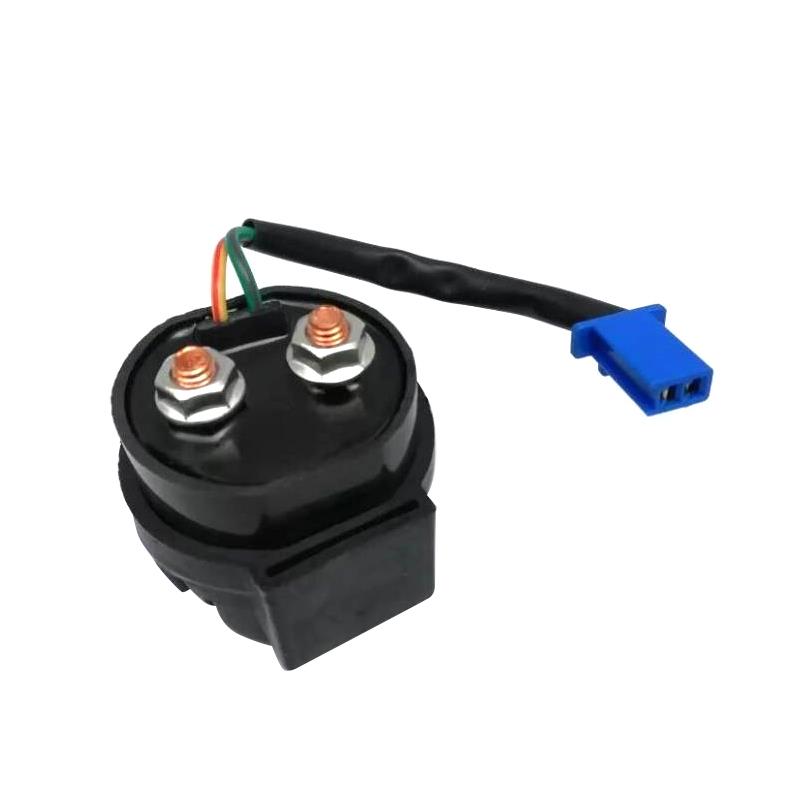
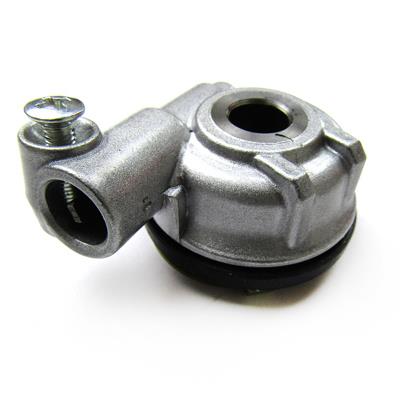
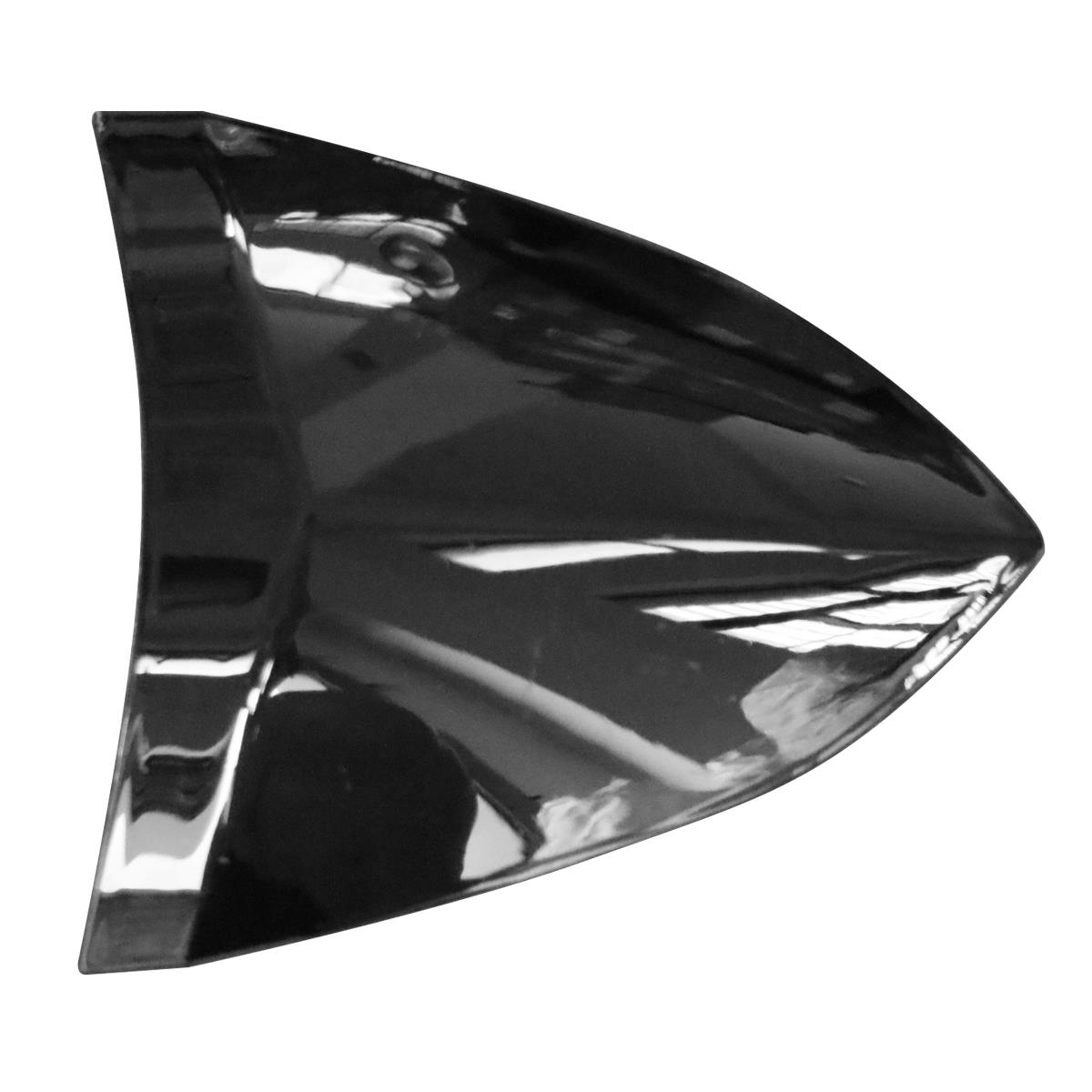
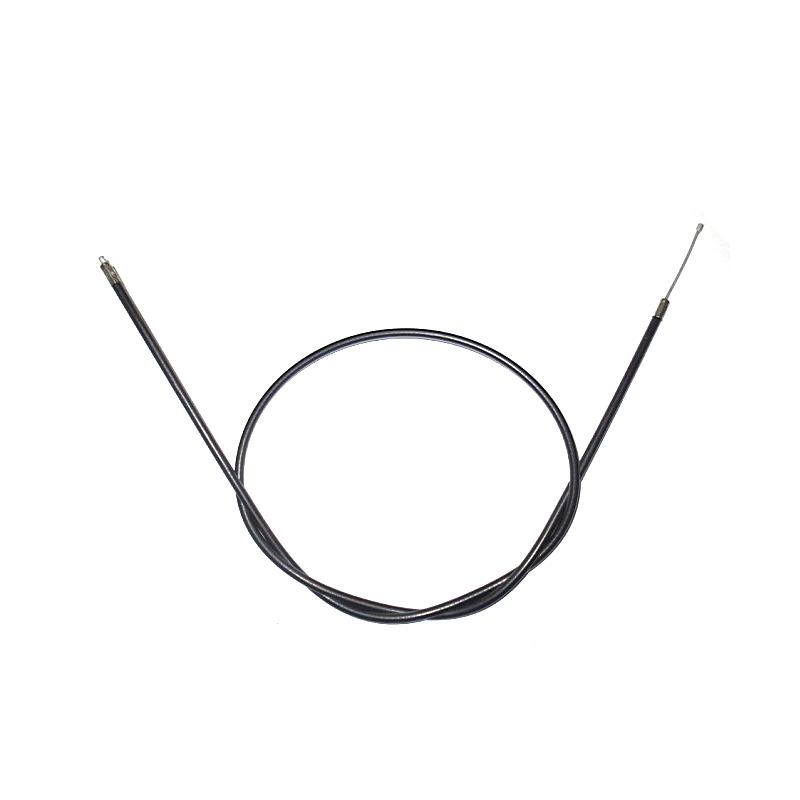
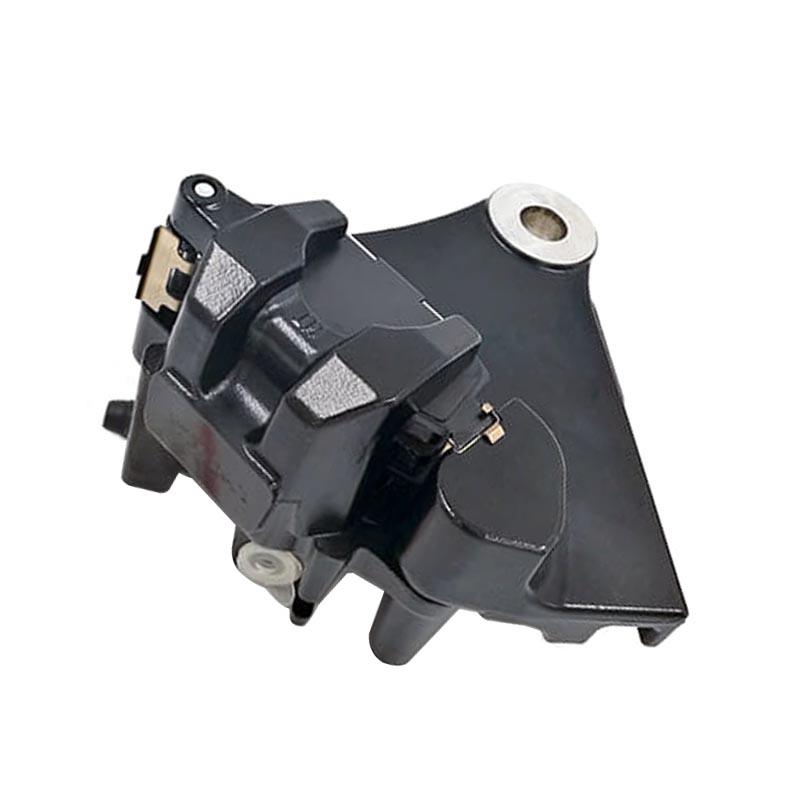
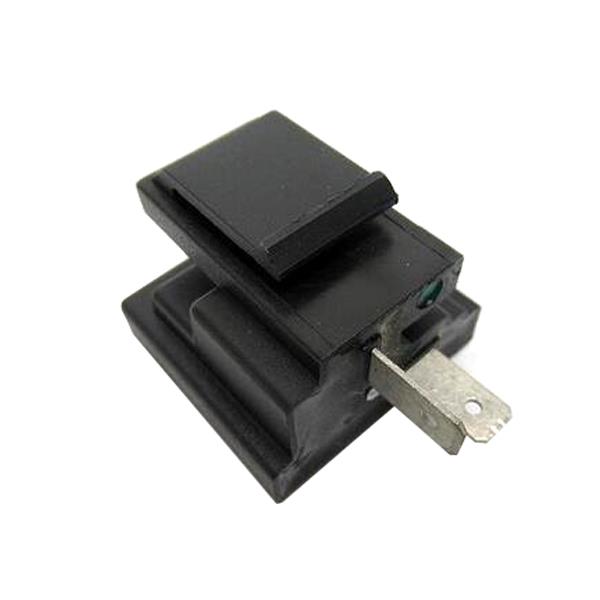
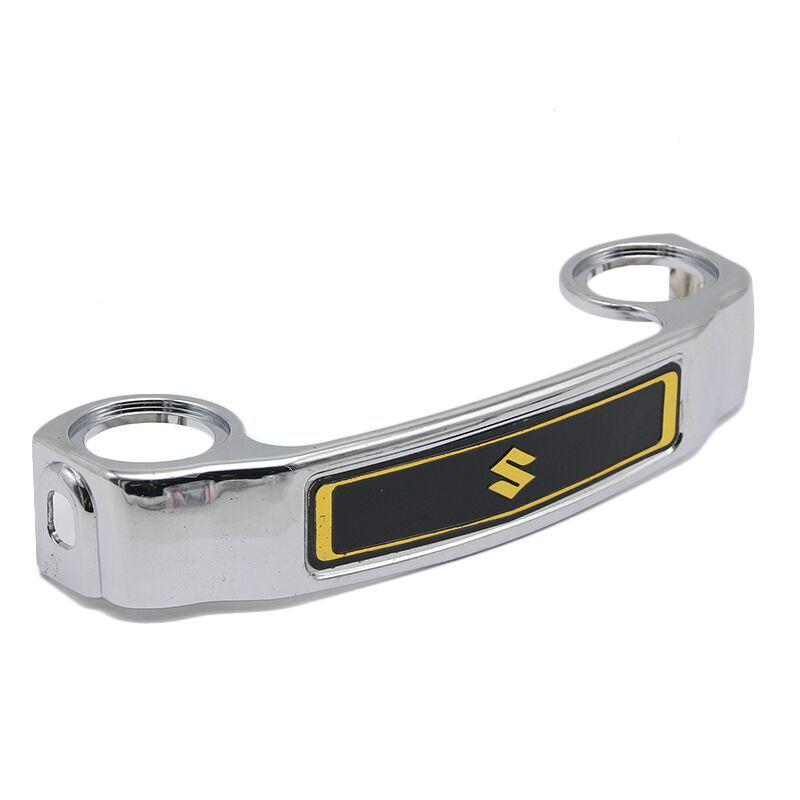
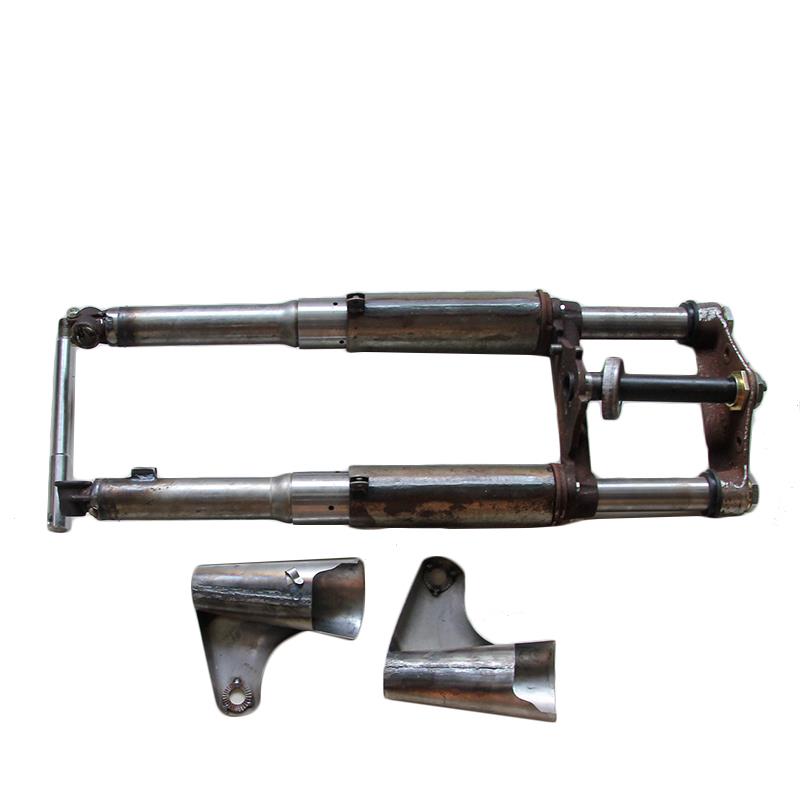
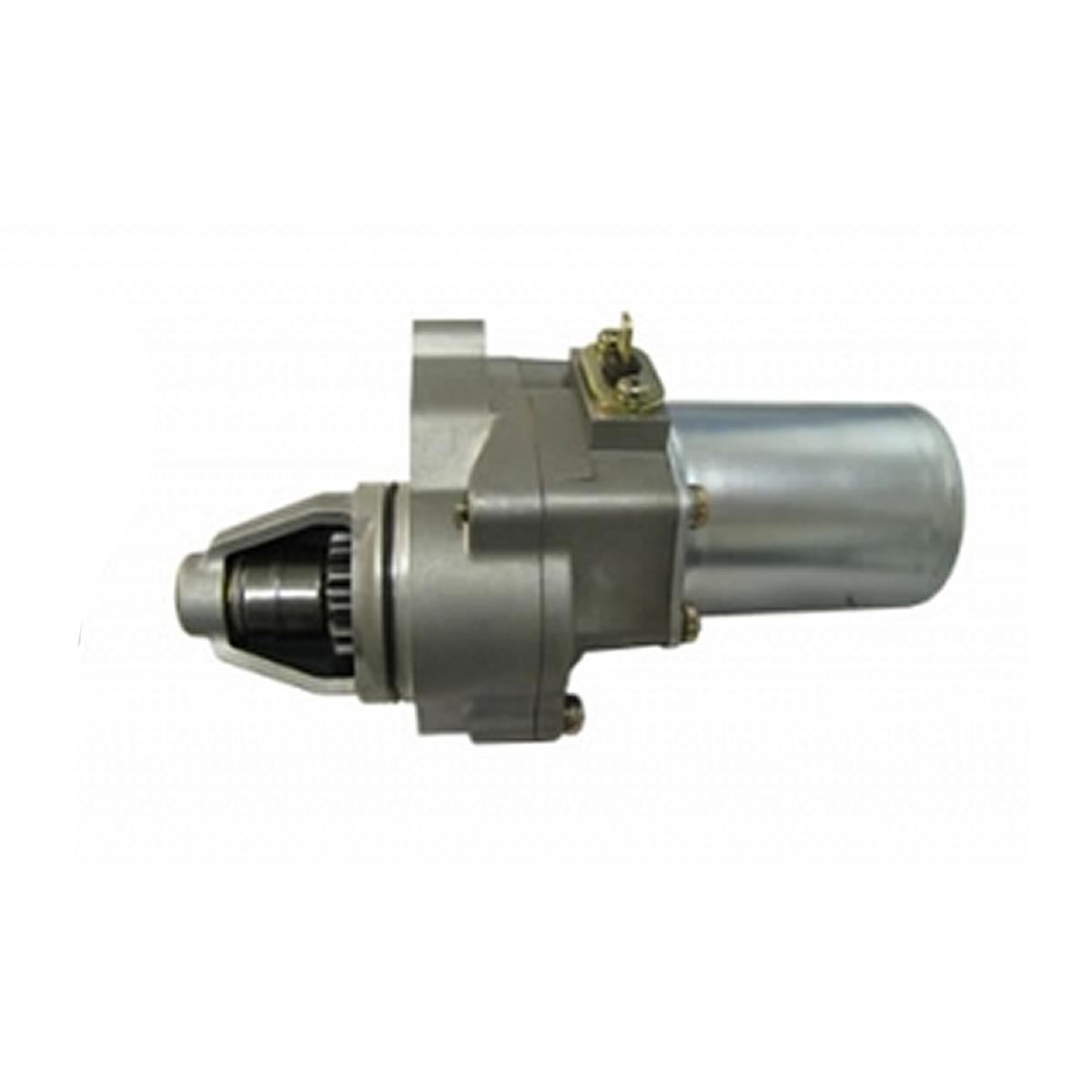
Starter Motor Assy. 10T PEUGEOT TWEET LUDIX PRO VIVACITY 3L SIXTIES SYM MIO SYMPHONY II S SR SYMPLY II FIDDLE II 50
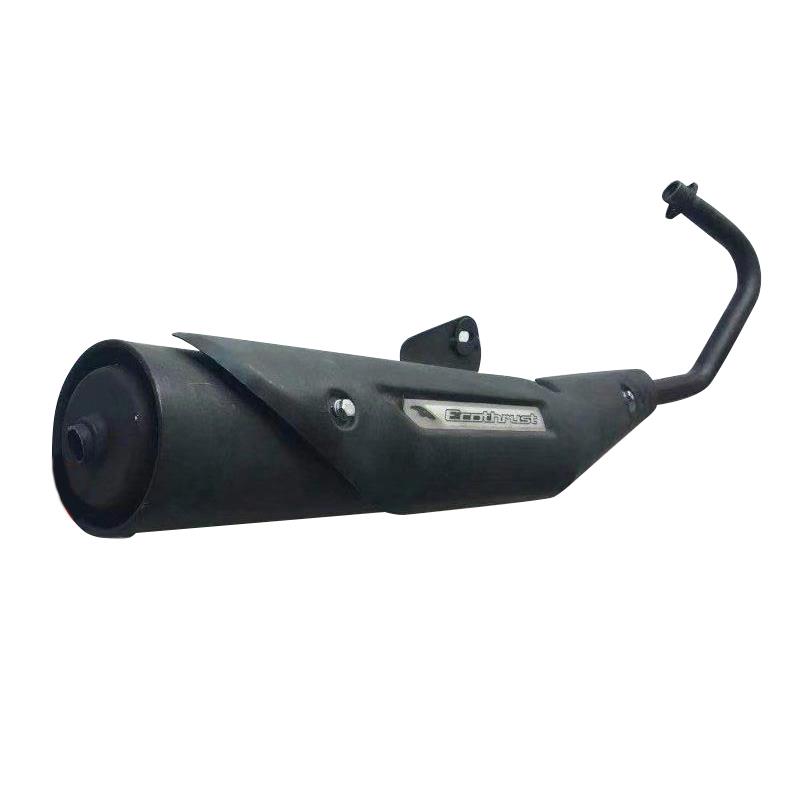
Muffler Motorcycle exhaust pipe modified stainless steel with universal back pressure
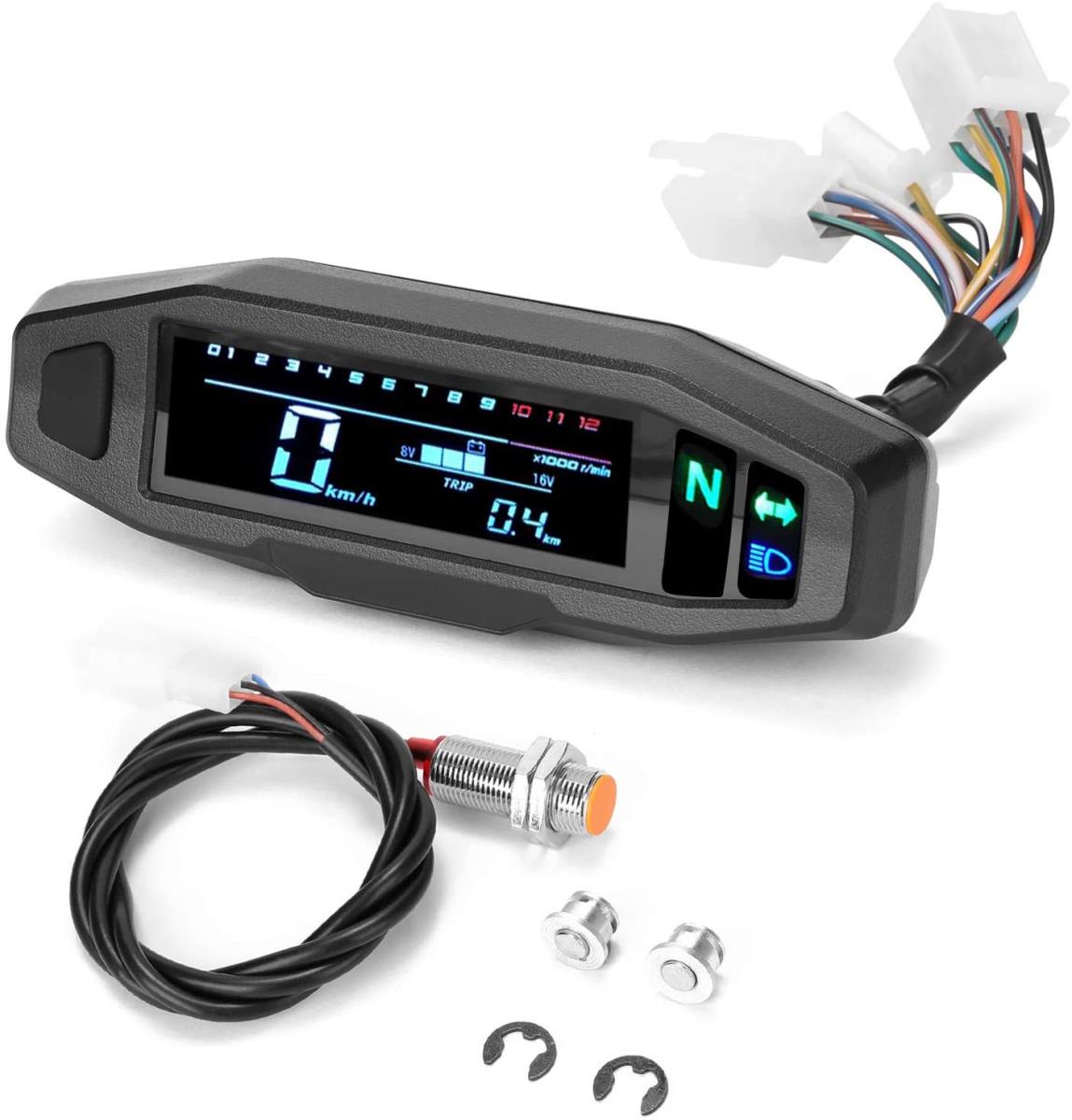
Meter Assy 0-120km 6 digits Mileage Display CHANGJIANG CJ750 24HP 6V 12V 32HP
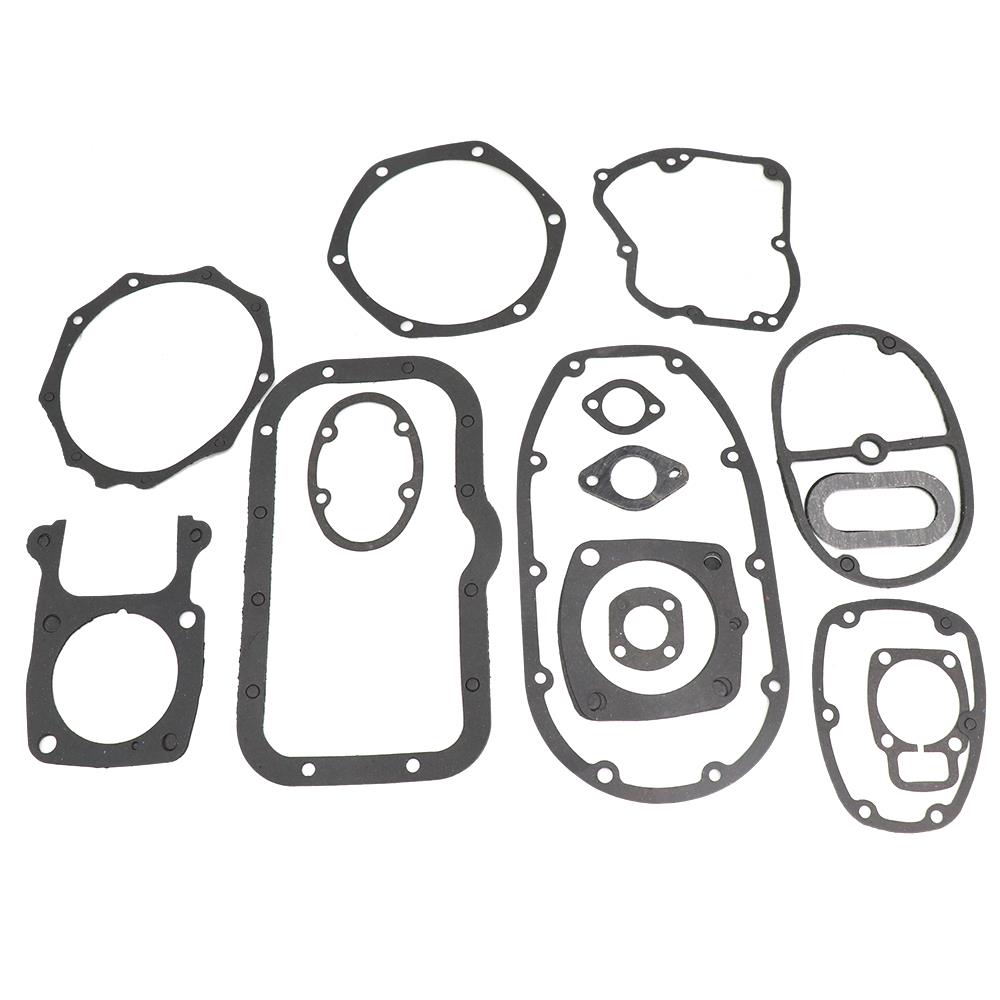
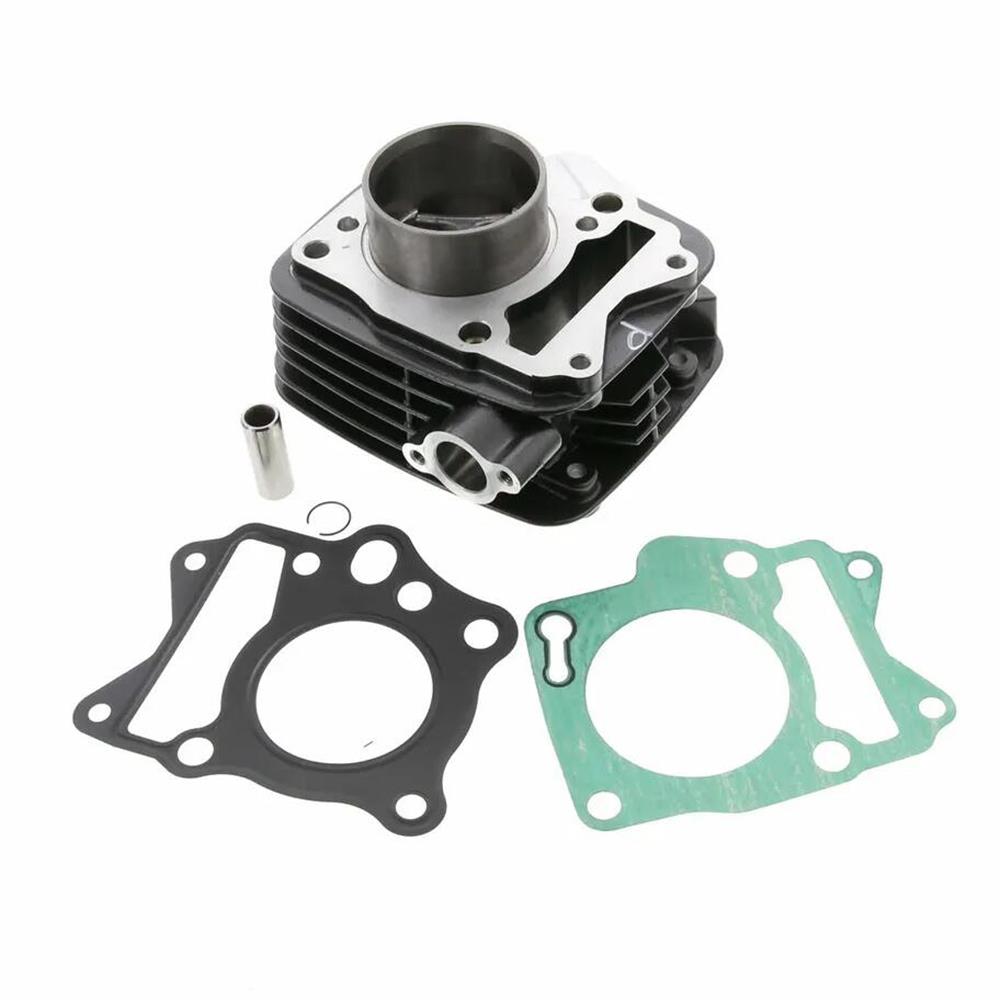
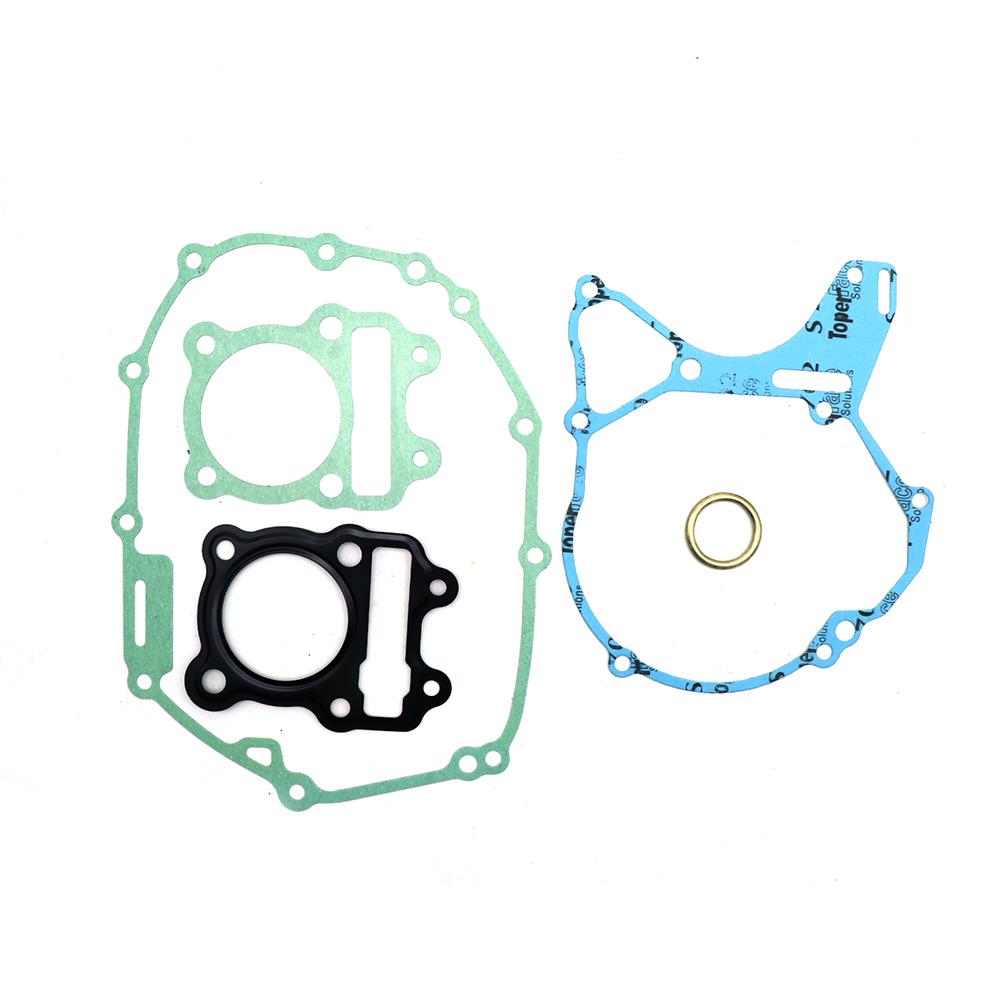
Engine Gasket Sheet Kit A CJ750 Complete Motorcycle Gasket Set For 24HP 32HP Flat Head Repair Gasket Kit
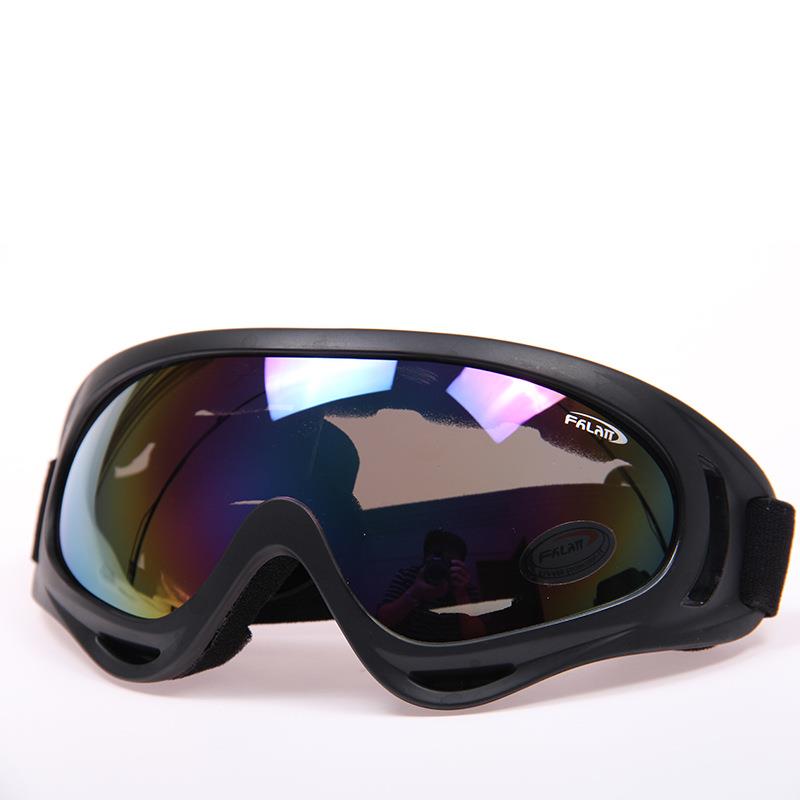
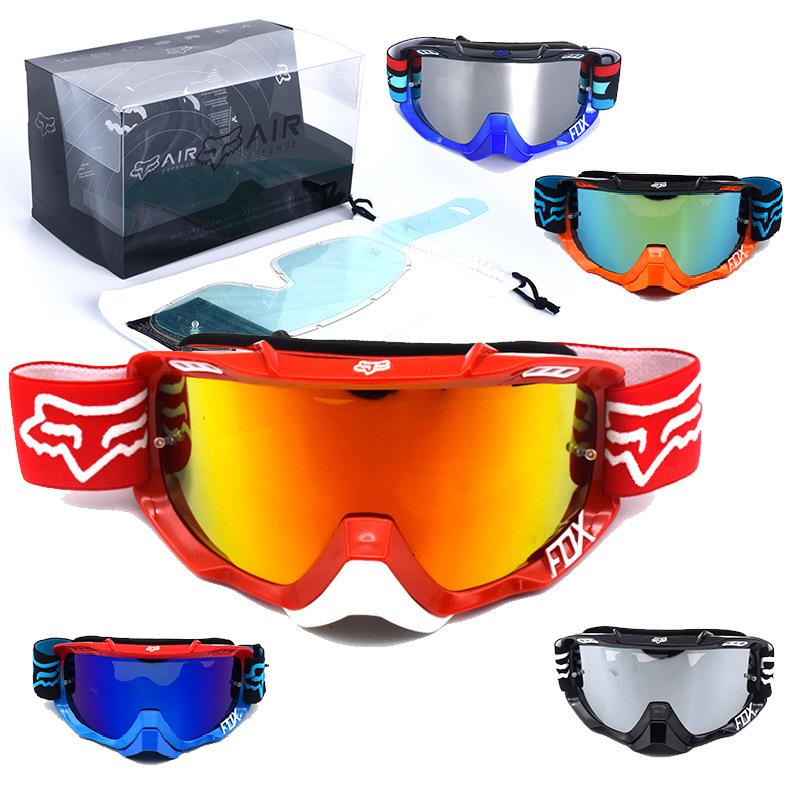
Goggles Bicycle Sunglasses Windproof Sports Goggles Cycling Riding Bike Eyewear Glasses
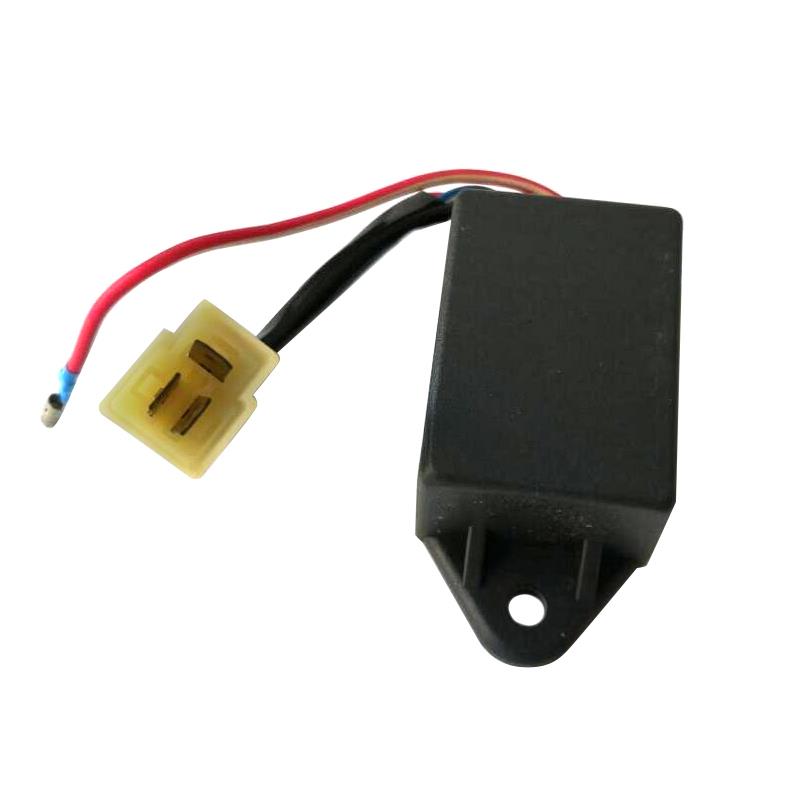
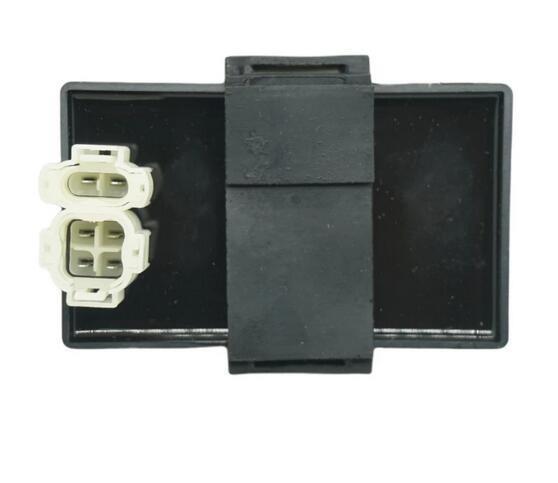
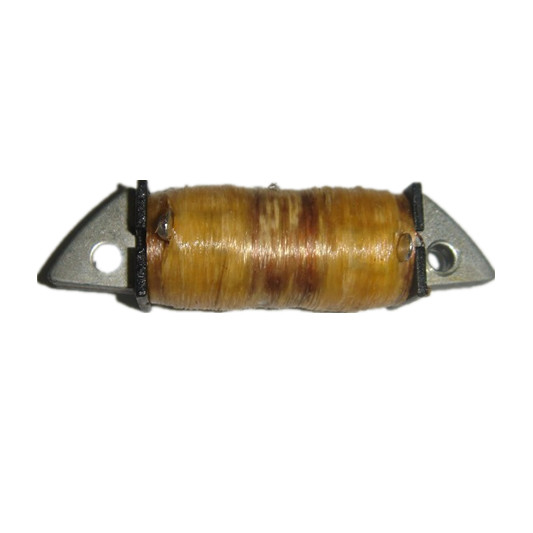
C.D.I. Unit Ignitor Box for Scooter Moped AG50 AG60 SJ50 AD50 ADDRESS 50 H1E41QMB
Racing Protective Armor JacketMotorbike Full Body Armor Protective Gear for Bike Motorcycle AVT Motocross Skiing Cruise
C.D.I. Unit BOX IGNITION 6PINS DC 12V Dayang DY150-20 DY150GY-6 Dayun DY150-22 DY150-EDF
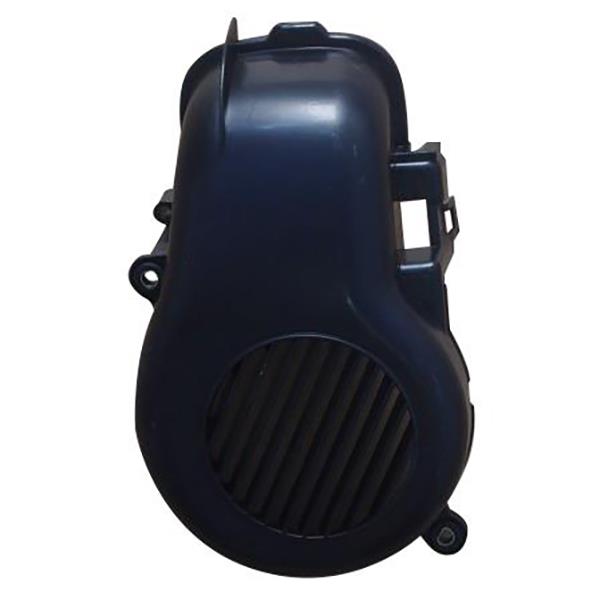
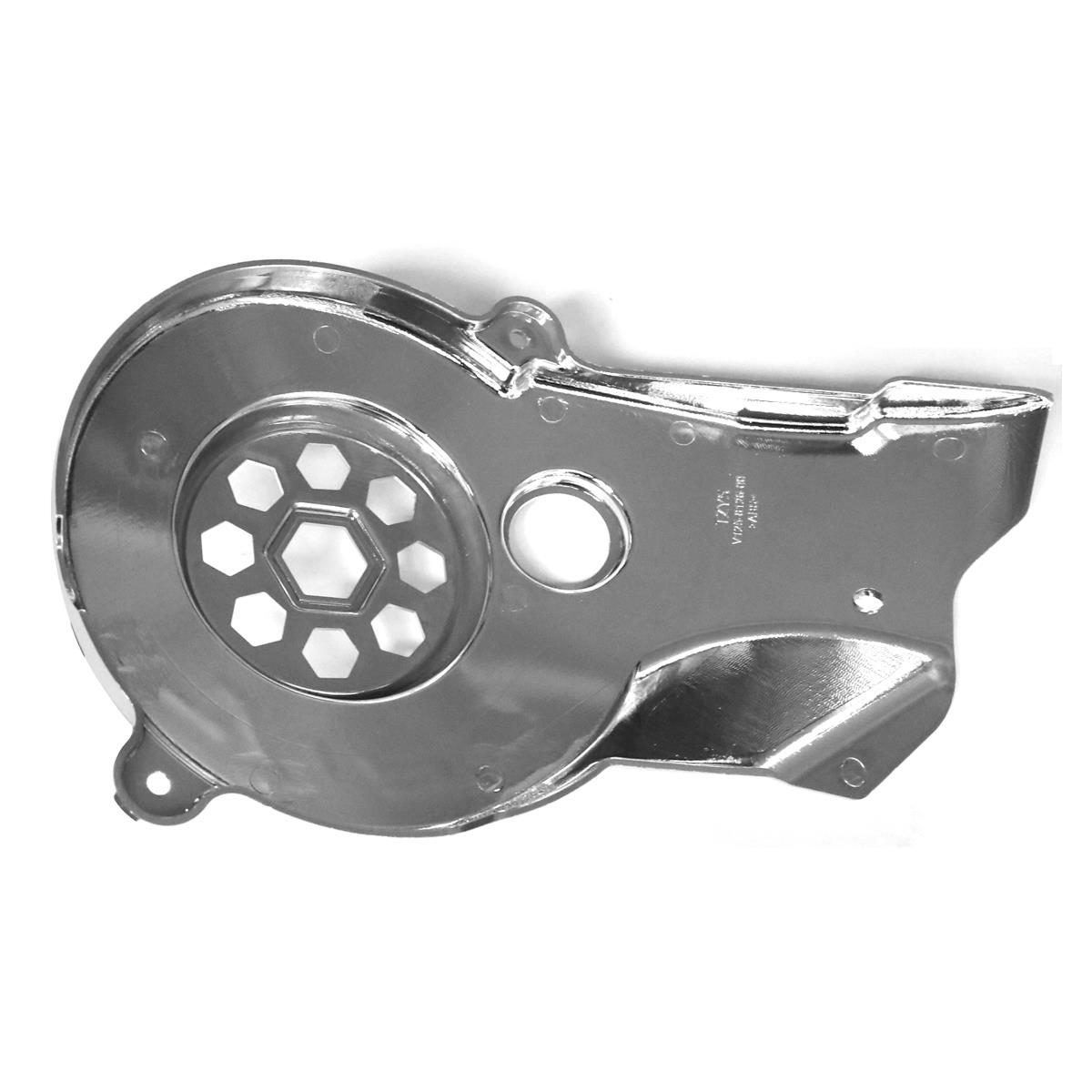
Fan Cover Comp. Cooling Fan Cover 3KJ-12653-01 Air Shroud-Fan YAMAHA CY50 JOG50 3KJ YG50 EX Jog
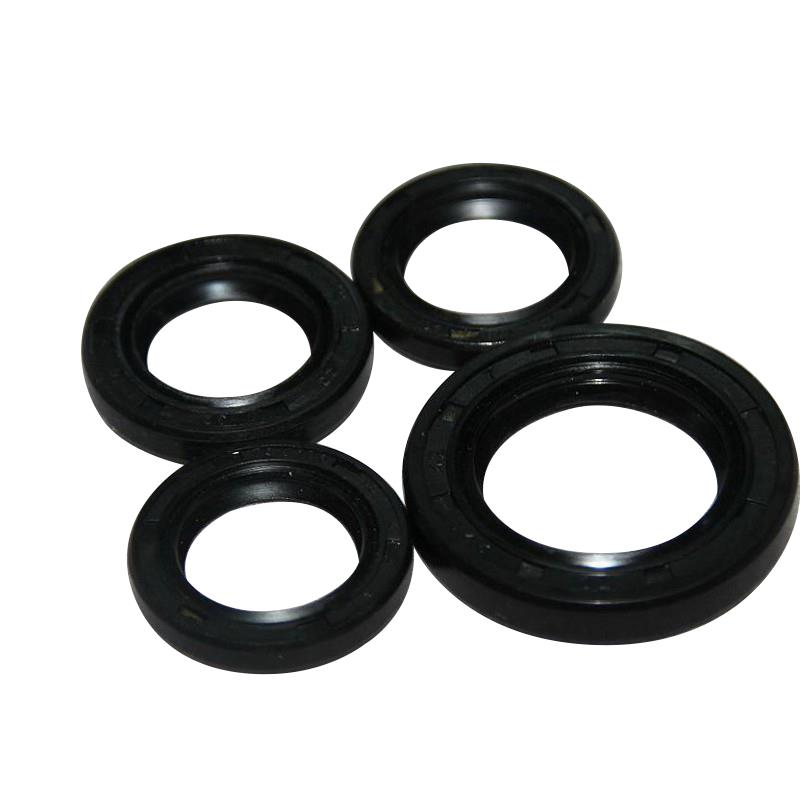
Engine Oil Seal Kit 4 pcs Engine Oil Seal Kit KYMCO GY6-125 GY6-150 GY6-80
Fan Cover Comp. Cooling Fan Cover 3KJ-12653-01 Air Shroud-Fan YAMAHA CY50 JOG50 3KJ YG50 EX Jog
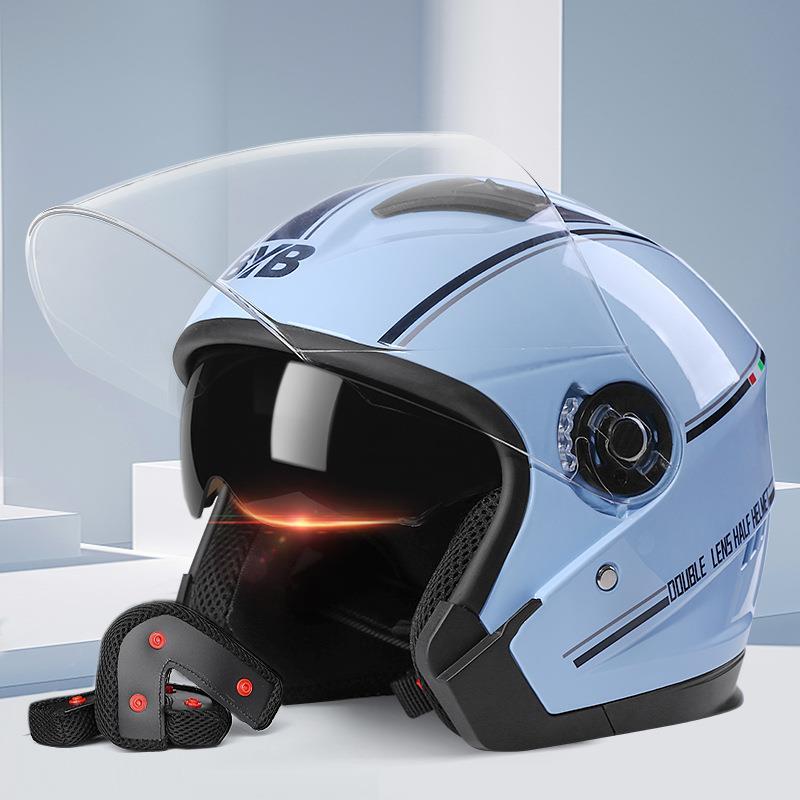
Helmet Open Face Seasons Cycling Motorcycle E-Bike Helmet with Anti-fog double lens
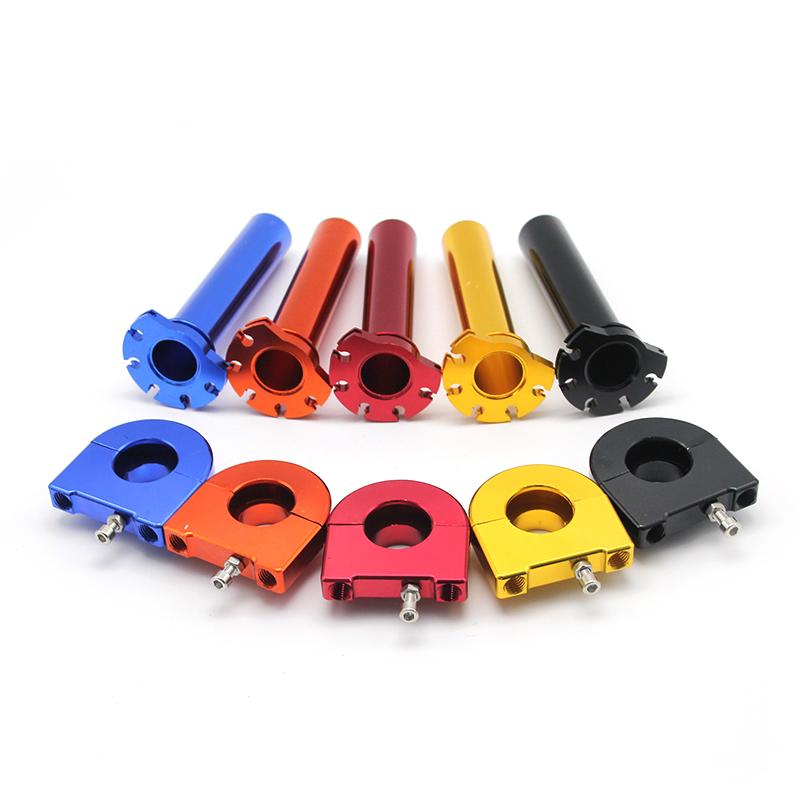
Throttle Sub Assy. Universal 7/8" 22mm Throttle Twist Handle Grip For CNC Motorcycle
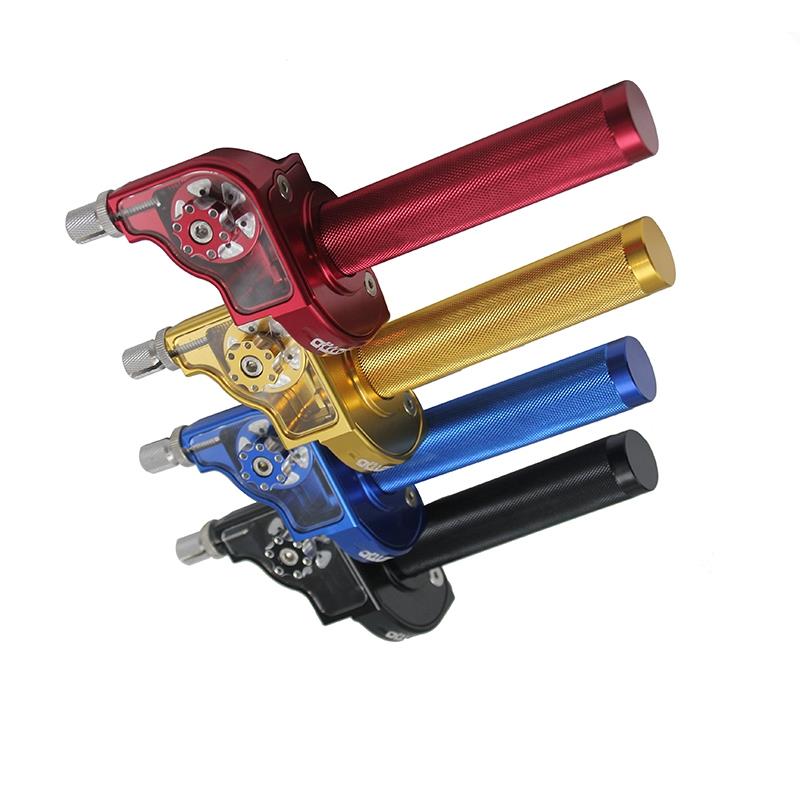
Throttle Sub Assy. Grips 7/8" Handle Throttle Hand Grip 50-250CC ATV Quad Pit Dirt Bike Motors
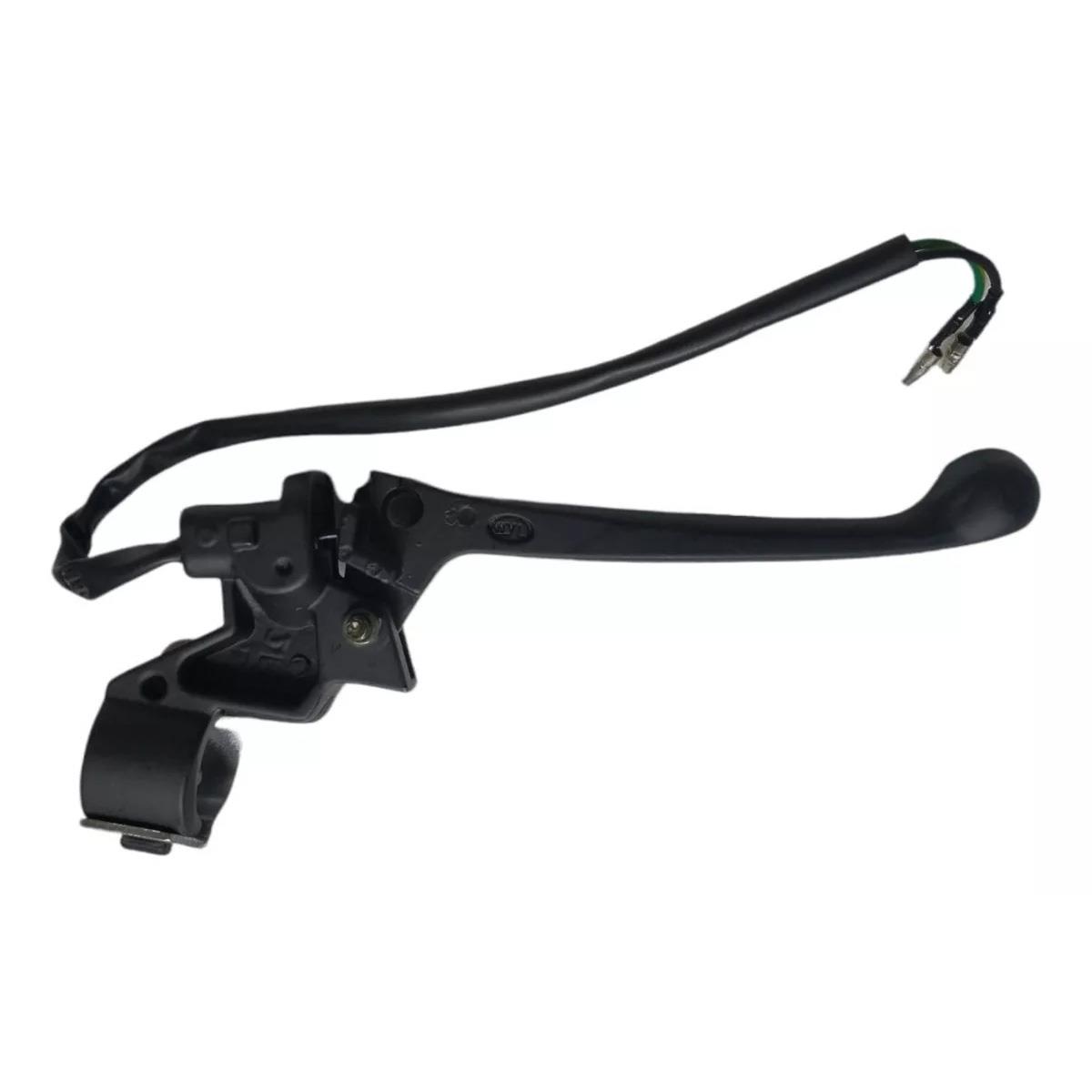
Steering Handle Lever Comp. Left Rear Drum Brake Lever with Mirror Holder for Italika Scooter DS125 DS150 XS150 GY6-125 150
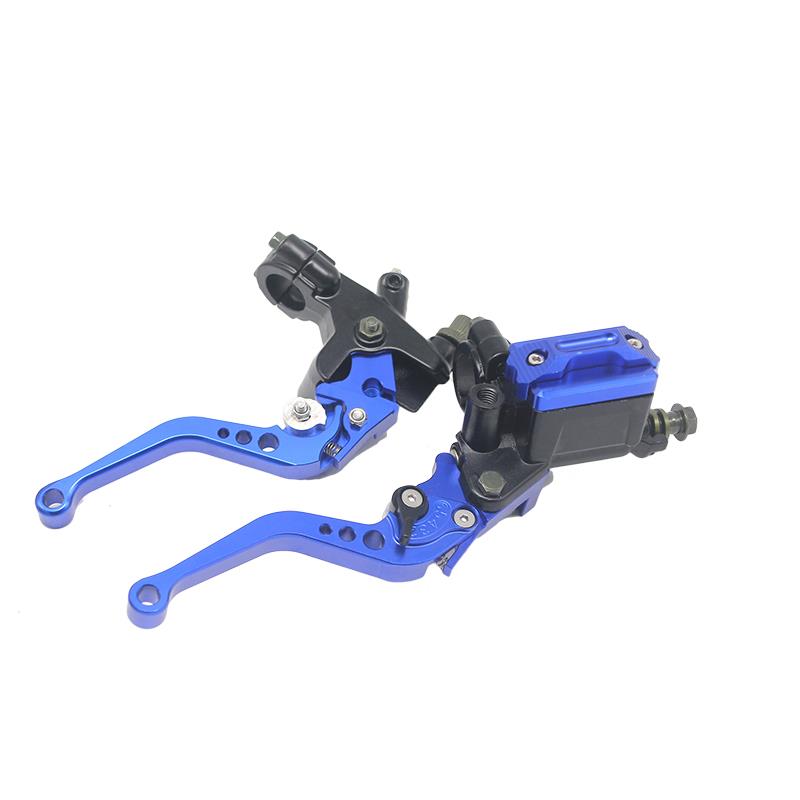
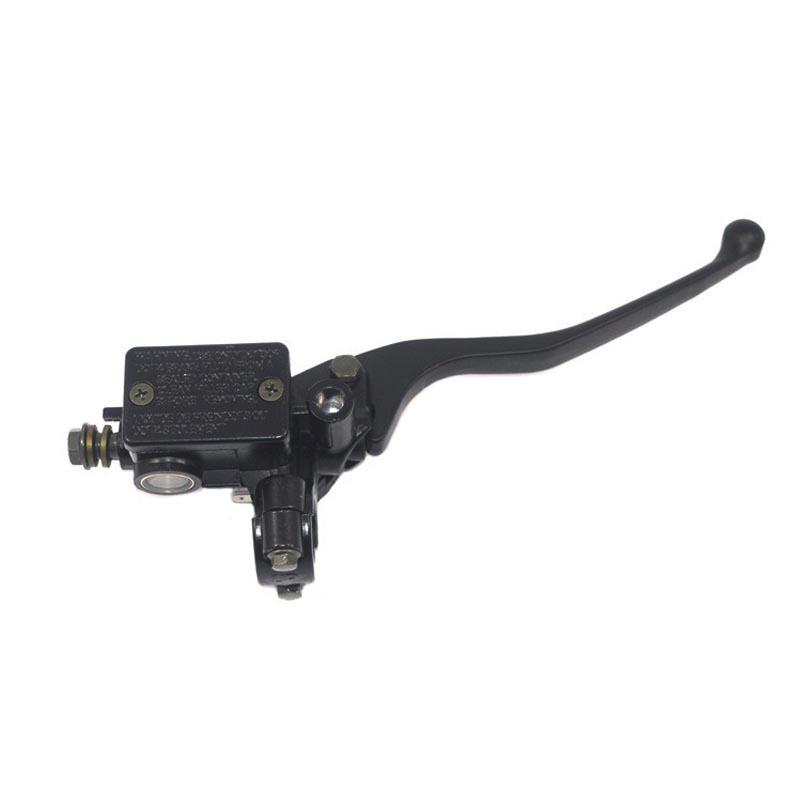
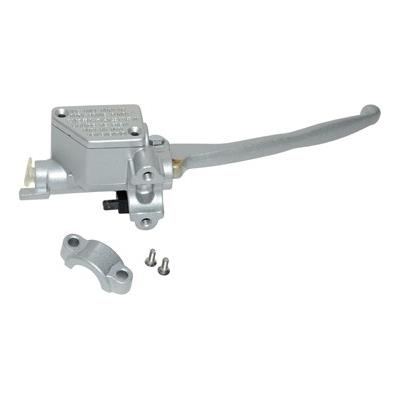
Front Brake Master Cylinder Disk Brake Clutch Master Cylinder Brake Lever Set Universal Red Green Blue for Yamaha Suzuki 12.7mm
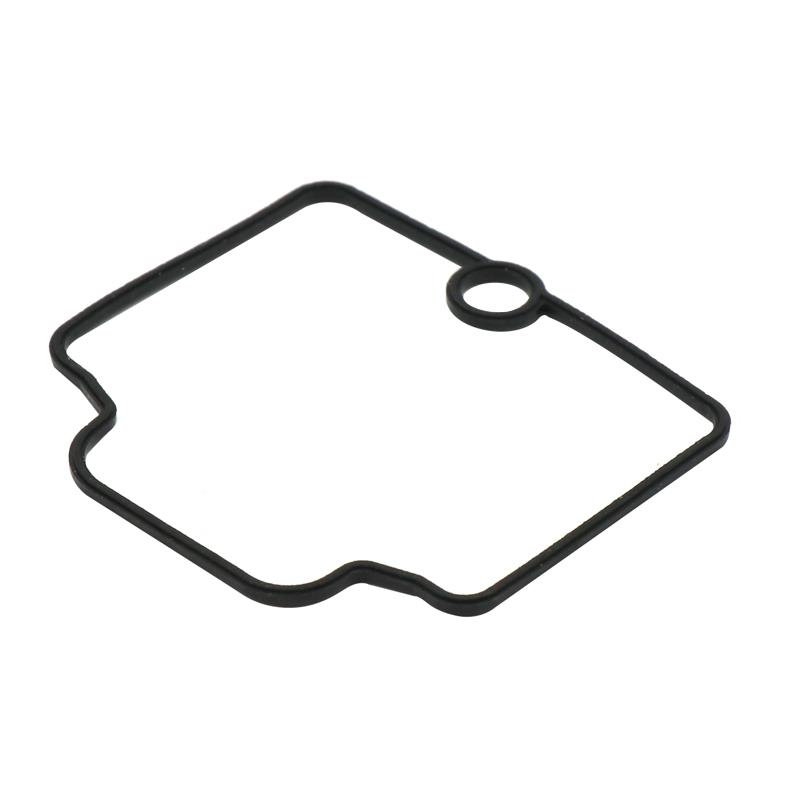
Gasket Carburetor Float Chamber NBR ring 21/24/26/28/30/34/34mm PWK I II III IV small
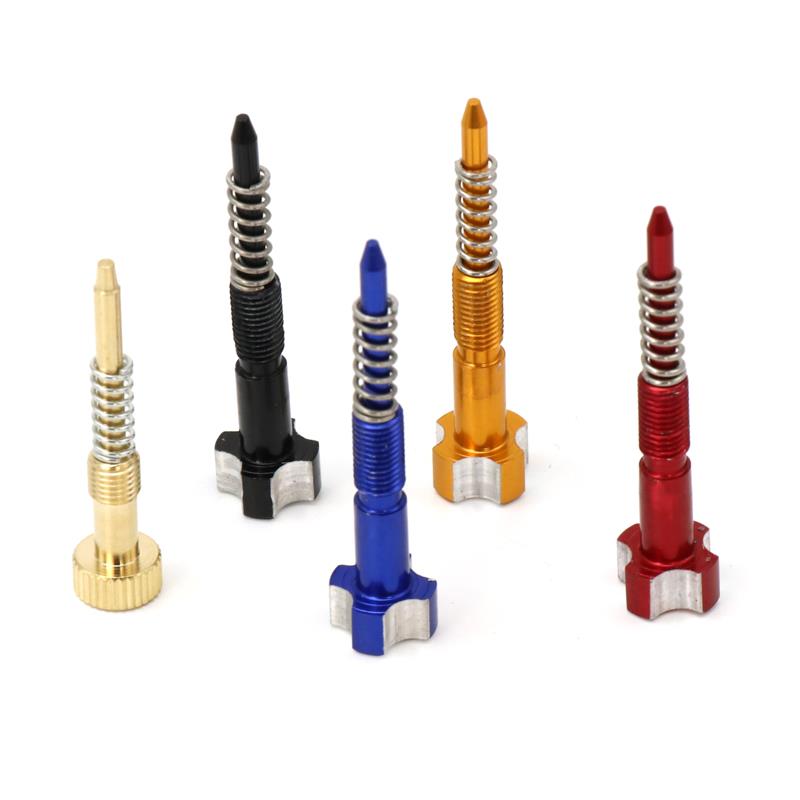
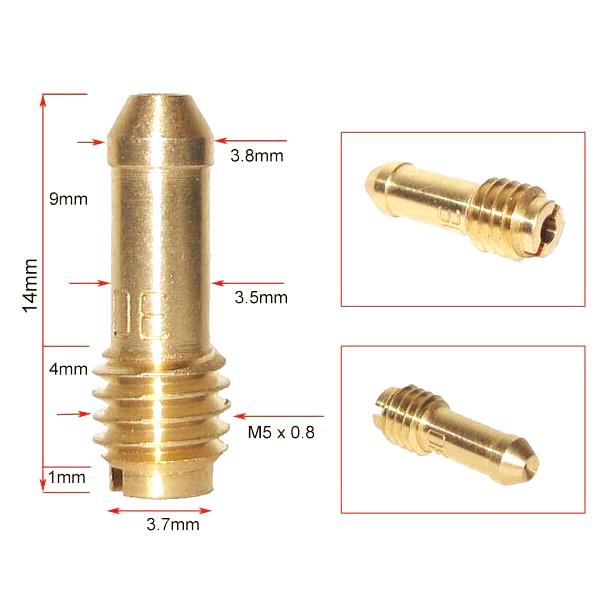
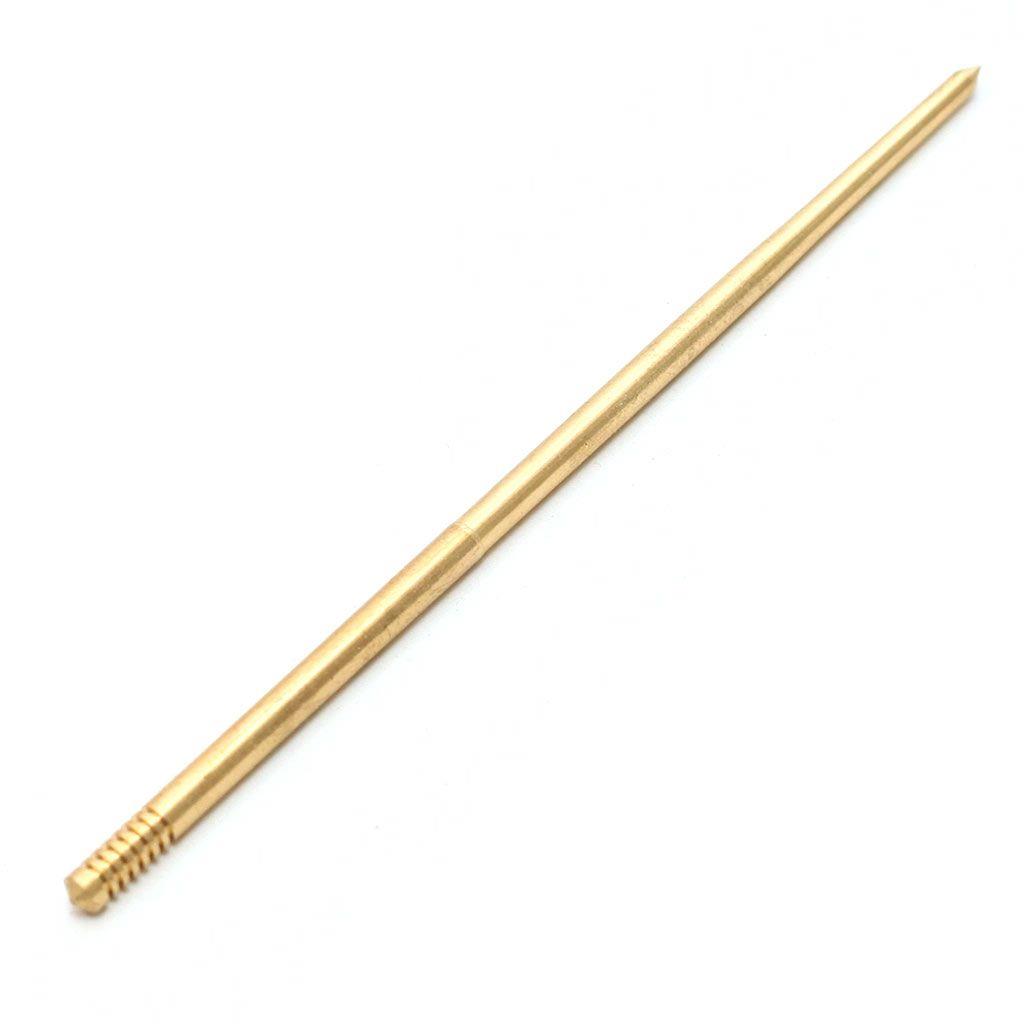
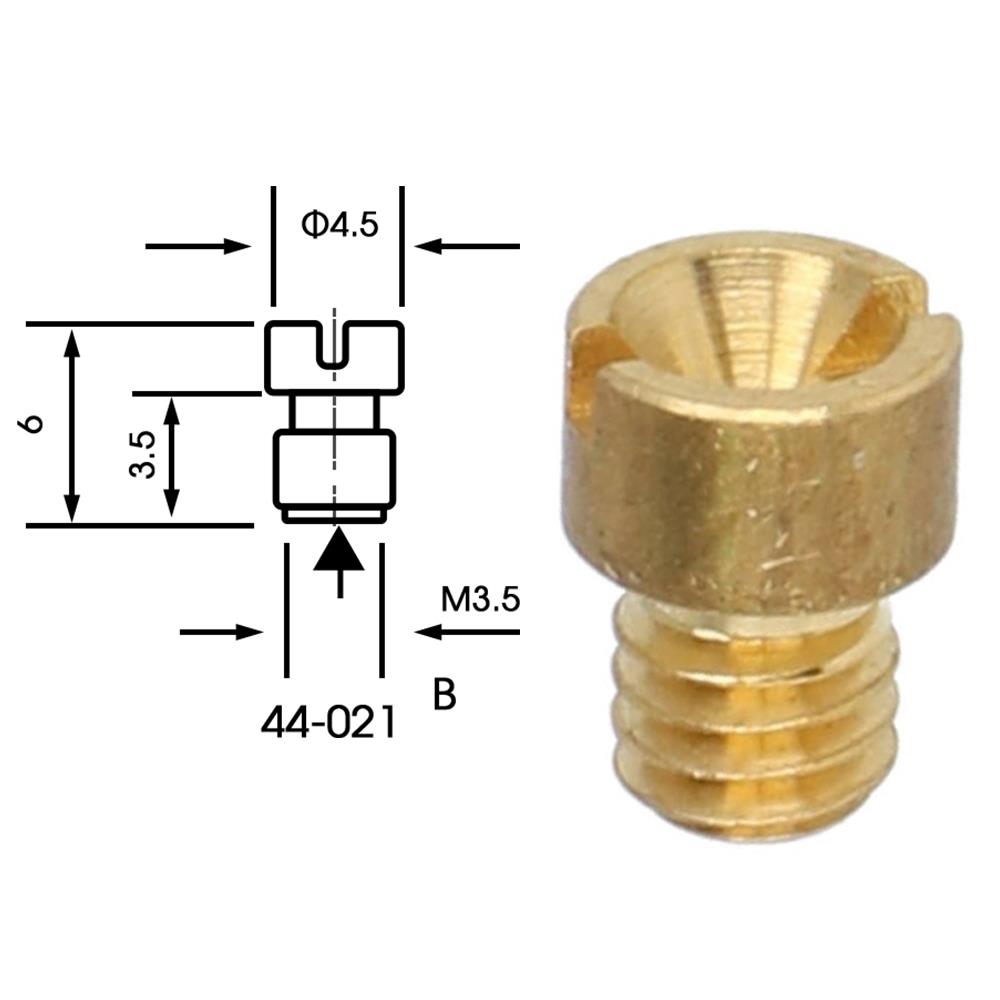
Air Fuel Mixture Screw Kit Colorfull Aluminum Alloy CNC Brass PWK 21/24/26/28/30/32/34
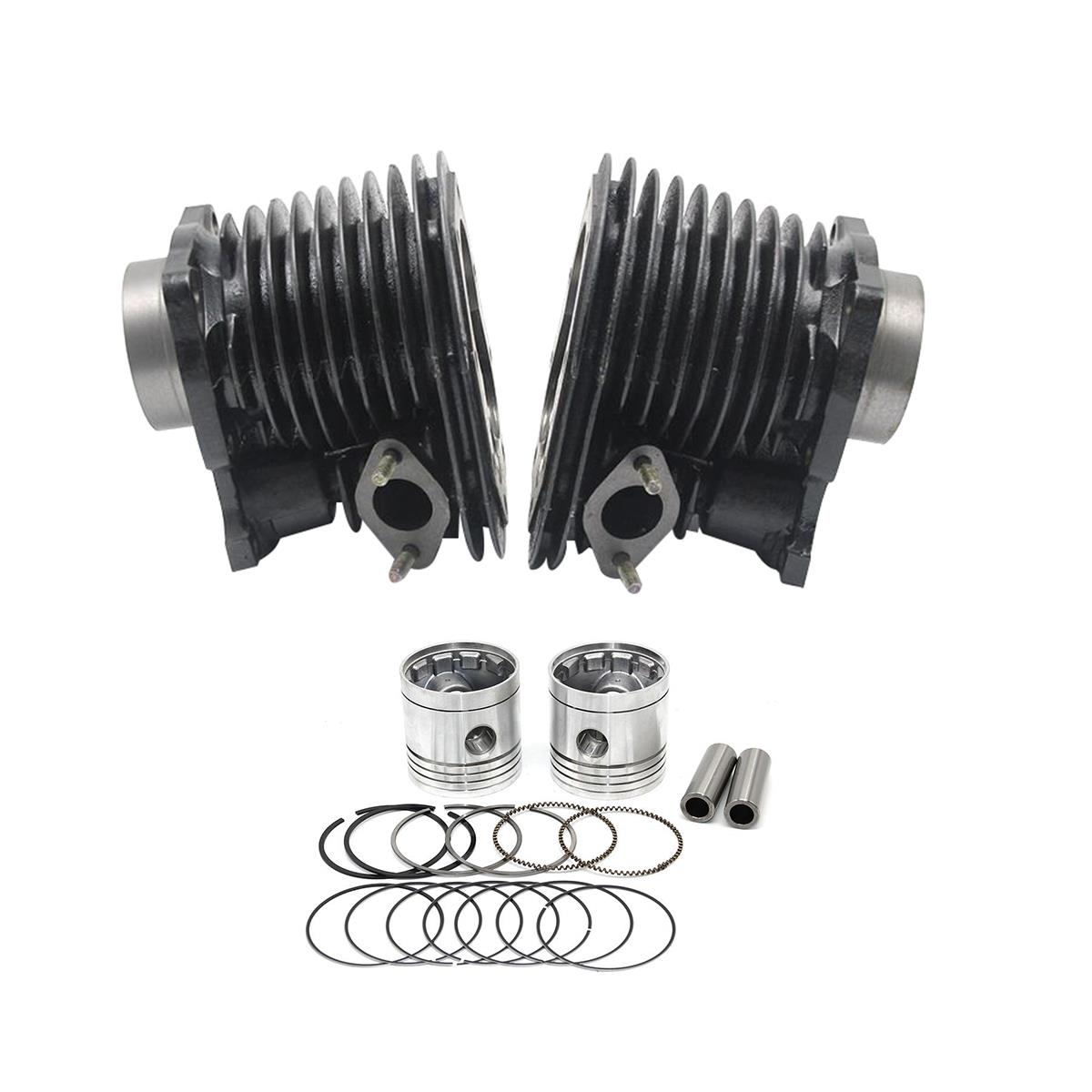
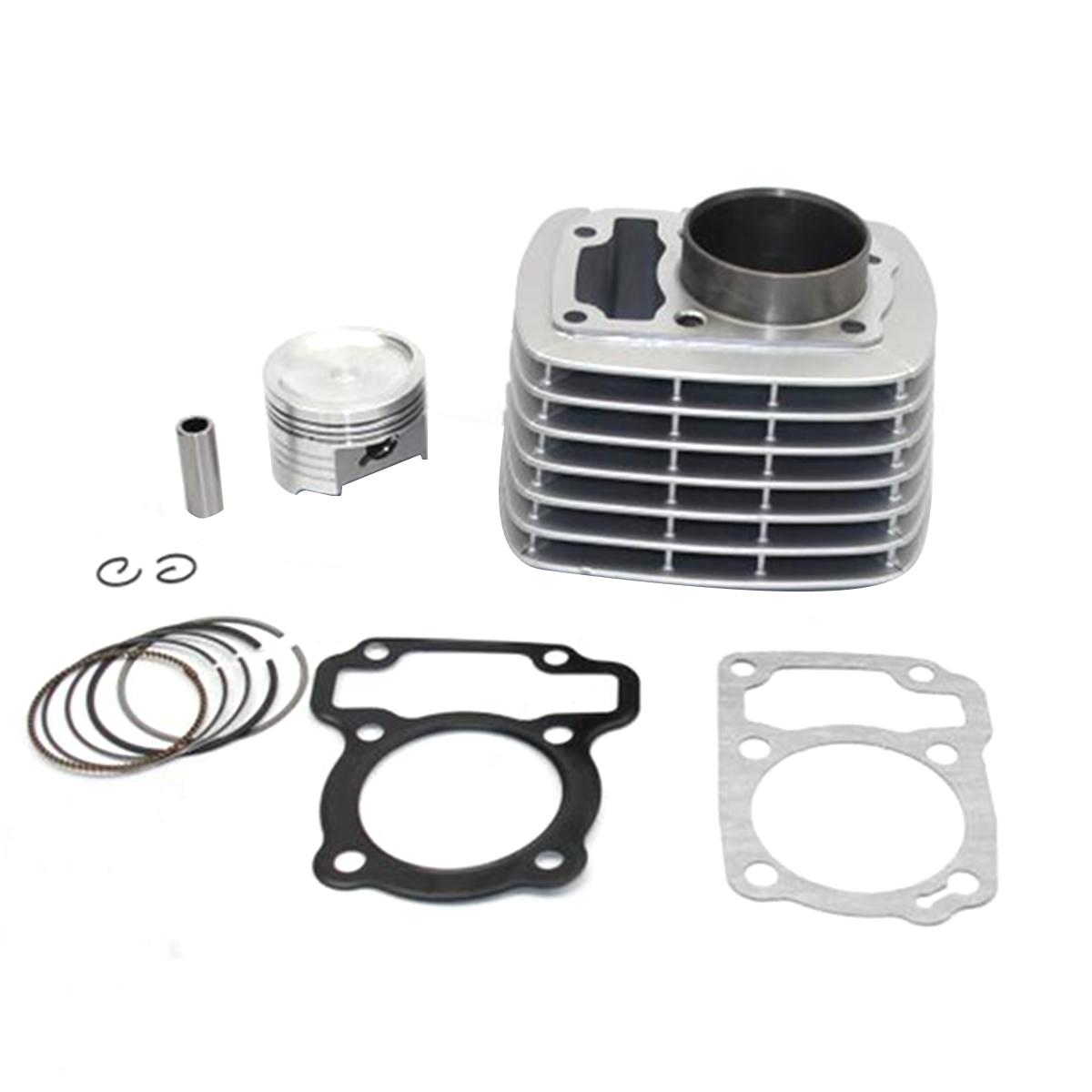
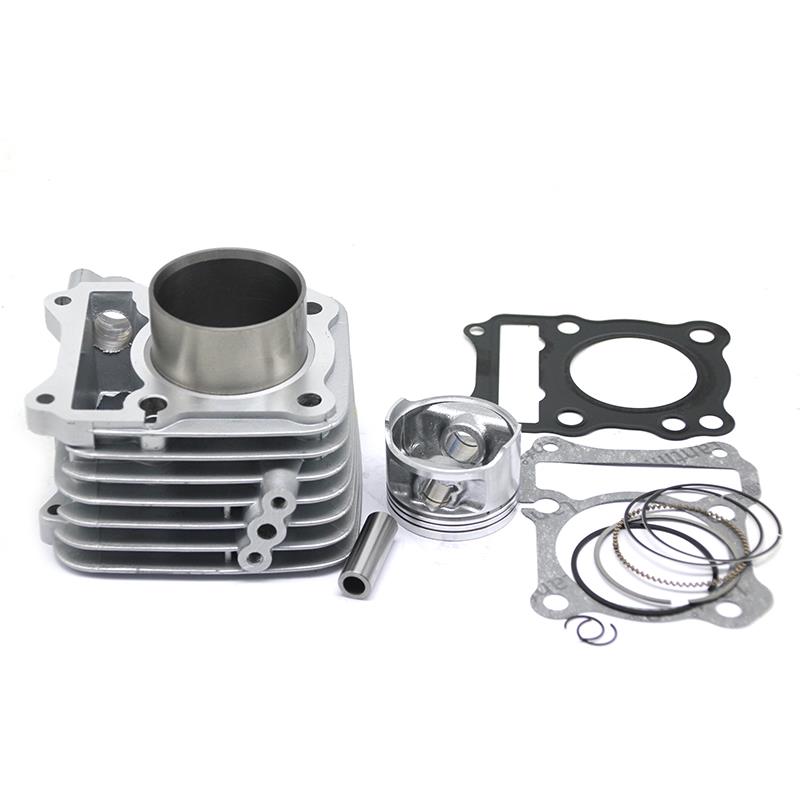
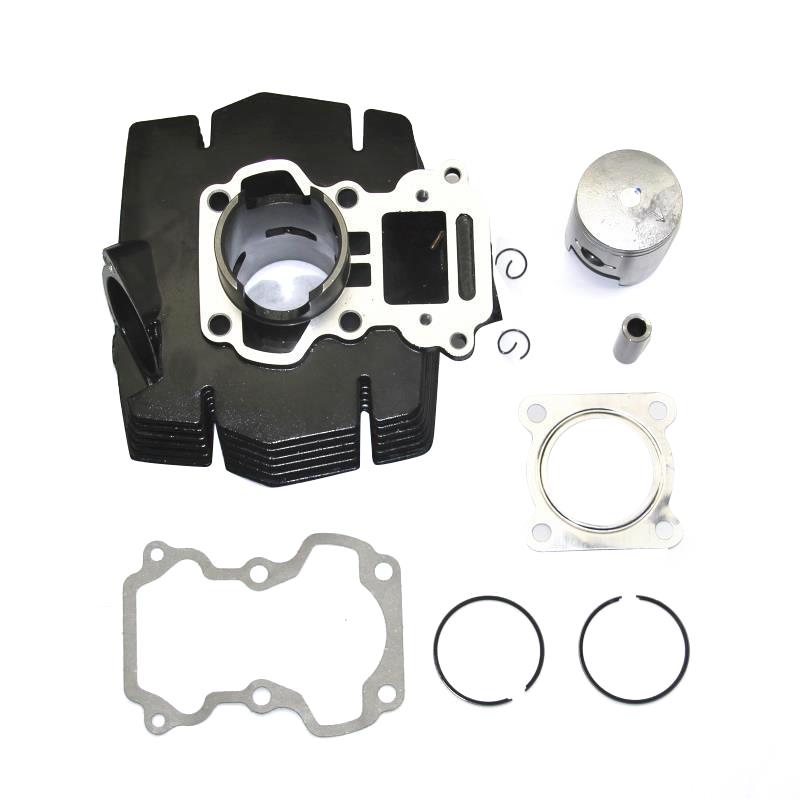
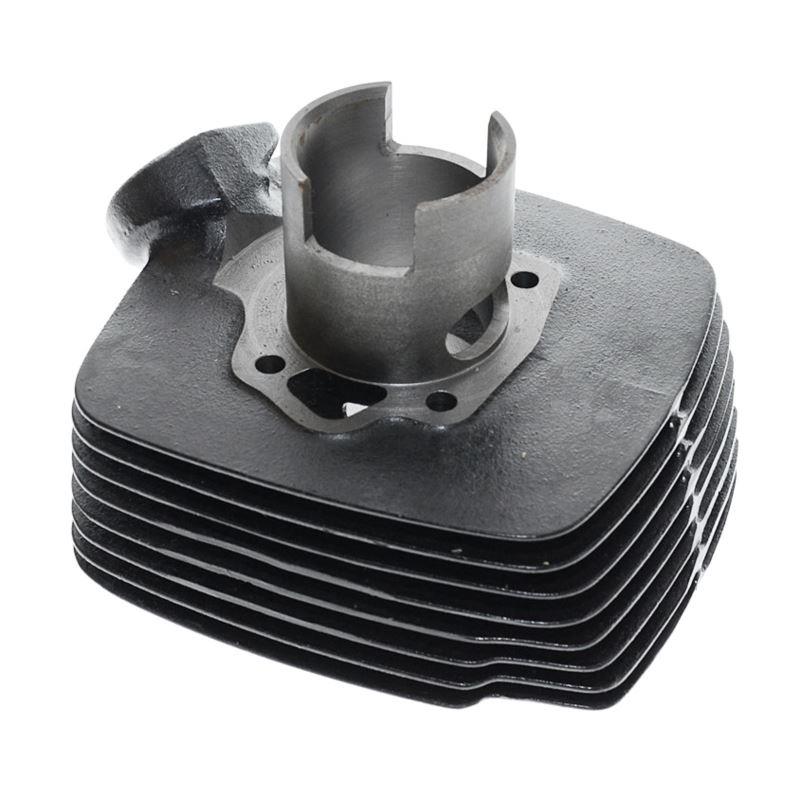
Cylinder Kit 24HP Motorcycle Engine Cylinder Block For CJ750 R12 R71 M-72
Front Brake Master Cylinder 11mm Piston Hand Brake Cylinder as Replacement for Original MZ ETZ125 150 250 251 301
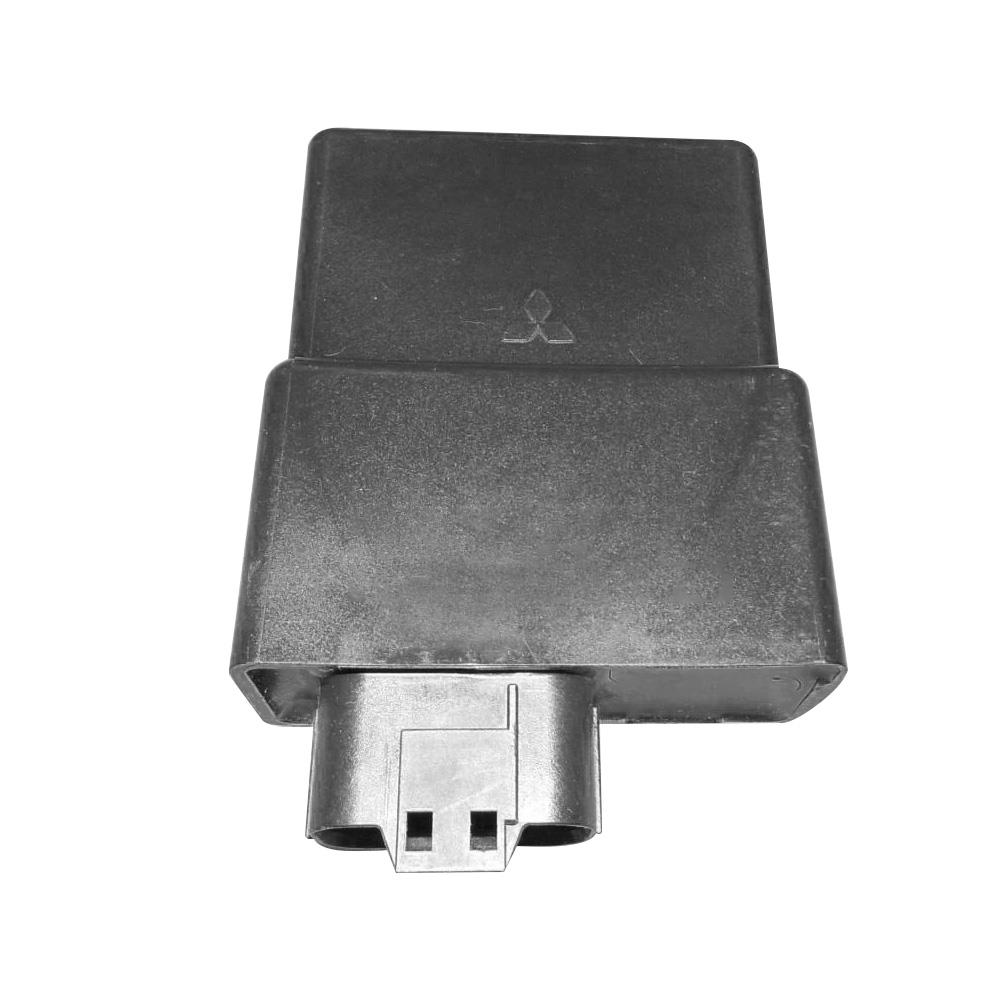
C.D.I. Unit Genuine CDI igniter ECU 32920-33G00 for Suzuki Address V125 V125G CF46A
C.D.I. Unit Genuine CDI igniter ECU 32920-33G00 for Suzuki Address V125 V125G CF46A
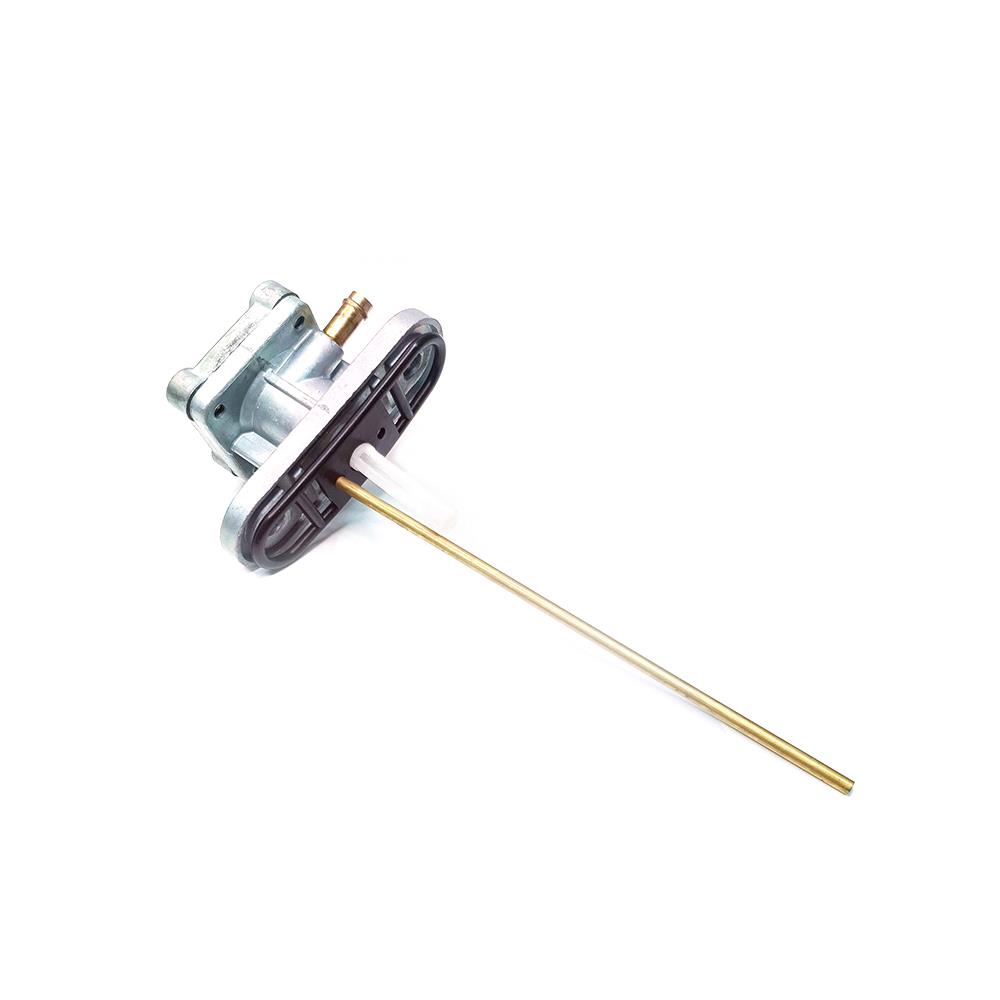
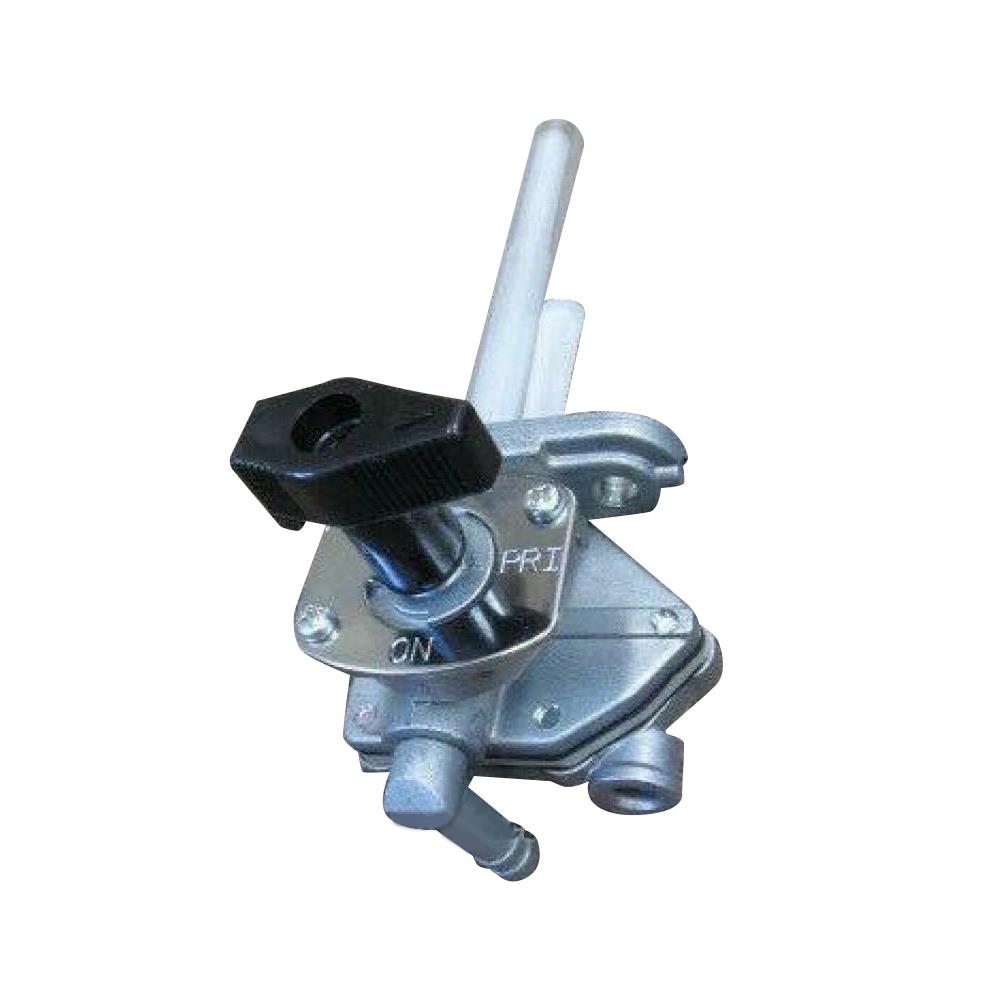
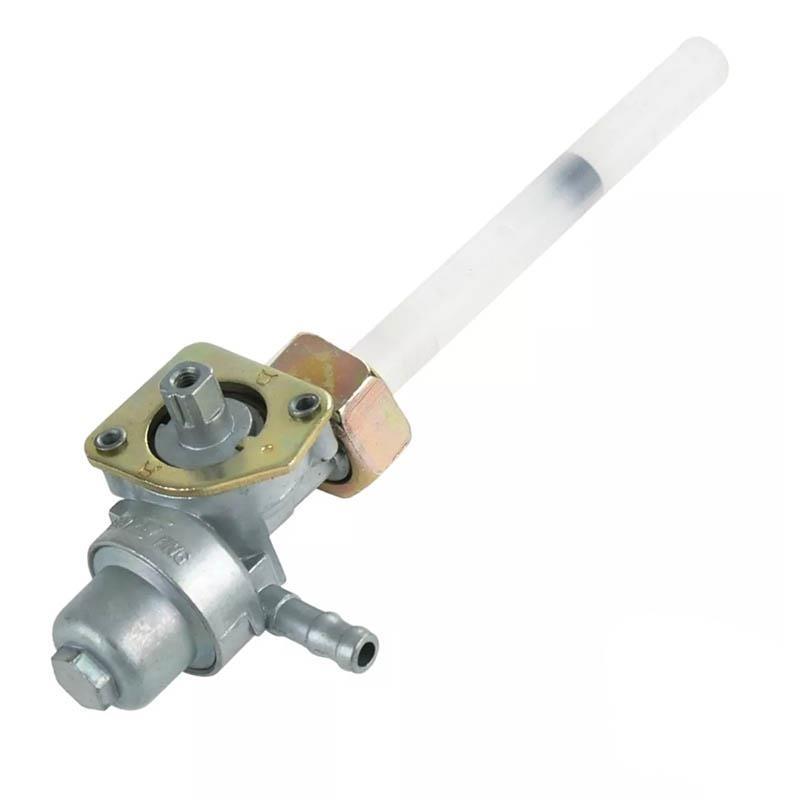
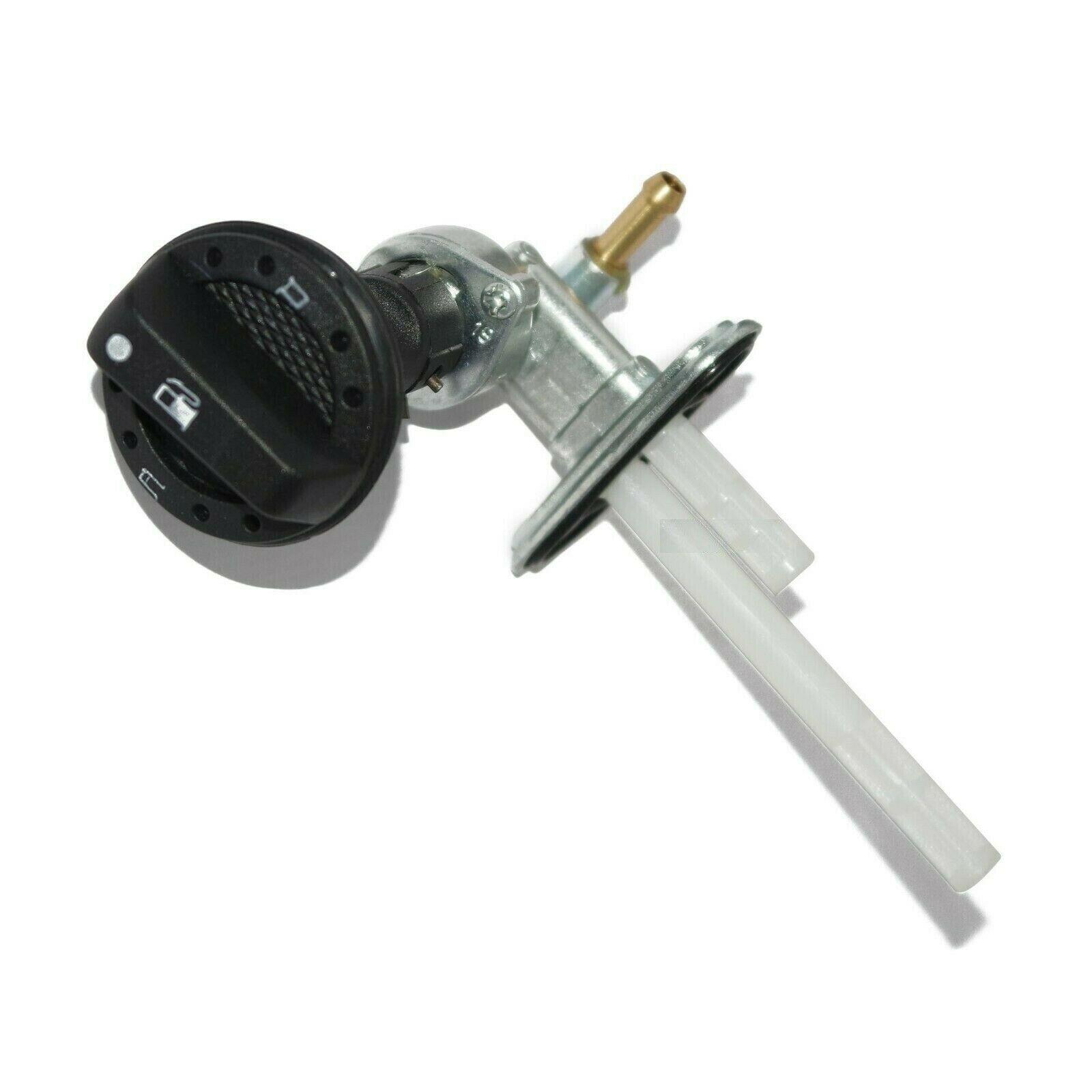
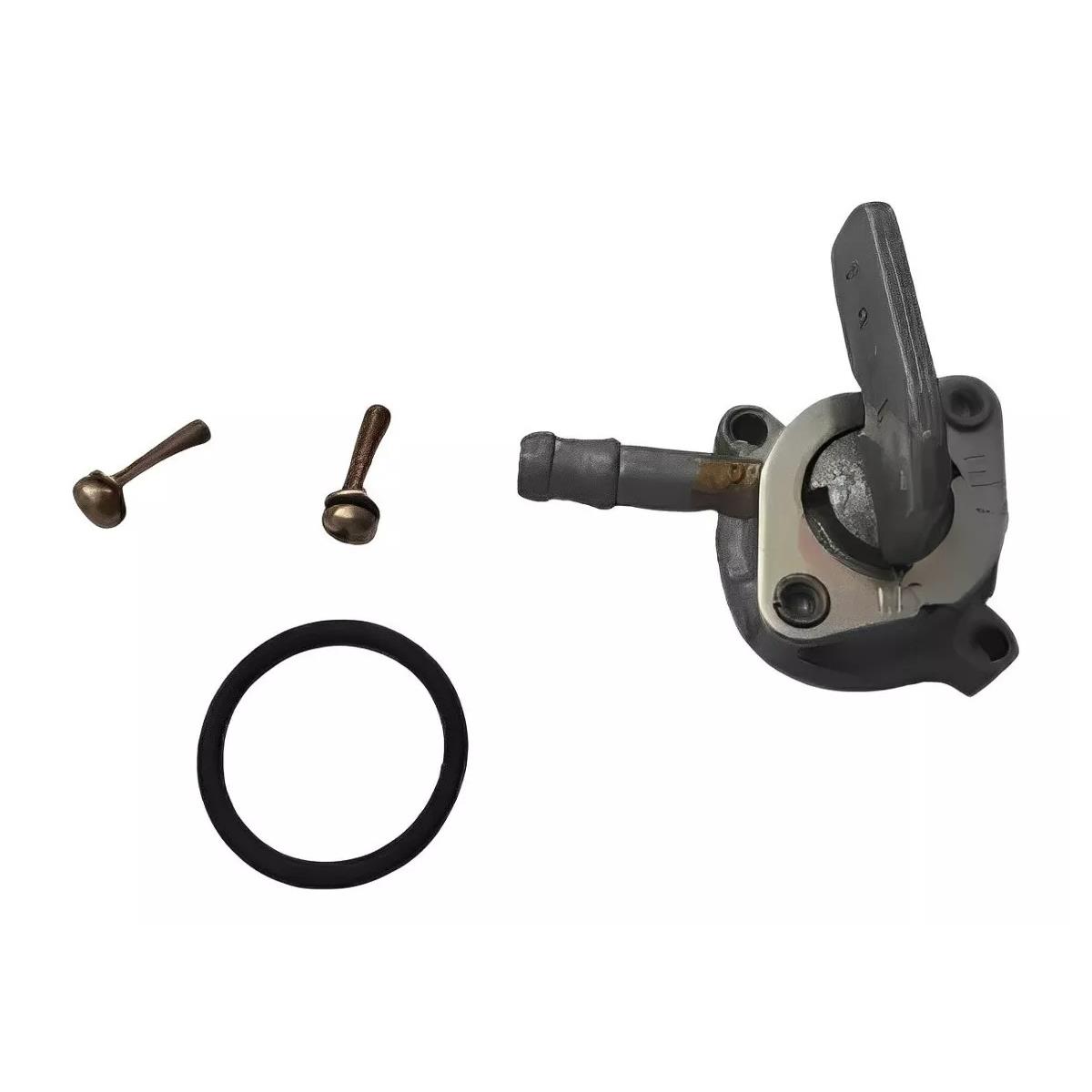
Fuel Cock Assy Kawasaki Genuine Parts 51023-1340 Fuel Tap for Kazer 112 AN112 Motorcycle Cub
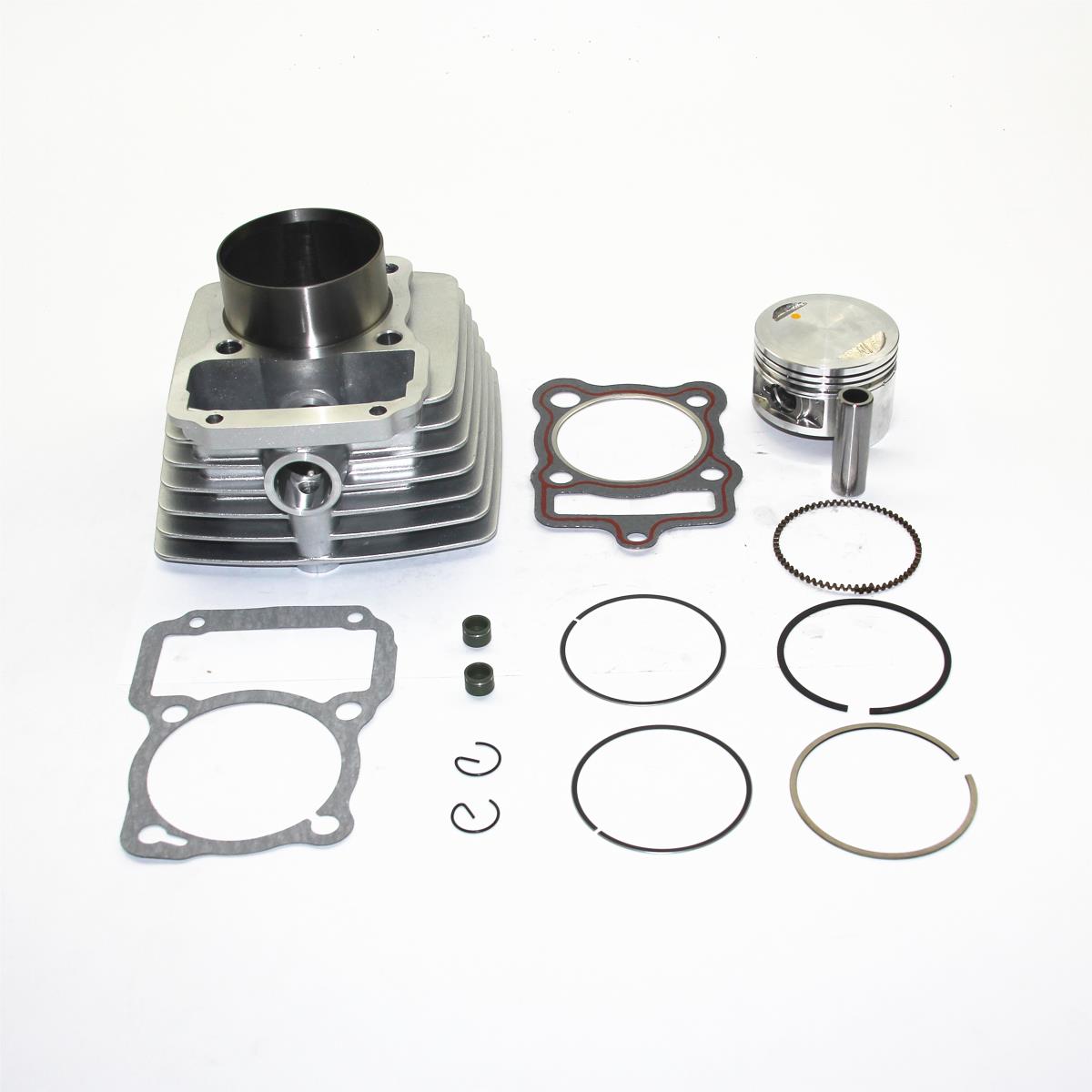
Cylinder Block 52.4mm Aluminum Cylinder with Piston Gasket Set for HONDA KYY ACE CB1 CB CRF GL CGX 125FL
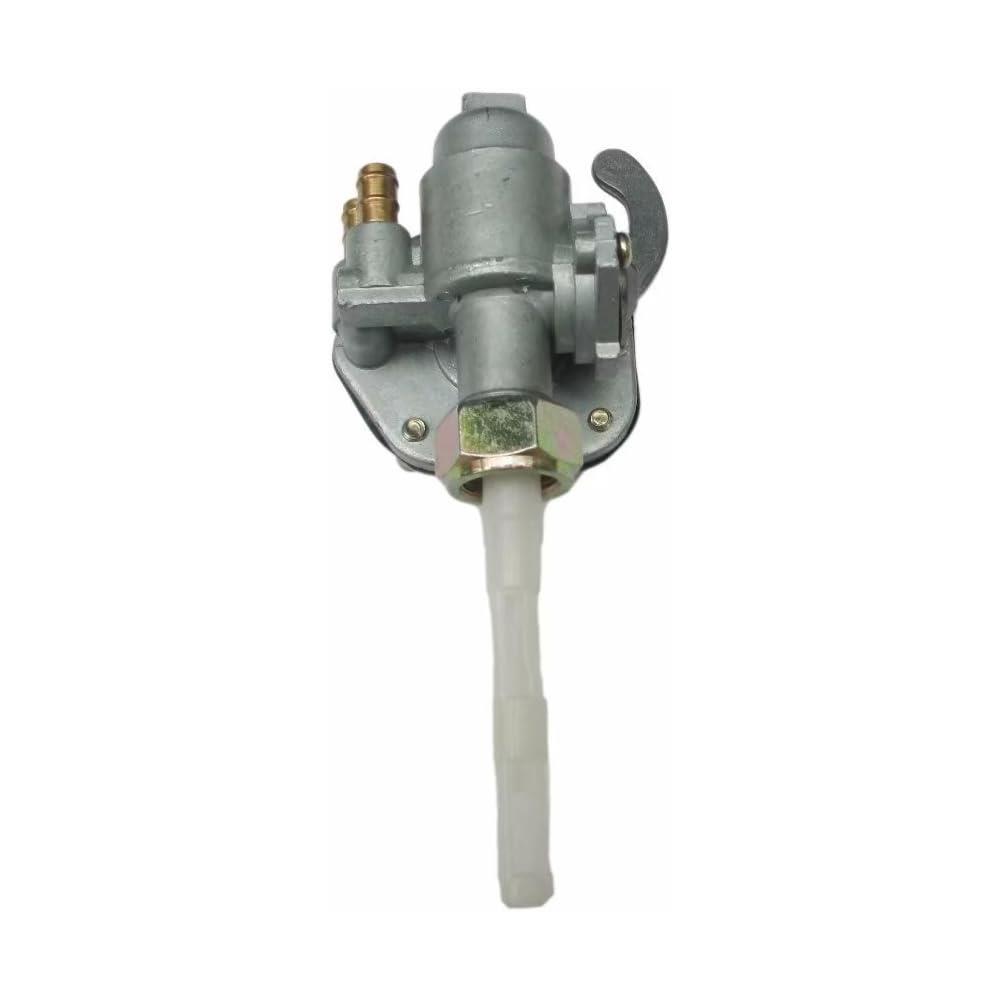
Fuel Cock Assy Yamaha Genuine Parts 3E1-24500-00-00 Pet Cock for YAMAHA Y80 Y75 V80 Chappy LB50 LB80
Tool Box CoverBlack & Gray Luggage Carrier Box MotorcycleFront Trunk Honda Navi 110 81140-K74-900
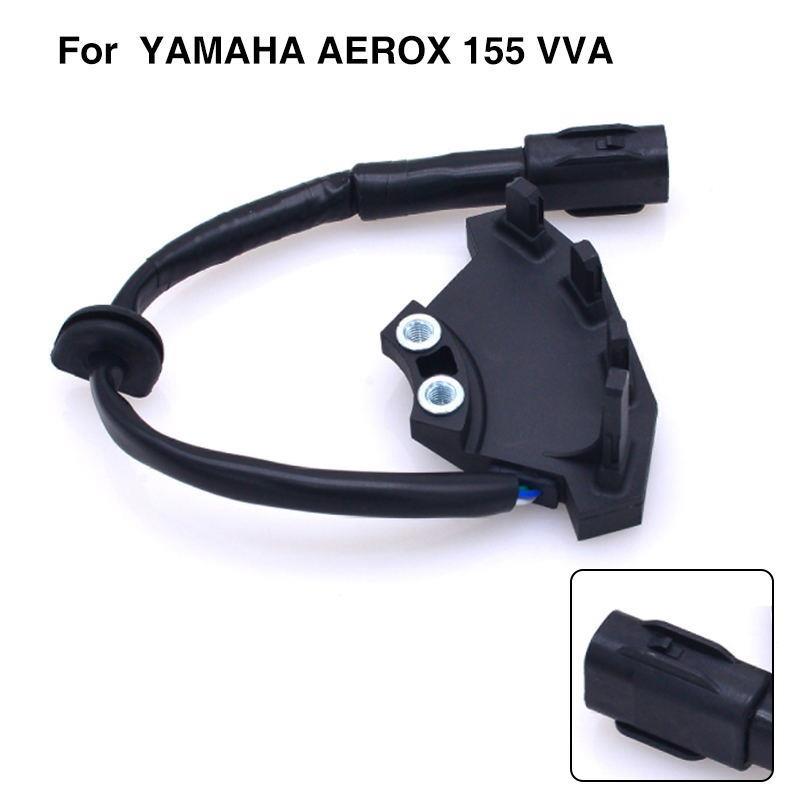
Crankshaft Position Sensor CKP Motorcycle Start Sensor B63-H1410-00 For Yamaha Aerox 155 VVA155
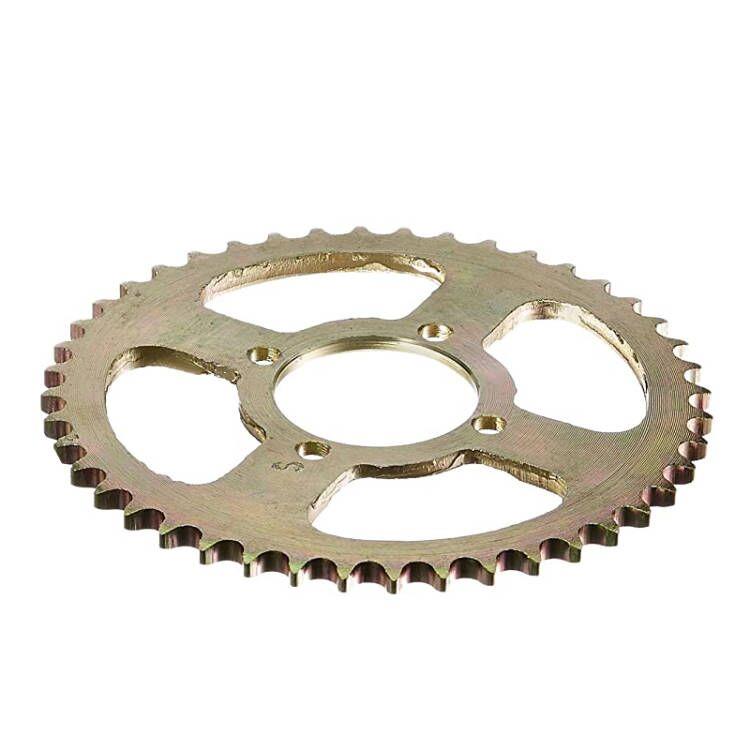
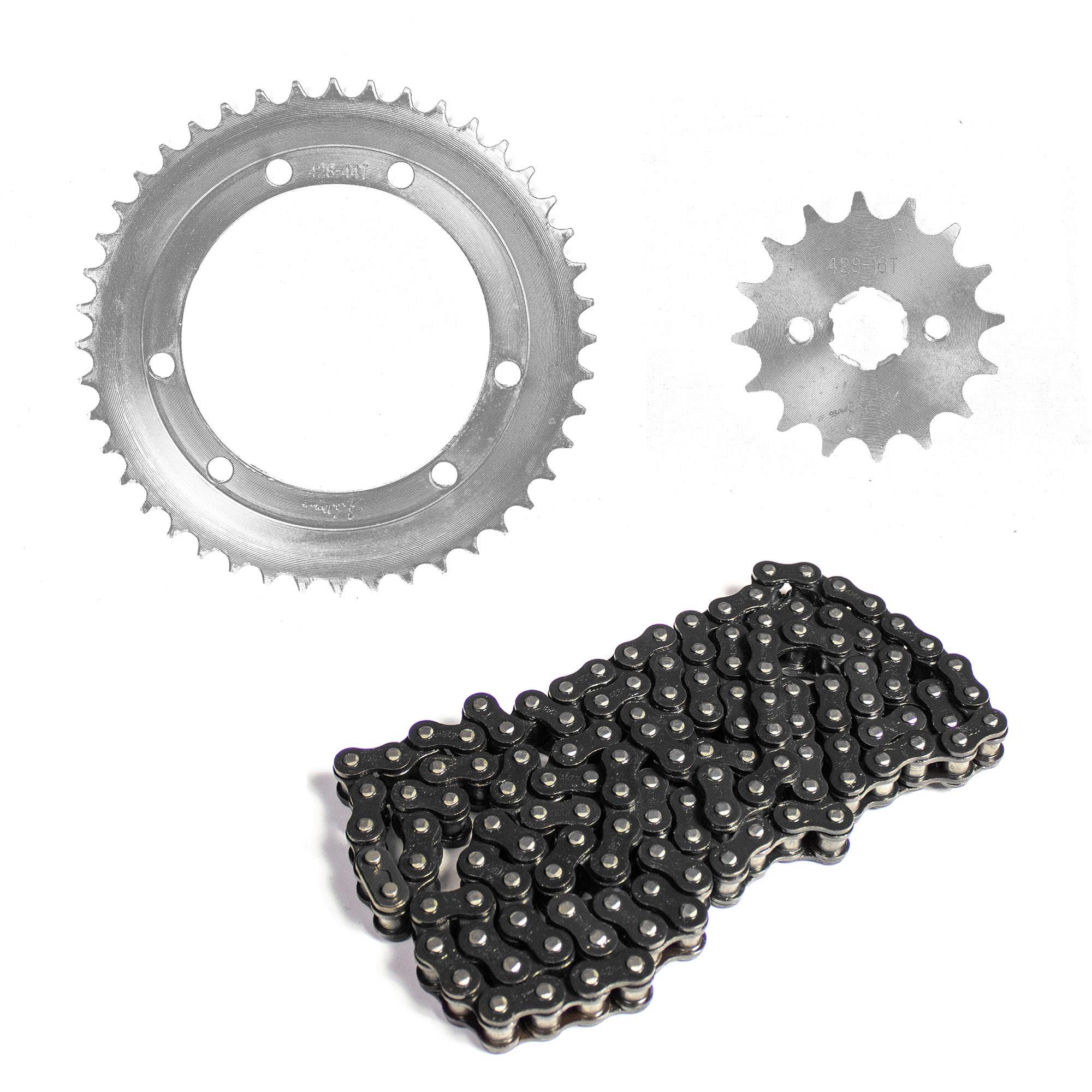
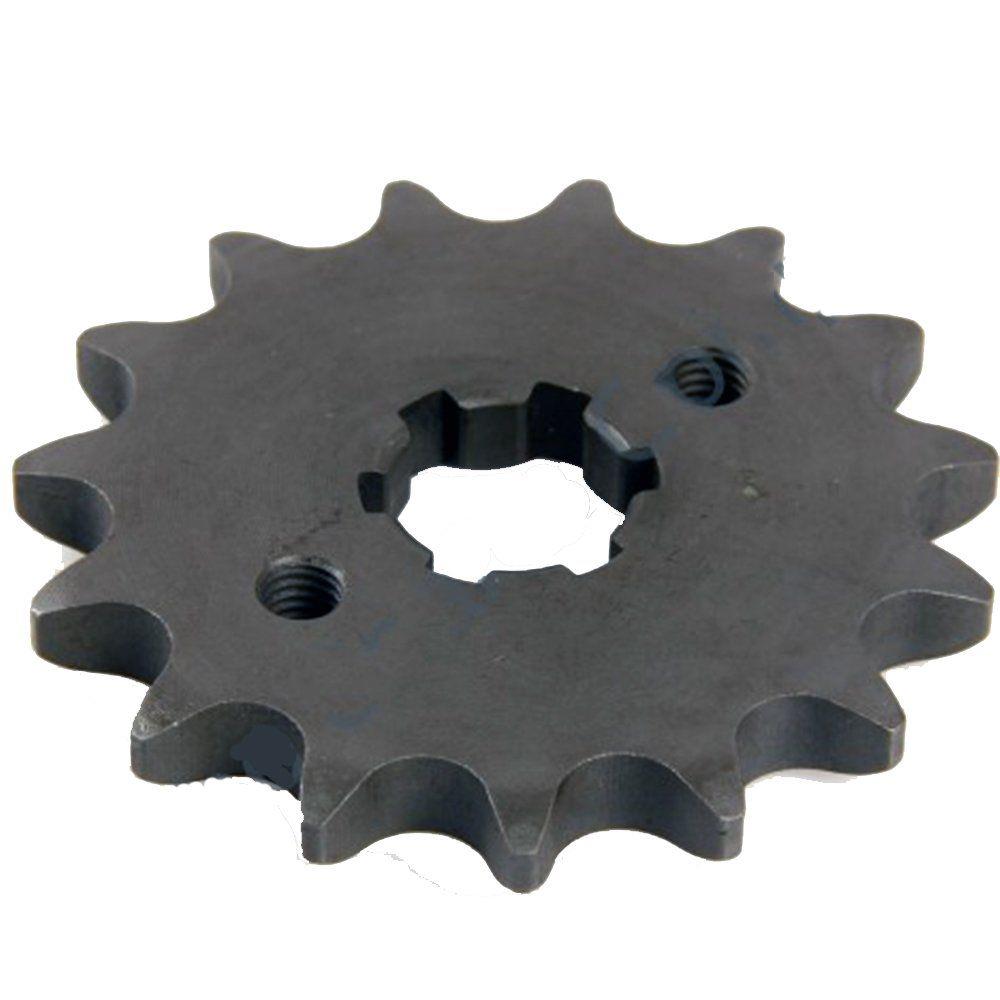
Final Drive Sprocket 428H-38T C45 steel zink 4H HERO HONDA Ambition 133 2002-2008
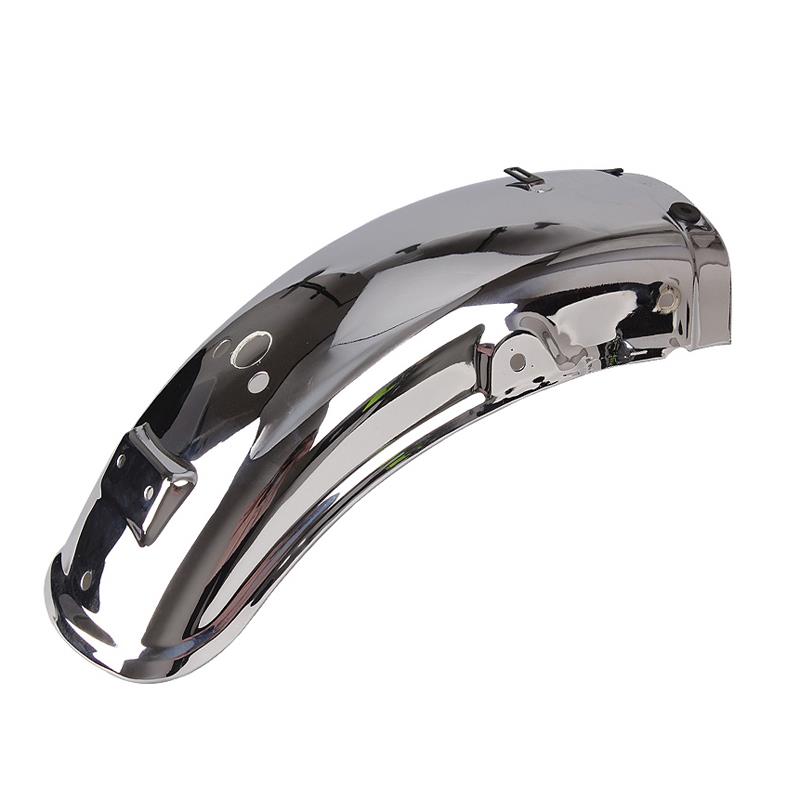
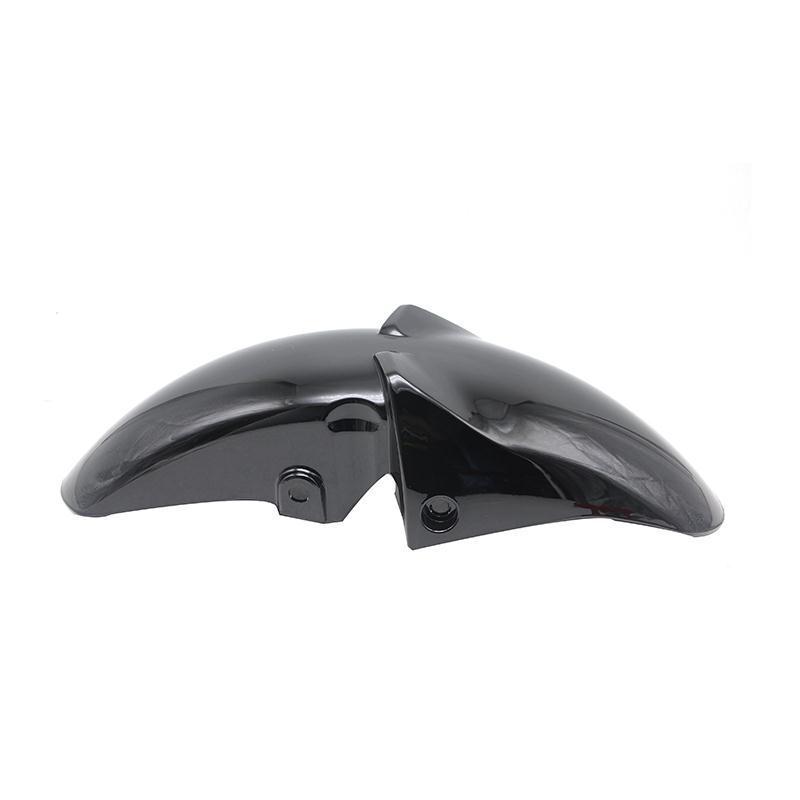
Rear Fender 63111-45F00-000 Rear Splash Guard SUZUKI EN125 GS125 YES125
Fuel Cock Assy Kawasaki Genuine Parts 51023-1340 Fuel Tap for Kazer 112 AN112 Motorcycle Cub
Slow/Pilot Jet KAWASAKI Z1000 KLX125 Z900 KZ900 TM33/36/40 HSR42/45/48 RS34/36/38/40 VM28/486 Pilot Jet
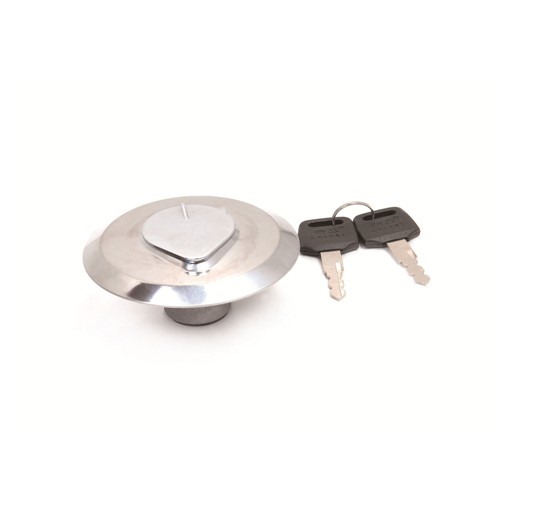
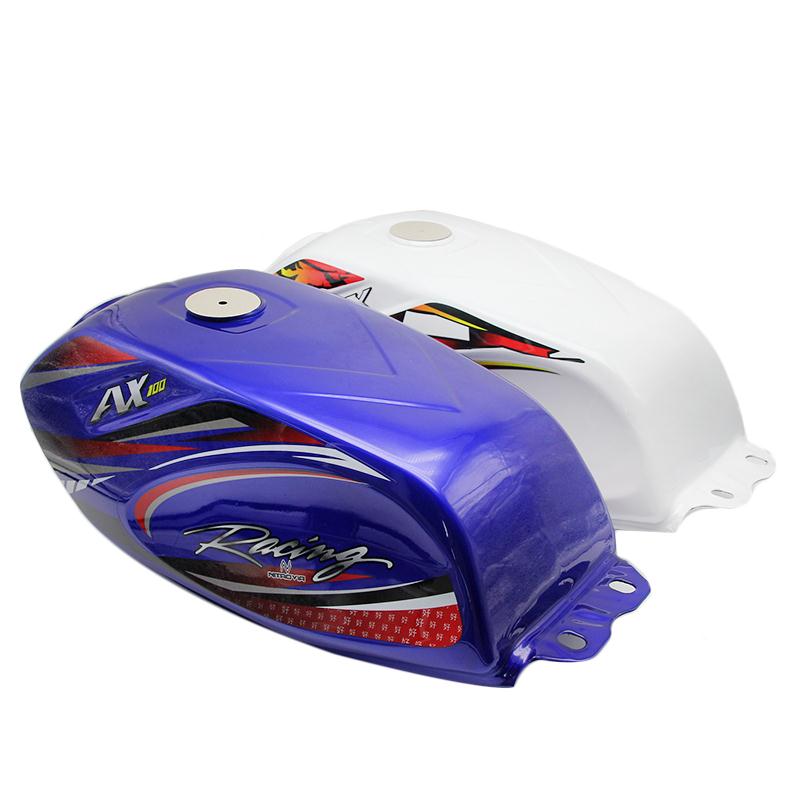
Fuel Tank Cap KEEWAY TX 200 QJ200GY-A 88400J410000 KEEWAY TX 125 QJ125GY-17 QJ150GY-8A
Fuel Tank Cap KEEWAY TX 200 QJ200GY-A 88400J410000 KEEWAY TX 125 QJ125GY-17 QJ150GY-8A
Fuel Tank Cap KEEWAY TX 200 QJ200GY-A 88400J410000 KEEWAY TX 125 QJ125GY-17 QJ150GY-8A
Mudguard Fender Bajaj Genuine Parts JL181405 Front Mud Flap for Pulsar AS200 NS200 Rouser NS200
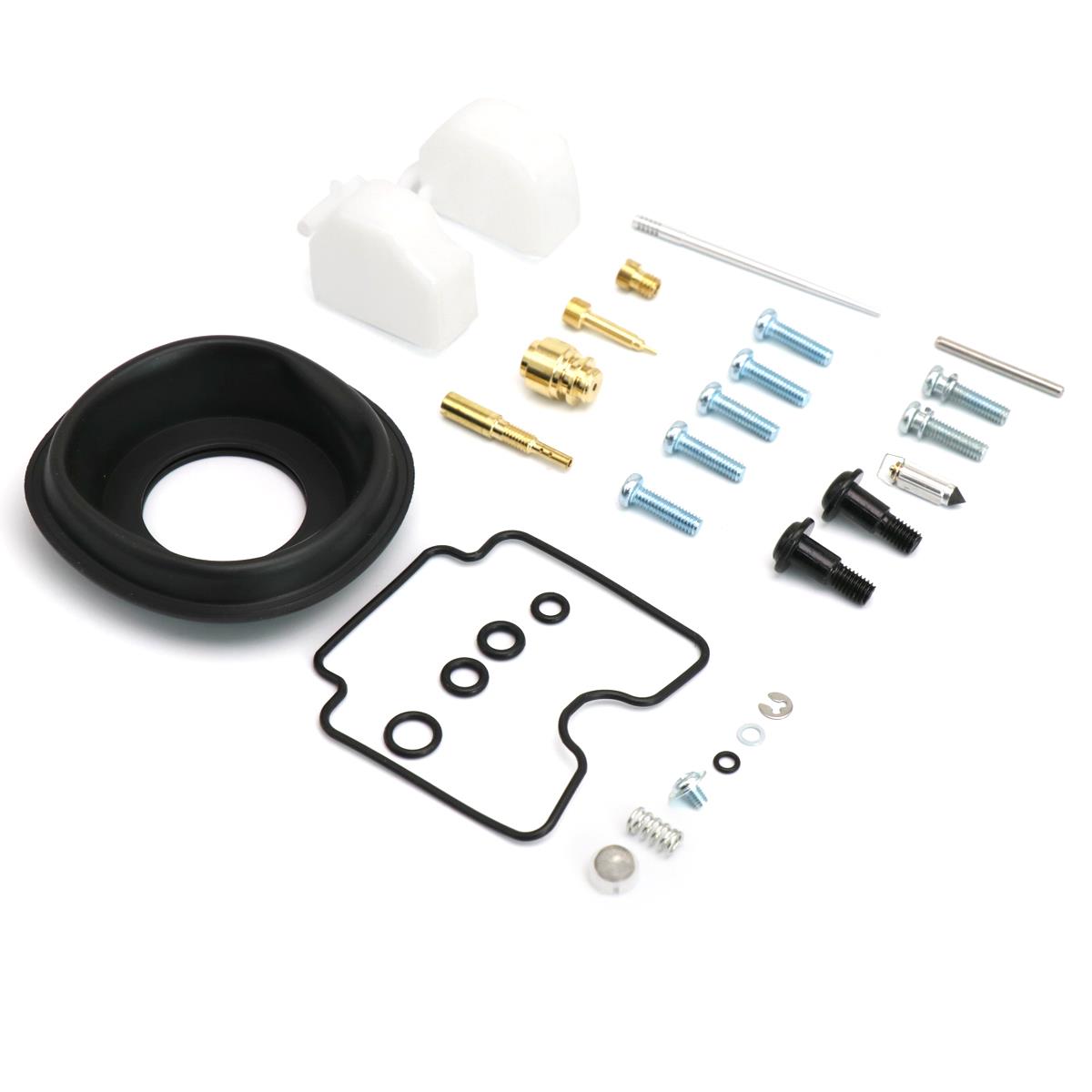
Carburetor Repair Kit Carburetor Repair Kit Air Screw For BT1100 Bulldog XVS1100 Dragstar V-star 1100
Fuel Tank Cap CG125 titan cargo CD110 AKT AK125 HONDA XR250 Turnado XR200R NX200
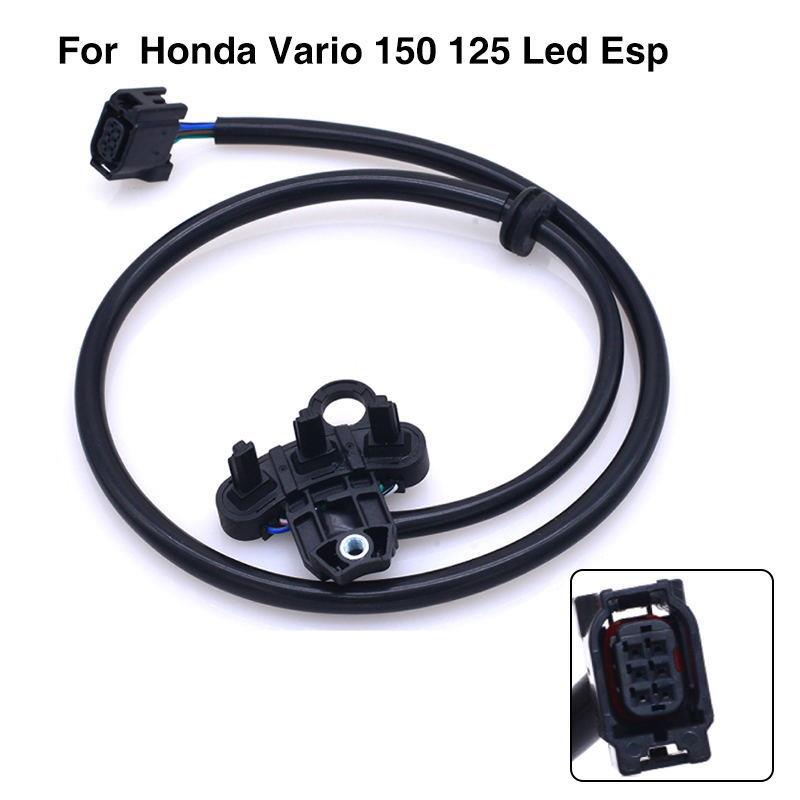
Crankshaft Position Sensor CKP Coil Sensor 31220-K36-J01 For Honda Vario 125 150 LED ESP PCX150
Meter Assy Motorcycle universal modified Mini high-definition adjustable LCD speedometer with oil gauge
Rear Fender Motorcycle Rear Wheel Metal Mudguard Suzuki GN125F Haojue HJ125-8E 63011H05300H000
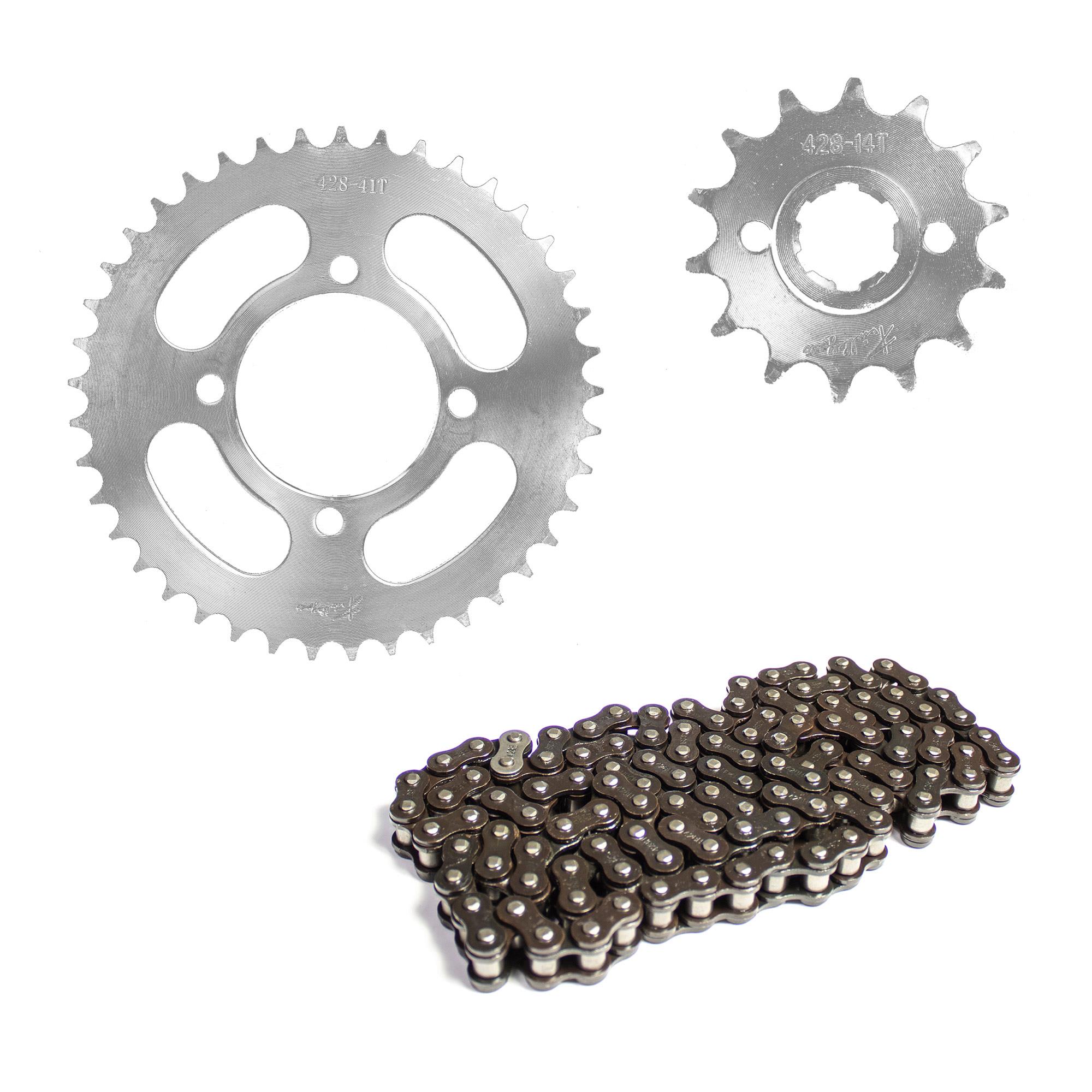
Drive Sprocket & Chain traction kit 44D-16D 428Hx130L for Italika DM200 F0203KS23
Headlight Inner Visor Motorcycle Headlight Cover Inner Visor BAJAJ Pulsar 200 NS JL181203 Pulsar150 160
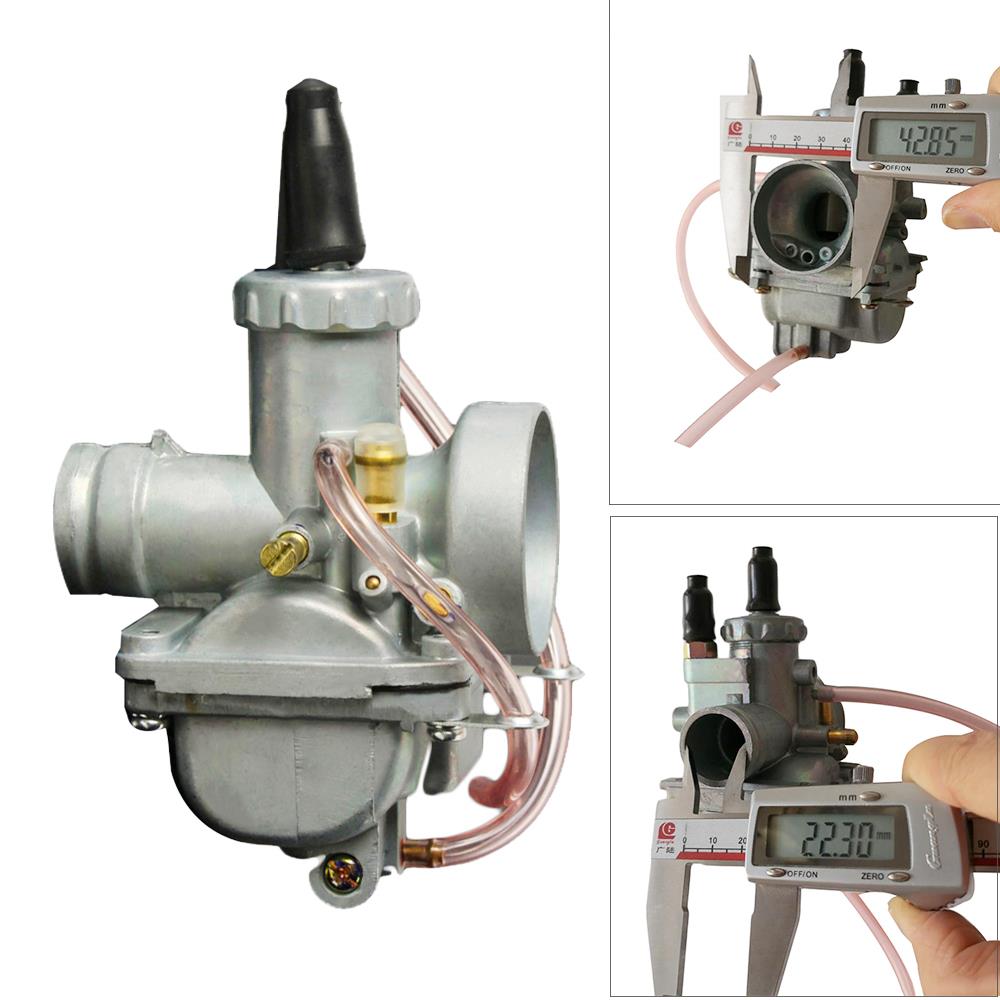
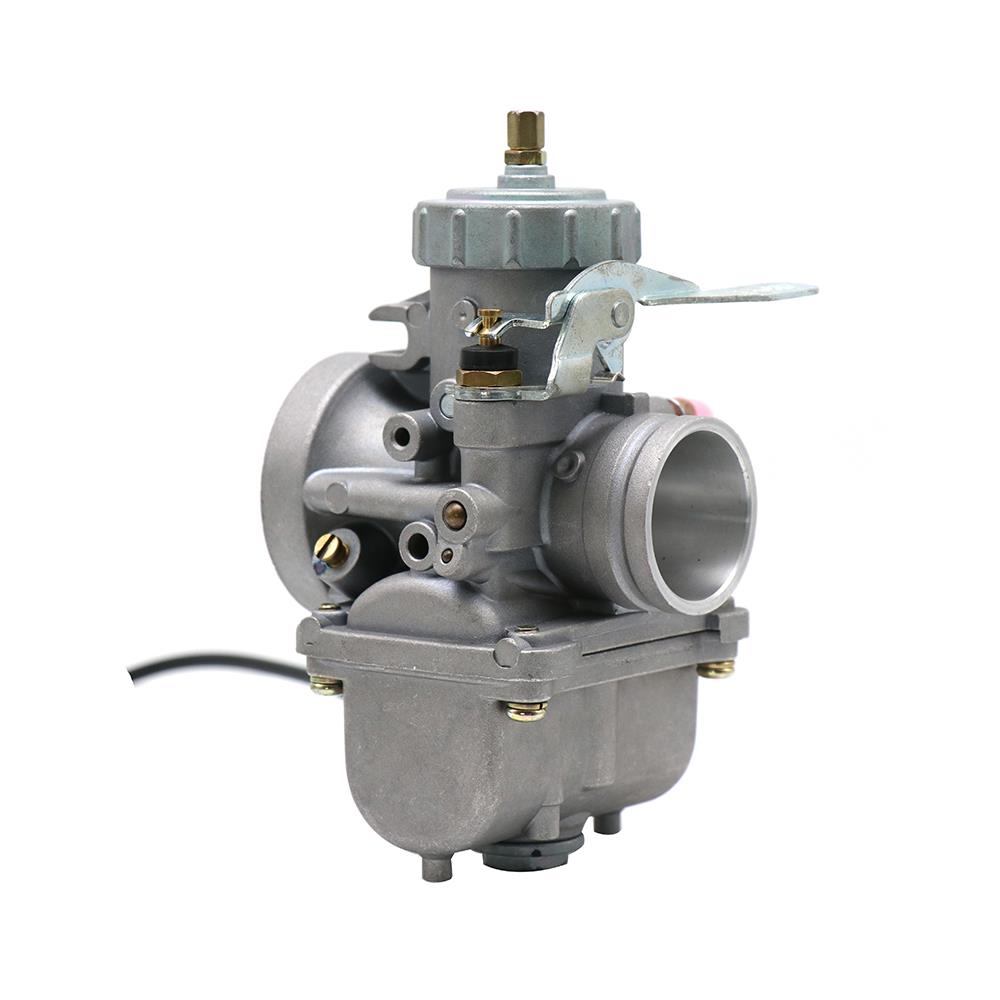
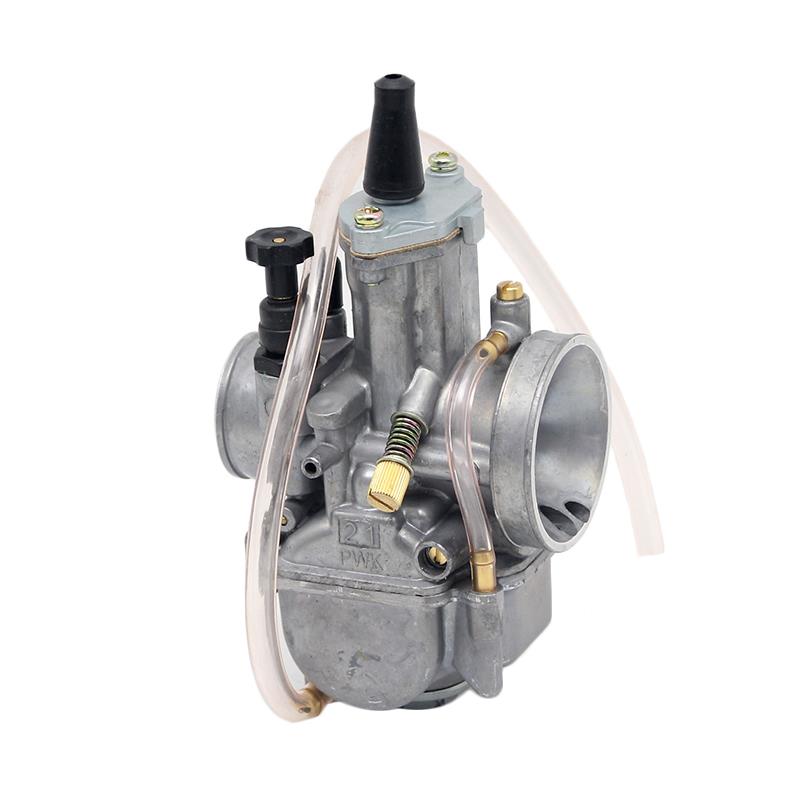
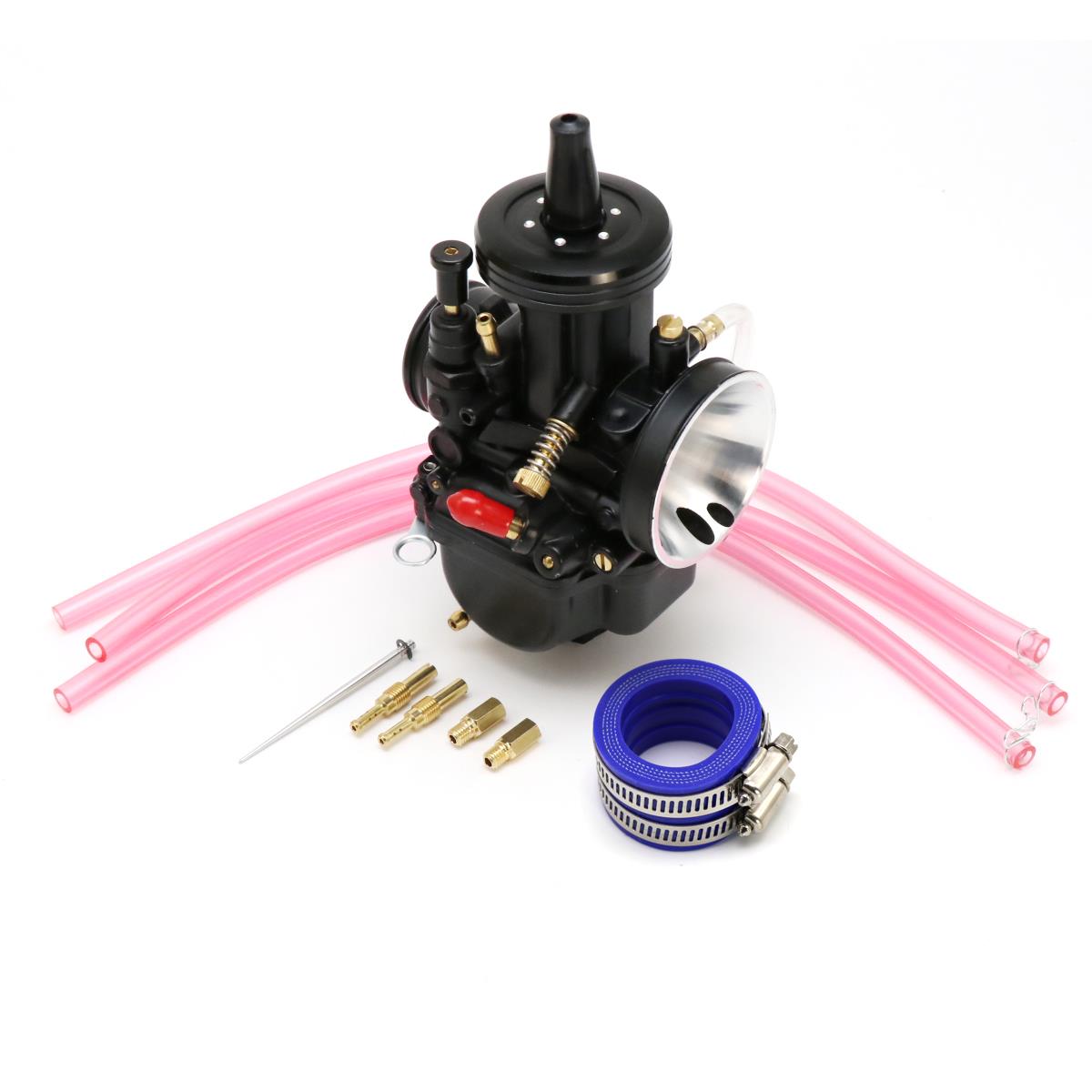
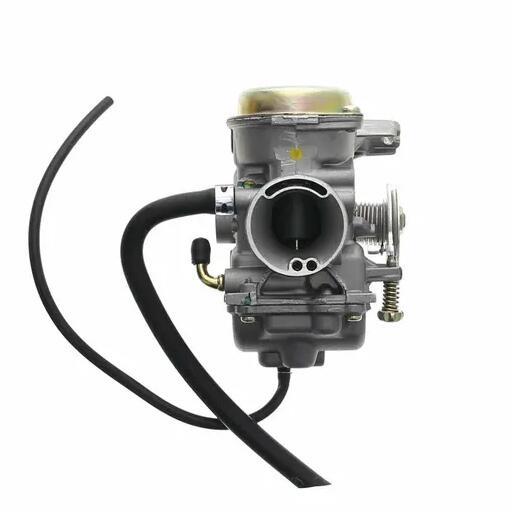
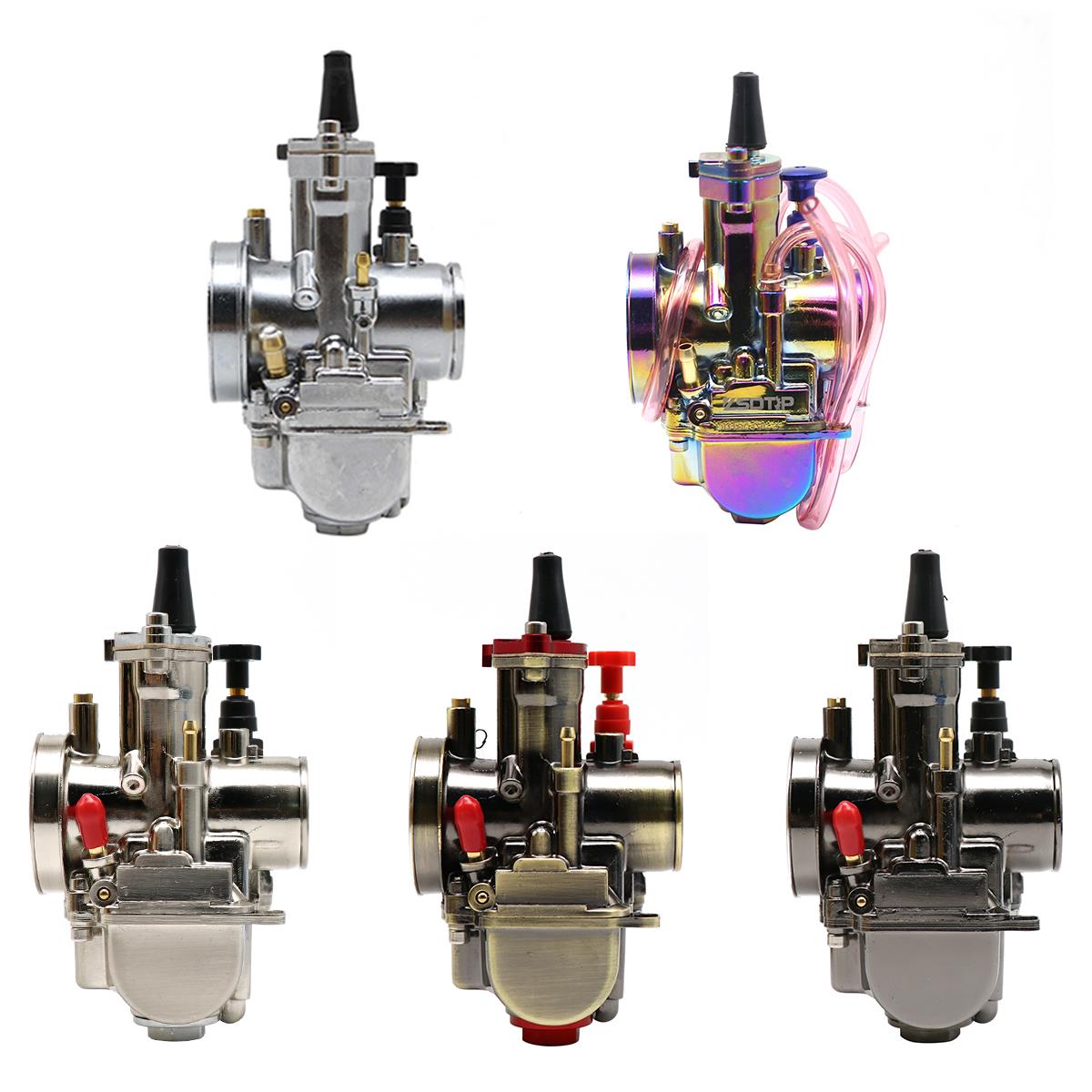
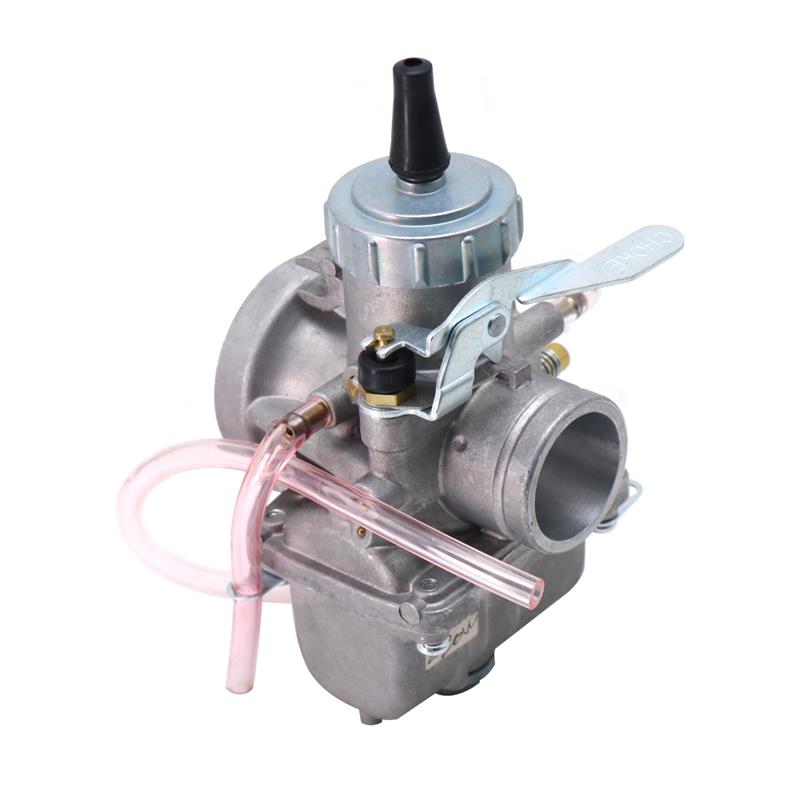
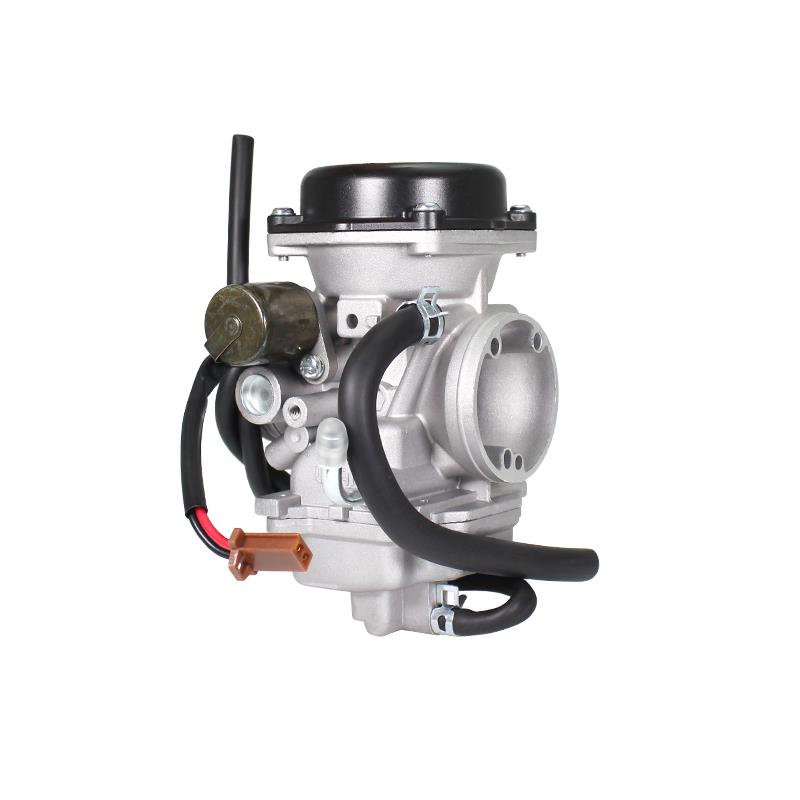
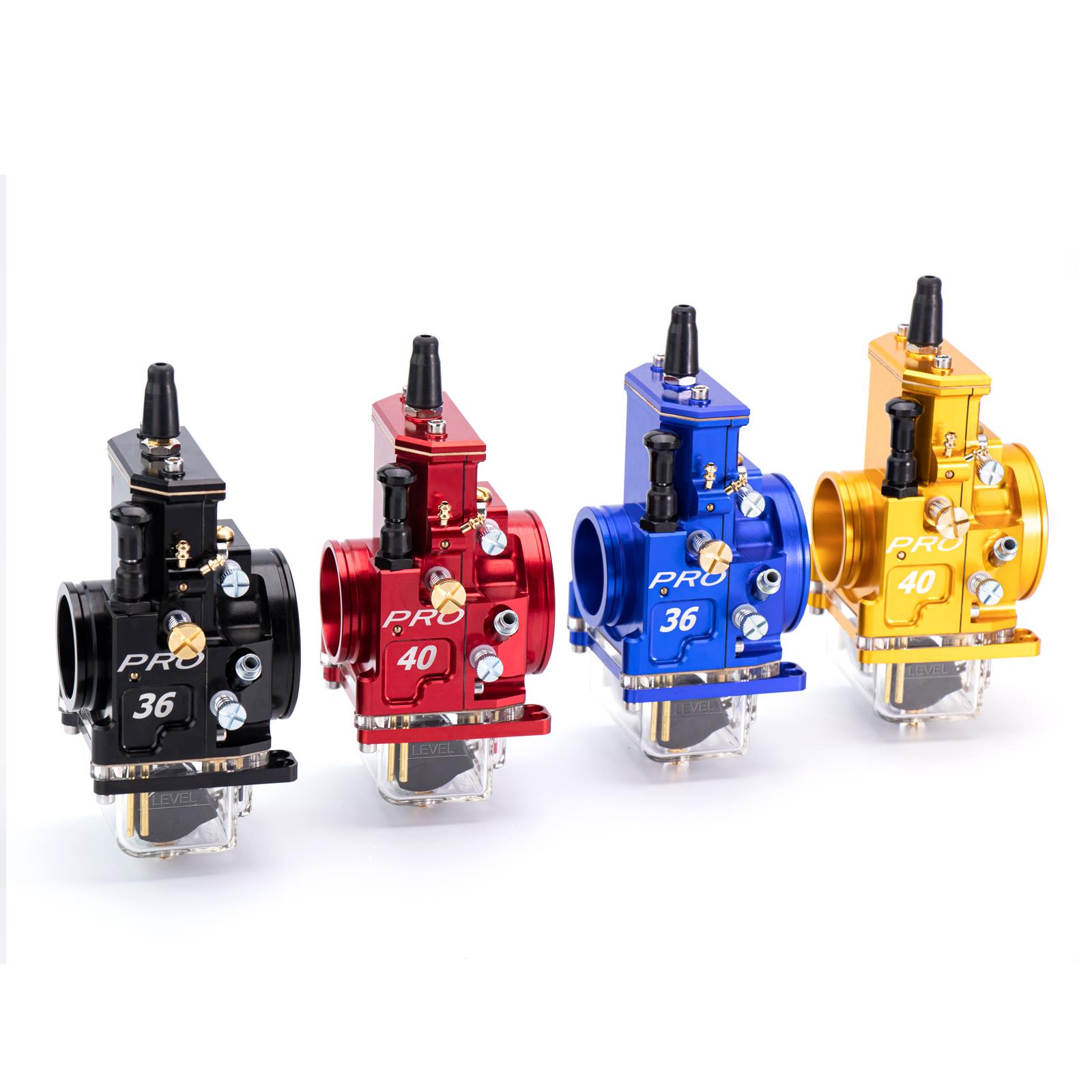
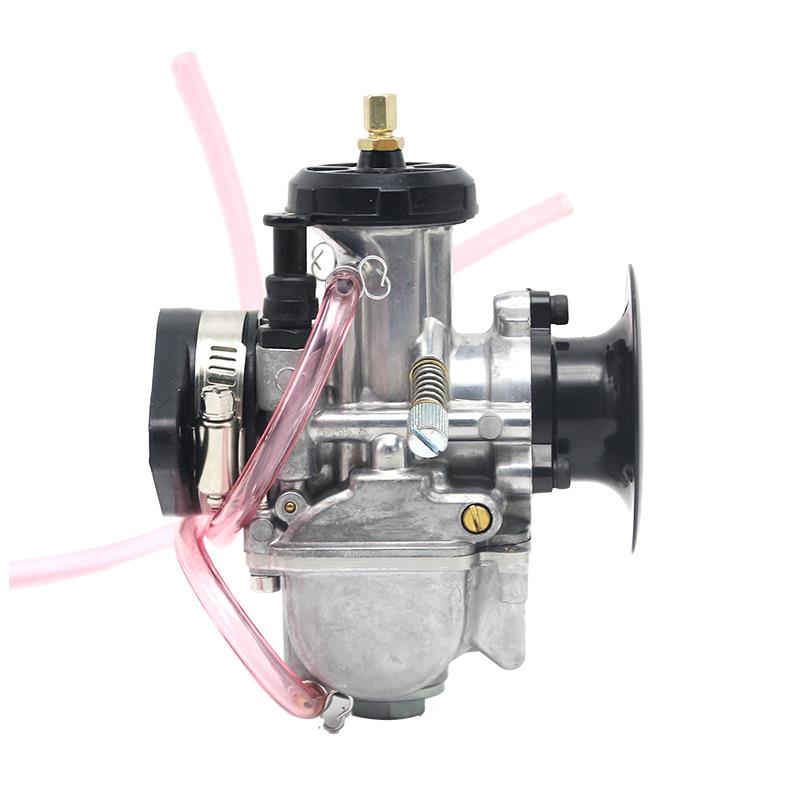
Carburetor Assy 2-Stroke Engine Motorcycle PWK Racing Carburetor For Motorcycle Scooter ATV Quad Dirt Bike
Front Fender ABS Mudguard Fender with Stay HONDA KGA CG125 Cargo Fan125 Titan 2000
Cable Stop Buckle Universal Wire Core Clamp Throttle Cable Pull Brake Stop Bolt Pin For 50CC-250CC
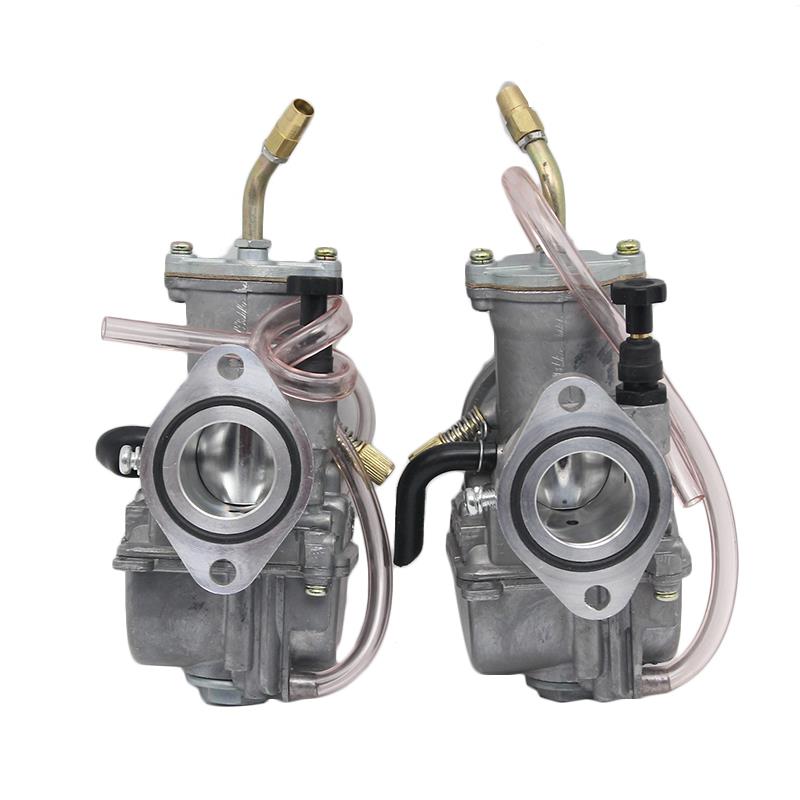
Carburetor Assy Motorbike Motorcycle Racing Carburetor Power Jet PWK 21/24/26/28/30/32/34 Modified Carburetor
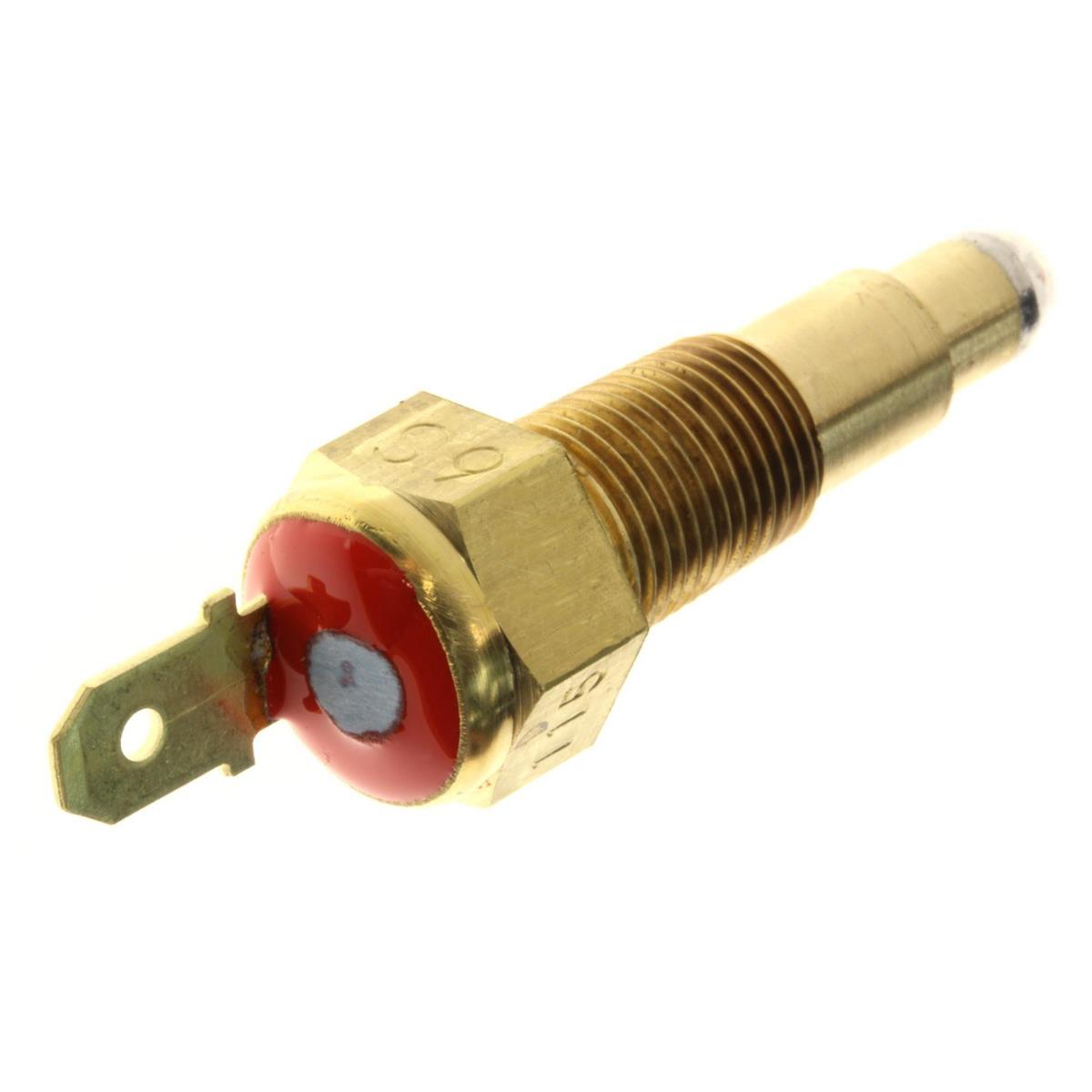
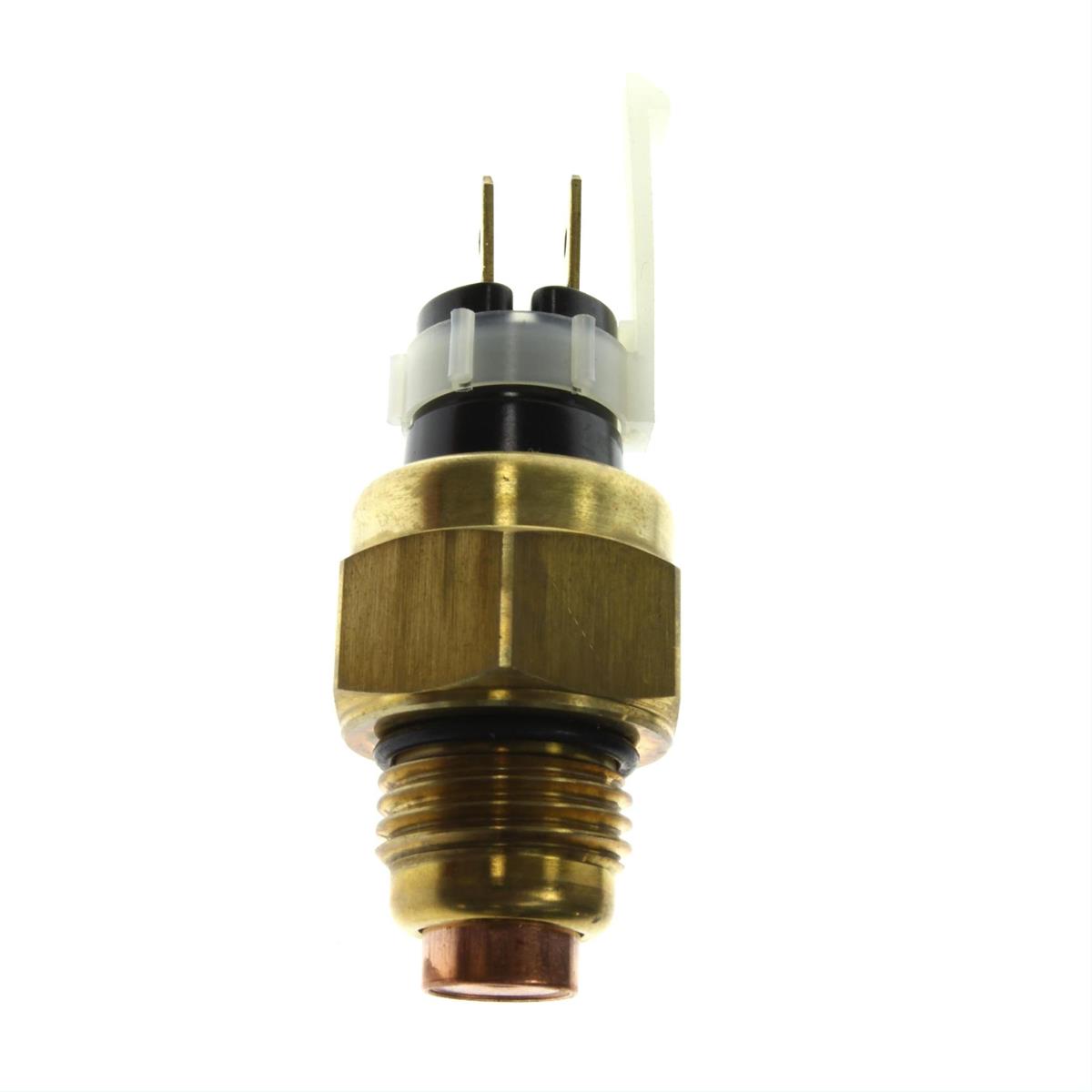
Thermostat Switch Assy Honda 37760-MAV-003 Thermo Sensor for VLX600 VT600 750 Shadow Black Widow VTR250 VTX1300
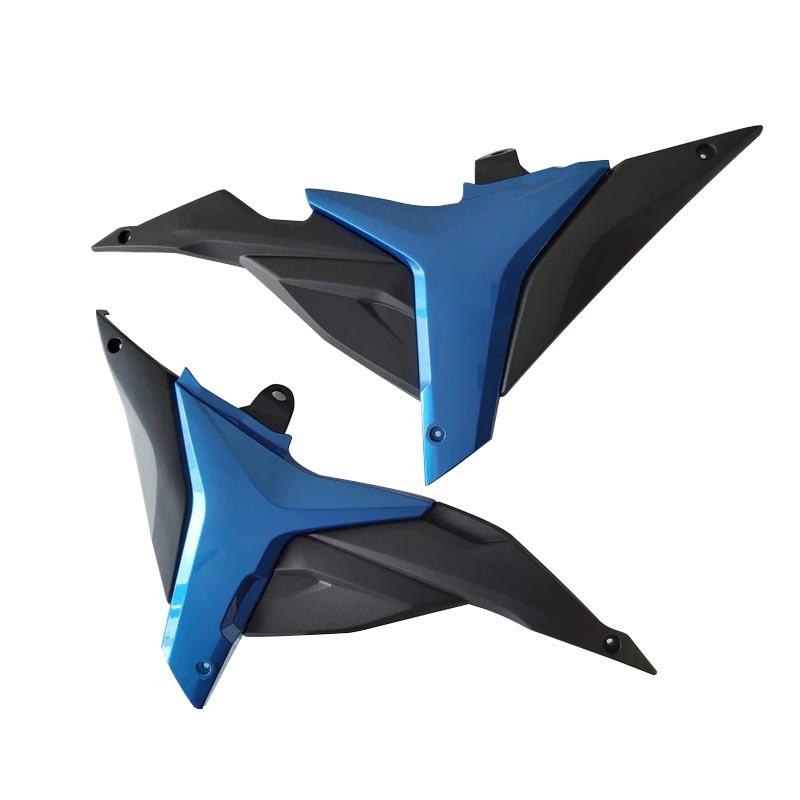
Under Cowl Lower CTR Cowling 94498-34J00-000 for SUZUKI GSX150F Gixxer SF 2016-2019
Fork Air Bleeder Valves CNC Fork Preload Adjusters with Bleeders for KAWASAKI KLX230 KLX230R 230S 230SM
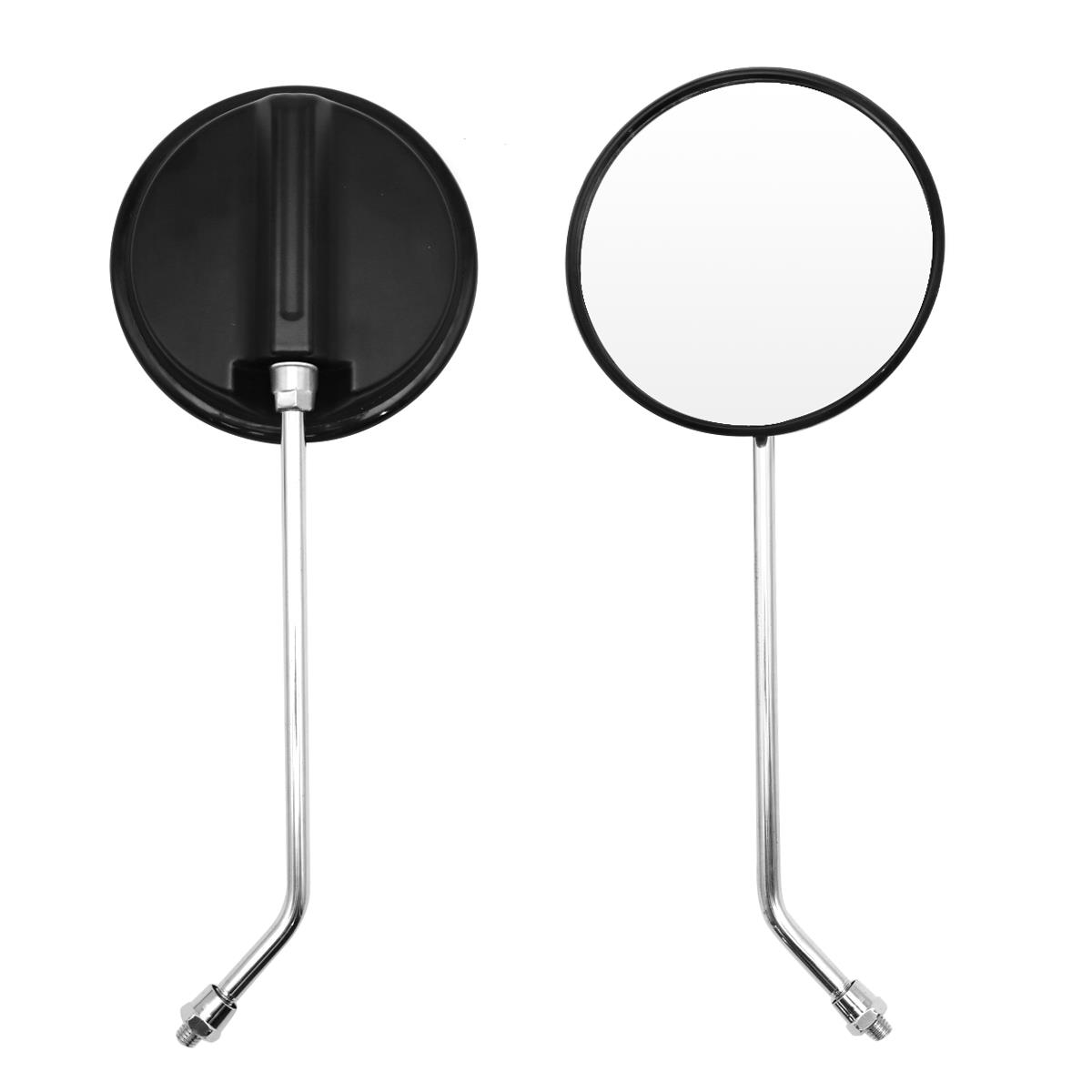
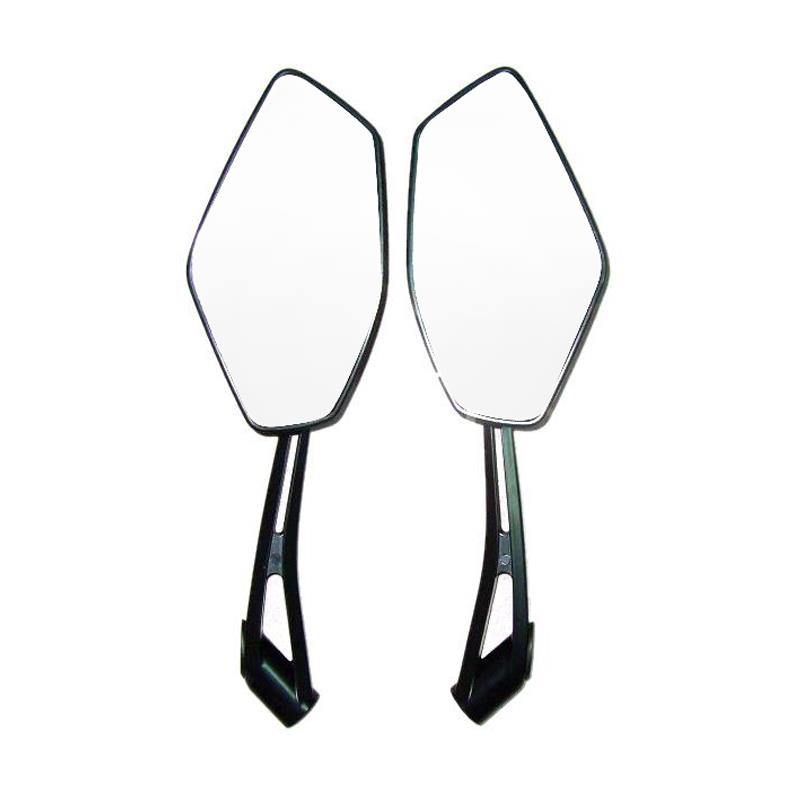
Rear-view Mirror Comp. Round Dia. 128mm M8 Stainless Chormed bar For Simson S50 51 53 70 83 SR50 80 KR51/2 Schwalbe
Side Cover Bajaj Genuine Side Panel Cover for Bajaj Discover125 ST Discover 100 T
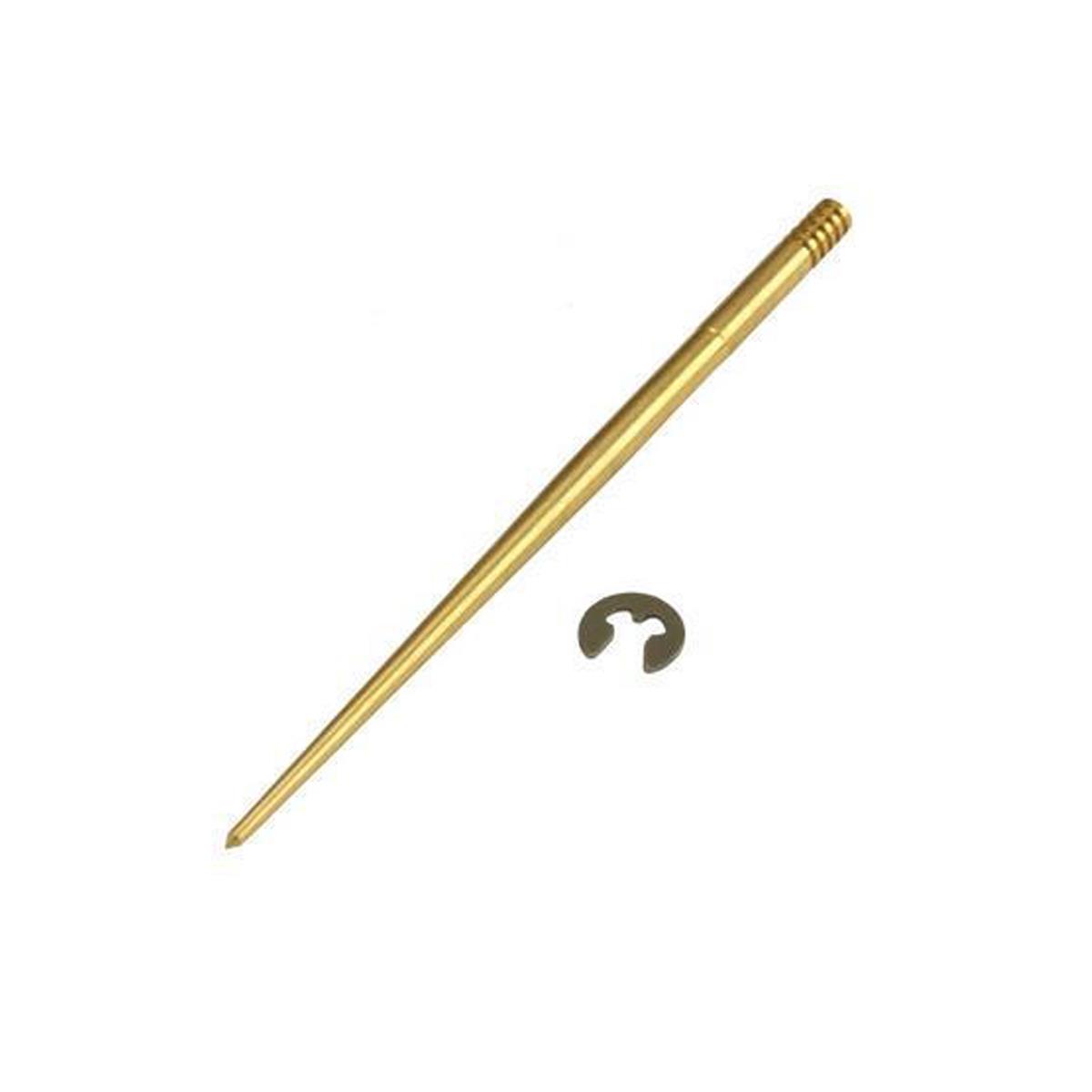
Carburetor Jet Needle CR26-33 5 CLIP POSITION Keihin N427-11YXX Genuine Keihin Clip For Needle 0403-802-1000
Rear Fender Genuine Frame Body Plastic Parts Inner Rear Fender India HONDA NAVi 110 CLIQ 110 80107-K74-N00
Choke Cable Comp. TVS Motorcycle Genuine Parts TVS Phoenix 125 P.No. N5170130
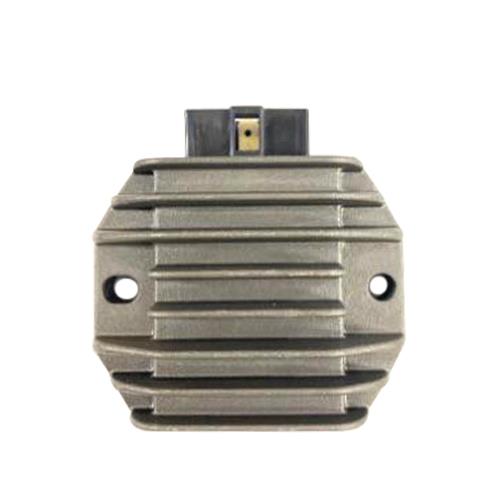
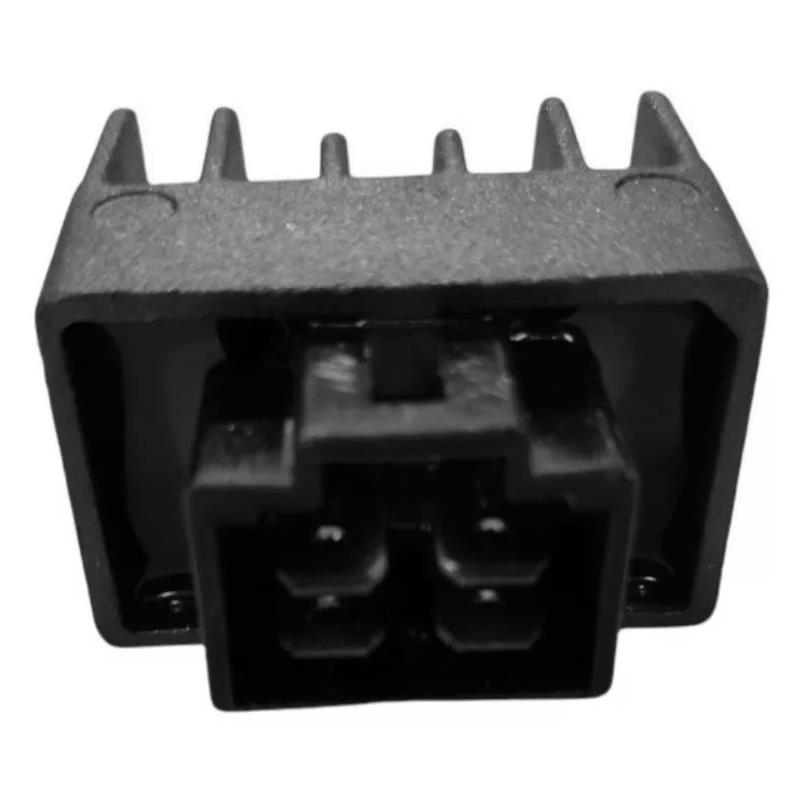
Regulator Rectifier Assy. 5 Pin BAJAJ Boxer BM100 CT100 Platino 100 Platina 100
Under Cowl Lower CTR Cowling 94498-34J00-000 for SUZUKI GSX150F Gixxer SF 2016-2019
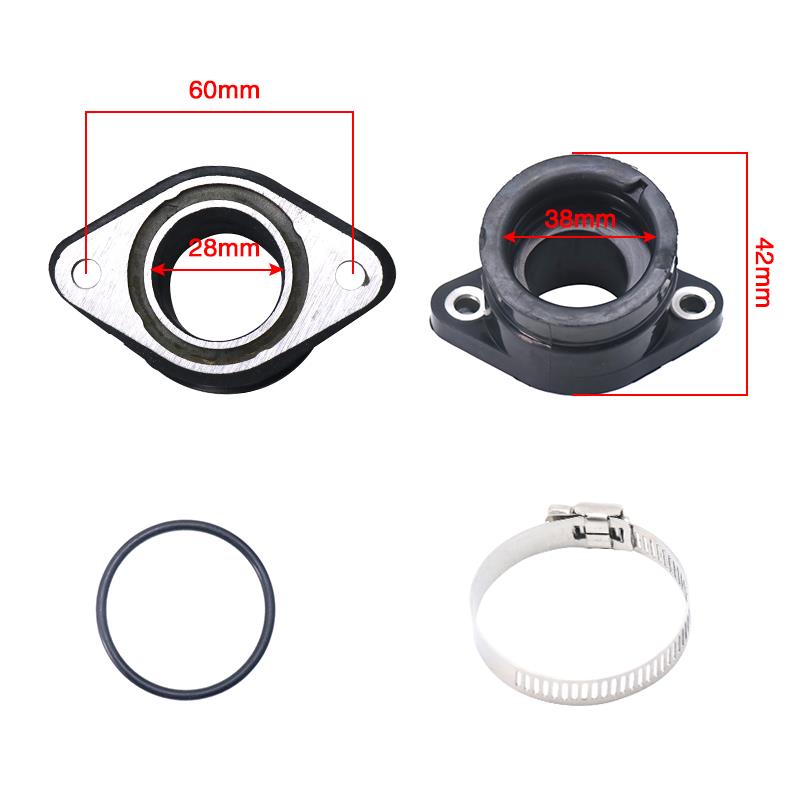
Inlet Pipe Comp. Intake manifold VM16 carburettor for MX50 DT50 RD50 353-13565-00
Thermostat Switch Assy Honda 37760-MB4-770 Thermo Switch for VF500 700 1100 Magna Sabre Interceptor
Carburetor Assy Motorbike Motorcycle Racing Carburetor Power Jet PWK 21/24/26/28/30/32/34 Modified Carburetor
Cam Chain Tensioner Lifter Comp. Bajaja DD101407 DD101487 BAJAJ Boxer BM100 CT100
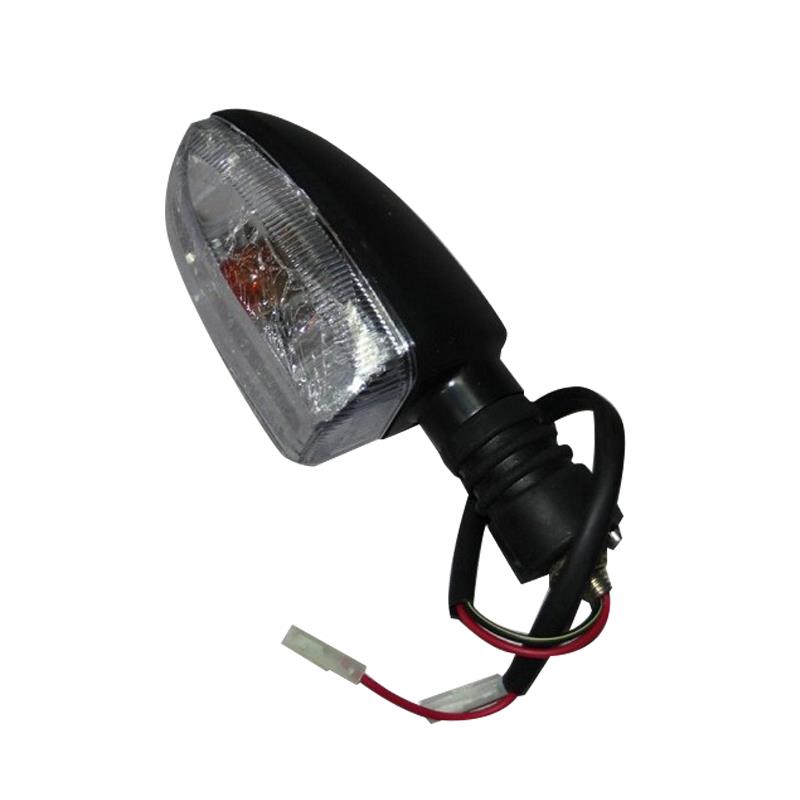
Winker Assy Plastic Bajaj UG3 Motorcycle Indicator Light For Pulsar 180 UG3 Discover 135 Rouser 180 200
Carburetor Jet Needle PJ34-38 PE36 PWK33-39 PWM38 Keihin N427-N3CX Genuine Keihin Clip For Needle 0403-802-1000
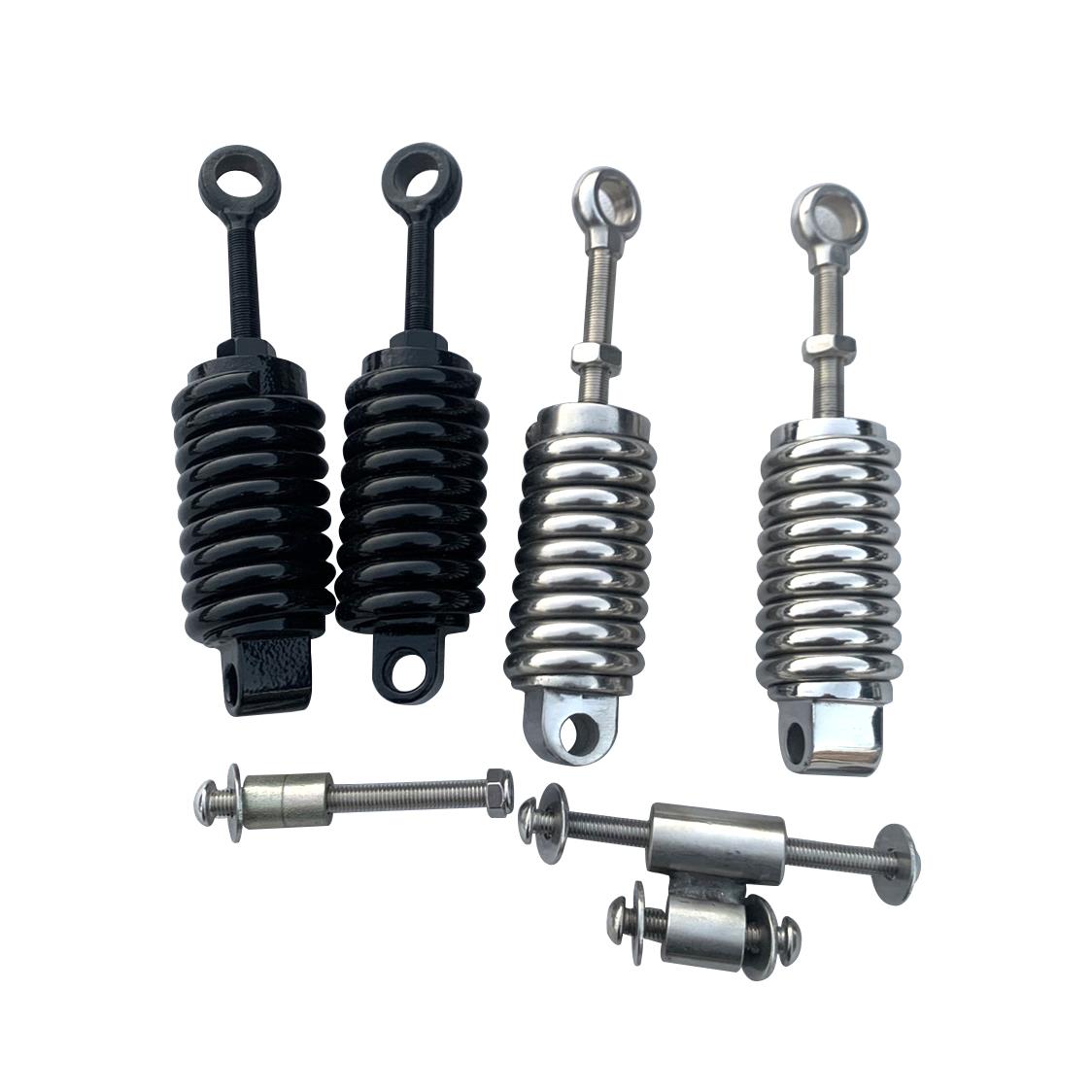
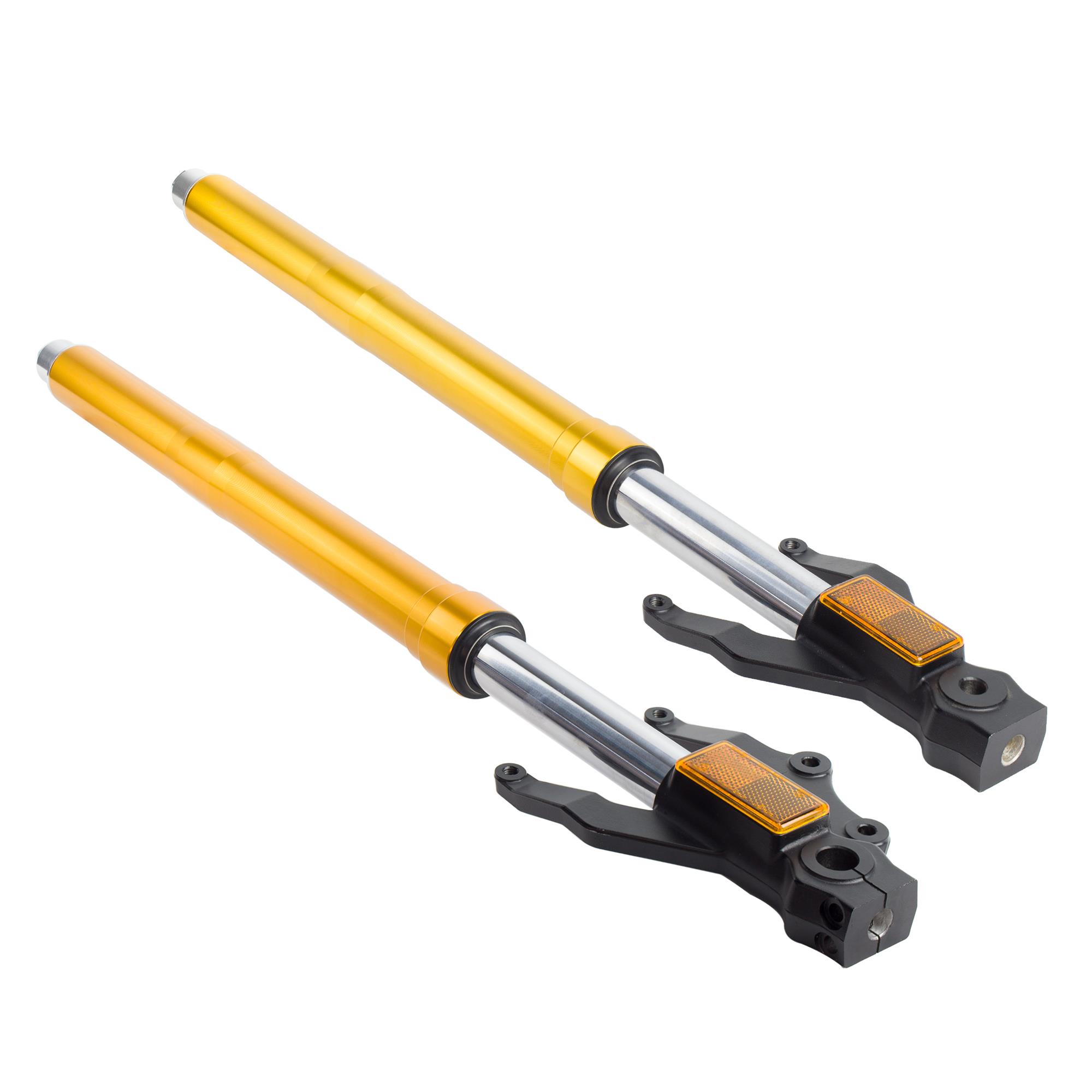
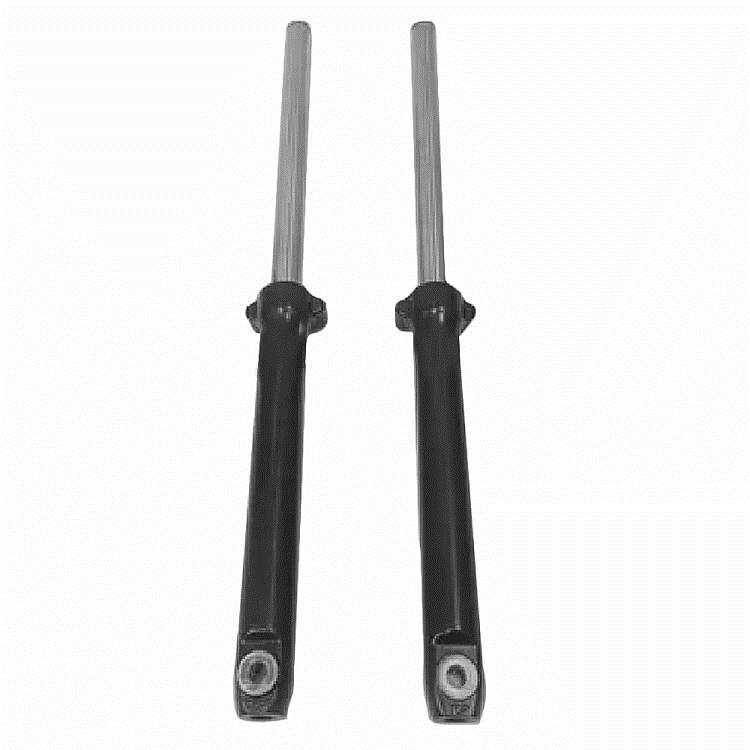
Front Shock Absorber L/R Inverted Front Bars Inverted Suspension Kit fit to VENTO Rocketman 250
Oil Level Gauge YAMAHA CY YA YG YV CS50 Jog R KYMCO GY6-125 150 SUZUKI EN GN GS 125
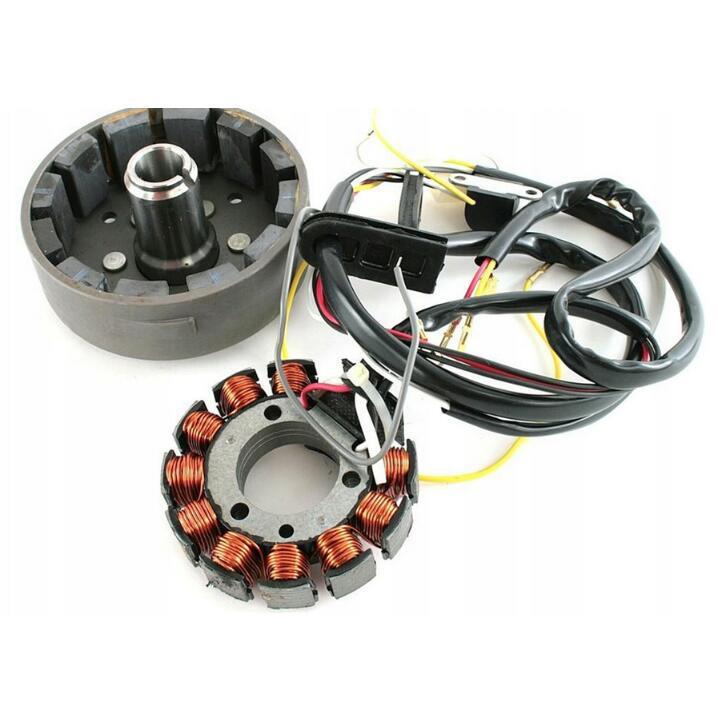
Magneto Generator Assy Magnetic needle 12V-2 cylinder complete Jawa 350 638-640 Rotor A67R-1 for magnet SZ17
Rear Brake Panel Sub Rear Wheel Hub Cover Kit for BAJAJ Boxer BM100 CT100 31151024
C.D.I. Unit Genuine CDI igniter ECU 32920-33G00 for Suzuki Address V125 V125G CF46A
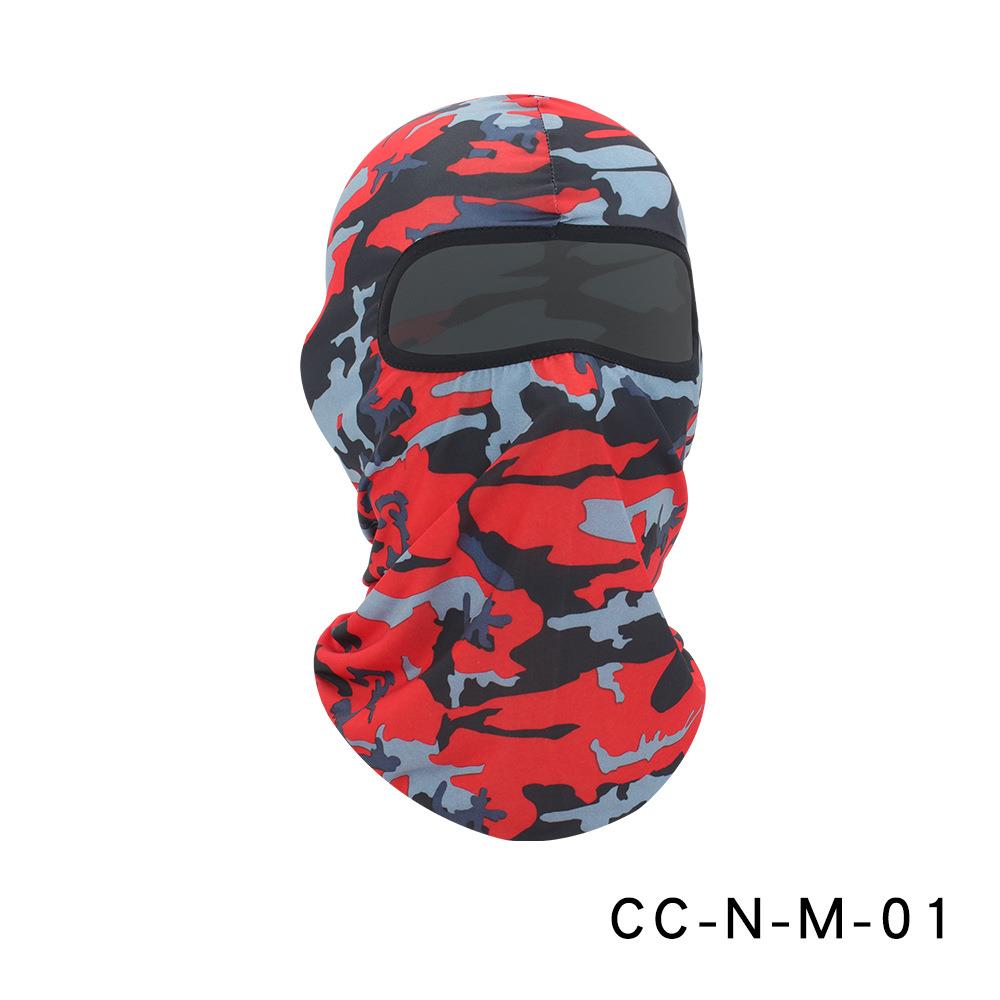
Riding Face Mask Ice silk Fabric Summer printed headgear mask environment: Cycling running mountaineering
Spare Wheel Holder CHANGJIANG 750 Side Car Spare Wheel Mount For CJ750 Dnepr Ural M72 BMW R71 R75 K750
Exhaust Muffler Comp. TVS Phoenix 125 Stryker 125 N5050760 Exhaust Guard N5223130 Logo N5225350
Crankcase Cover Left ABS black chromed protector SUZUKI V125 G Address Left
Carburetor Repair Kit Carburetor Repair Kit Air Screw For BT1100 Bulldog XVS1100 Dragstar V-star 1100
Rear Fender Genuine Frame Body Plastic Parts Inner Rear Fender India HONDA NAVi 110 CLIQ 110 80107-K74-N00
Engine Oil Seal Kit Gear Shift Shaft Clutch Lever Kick Start BAJAJ BM100 Boxer CT100
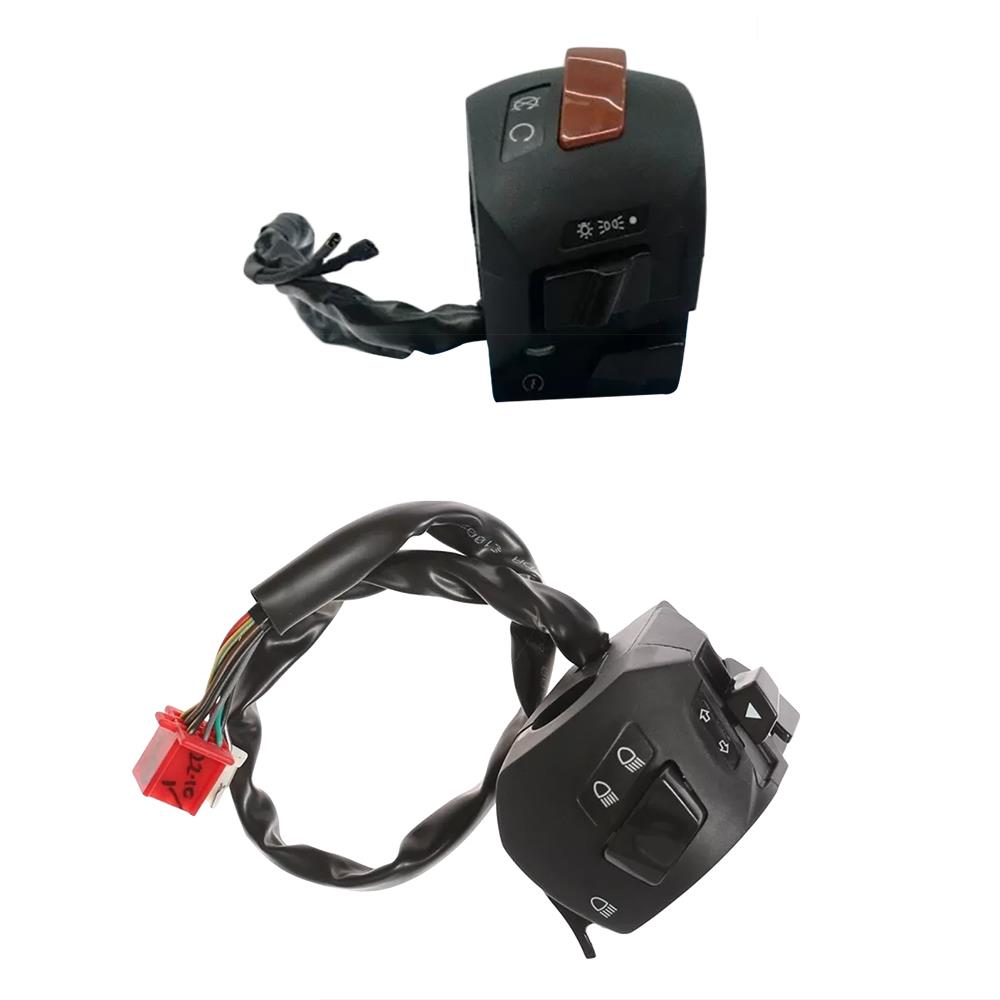
Handle Switch JF401401(R) JF401400(L) BAJAJ Pulsar 135 LS
Headlight Inner Visor Motorcycle Headlight Cover Inner Visor BAJAJ Pulsar 200 NS JL181203 Pulsar150 160
Fuel Tank Cap KEEWAY TX 200 QJ200GY-A 88400J410000 KEEWAY TX 125 QJ125GY-17 QJ150GY-8A
Flasher Relay 6V 3-pole HL-1202L Universal Flasher Relay For Simson Schwalbe Sperber Habicht Duo MZ
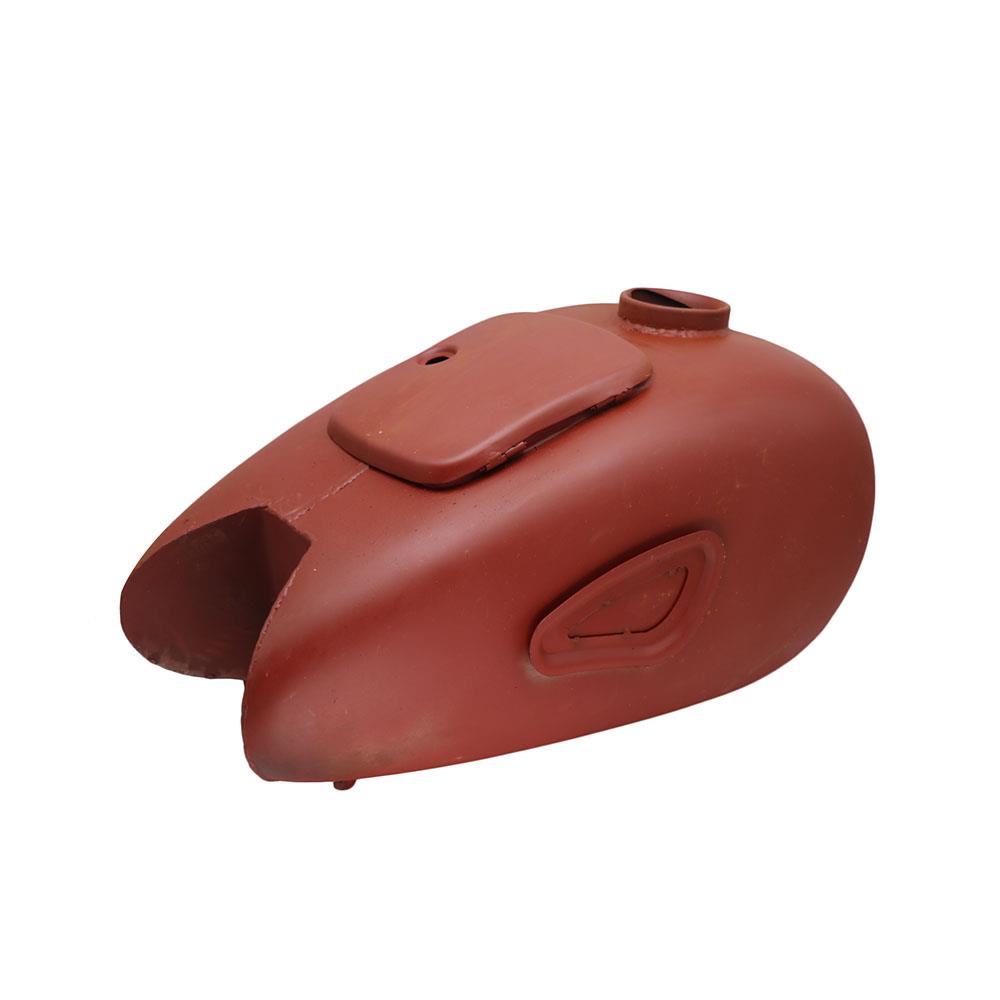
Fuel Tank Comp. Simson Fuel Tank SCHWALBE KR51/1 KR51/2 SIMSON KR51/1 KR51/2 347310 Moped Scooter
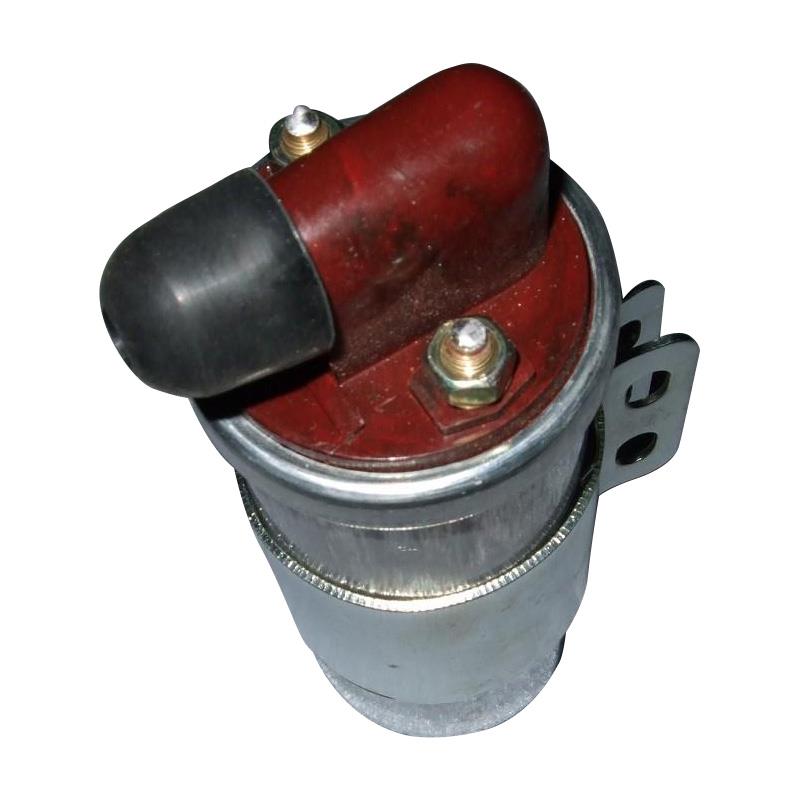
Ignition Coil Assy. HONDA 30510-K13 KRE K62 KWT MCG Pop110i NXR125 Bros 150 Bros NXR160 XRE300 NX400i Falcon
Rear Fender Genuine Frame Body Plastic Parts Inner Rear Fender India HONDA NAVi 110 CLIQ 110 80107-K74-N00
Rear Fender Genuine Frame Body Plastic Parts Inner Rear Fender India HONDA NAVi 110 CLIQ 110 80107-K74-N00
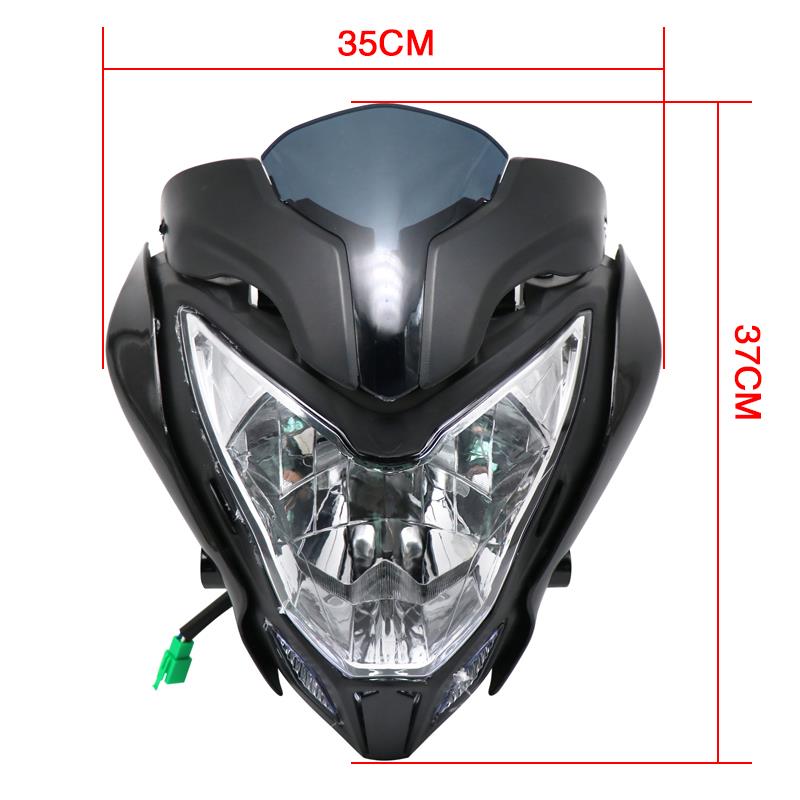
Headlight Comp. 61300-KPE-730ZA 61302-KPE-900ZD HONDA XR 250 Tornado 33100-KBB-901
Carburetor Jet Needle CR26-33 5 CLIP POSITION Keihin N427-11YXX Genuine Keihin Clip For Needle 0403-802-1000
Carburetor Jet Needle CR26-33 5 CLIP POSITION Keihin N427-11YXX Genuine Keihin Clip For Needle 0403-802-1000
Choke Cable Comp. 17950-MCG-000 HONDA NX 400 Falcon 1999-2009
Meter Assy Motorcycle universal modified Mini high-definition adjustable LCD speedometer with oil gauge
Carburetor Jet Needle CR26-33 5 CLIP POSITION Keihin N427-11YXX Genuine Keihin Clip For Needle 0403-802-1000
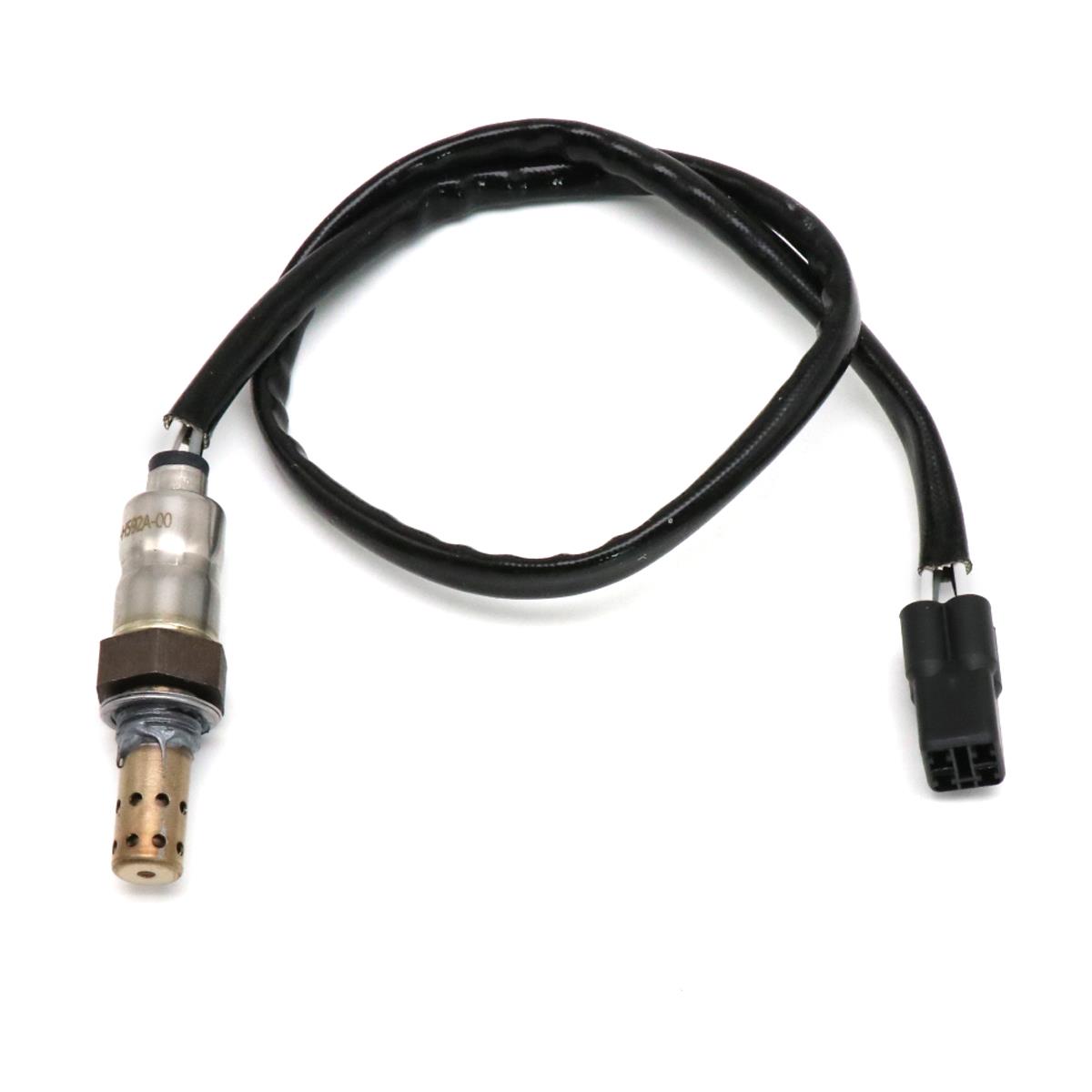
Oxygen Sensor Motorcycle Exhaust Oxygen Sensor 39450LEA6800 for KYMCO Dink 125 300
Rear Fender Genuine Frame Body Plastic Parts Inner Rear Fender India HONDA NAVi 110 CLIQ 110 80107-K74-N00
Rear Fender Genuine Frame Body Plastic Parts Inner Rear Fender India HONDA NAVi 110 CLIQ 110 80107-K74-N00
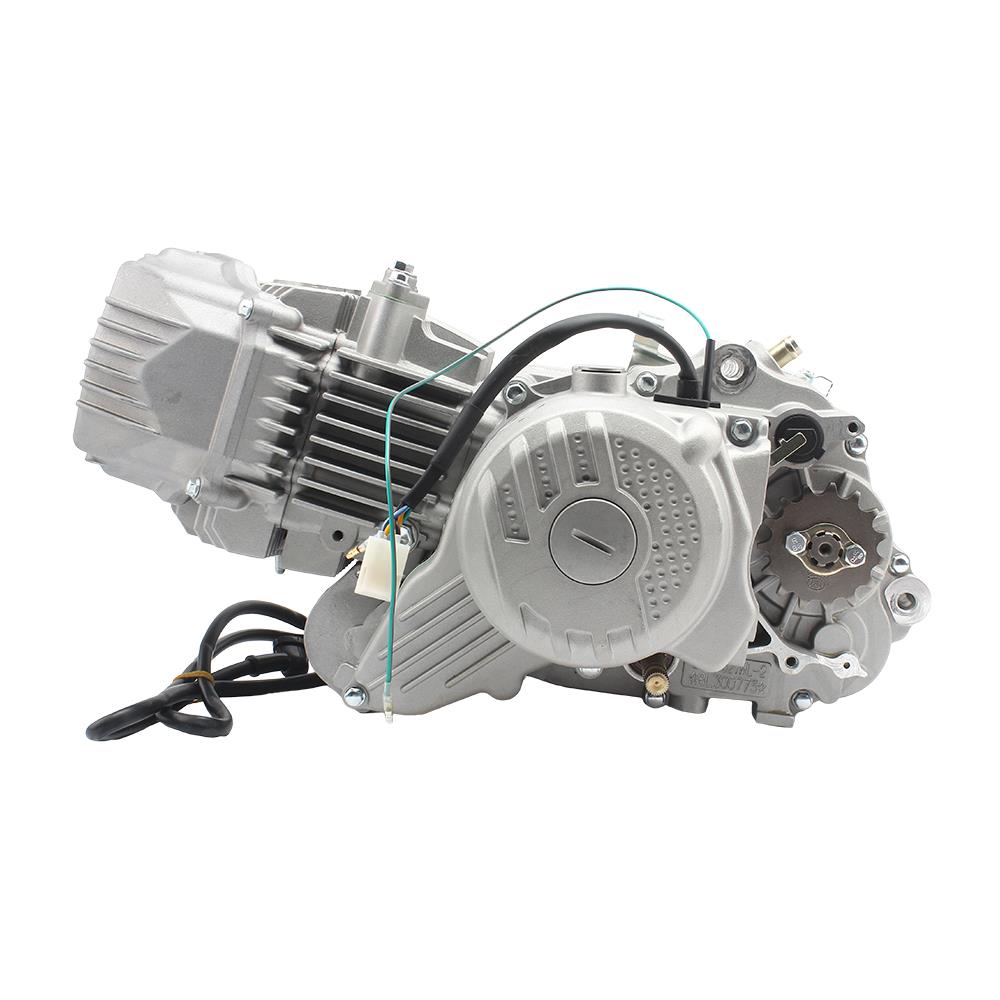
Engine Assy 750 cc Horizontally Opposed Boxer Engine CJ750 12V Type 331 or 52 Reverse Lever
Rear Fender Genuine Frame Body Plastic Parts Inner Rear Fender India HONDA NAVi 110 CLIQ 110 80107-K74-N00
Carburetor Assy Dellorto Carburetor Handle Lift Choke For universal motorcycle scooter
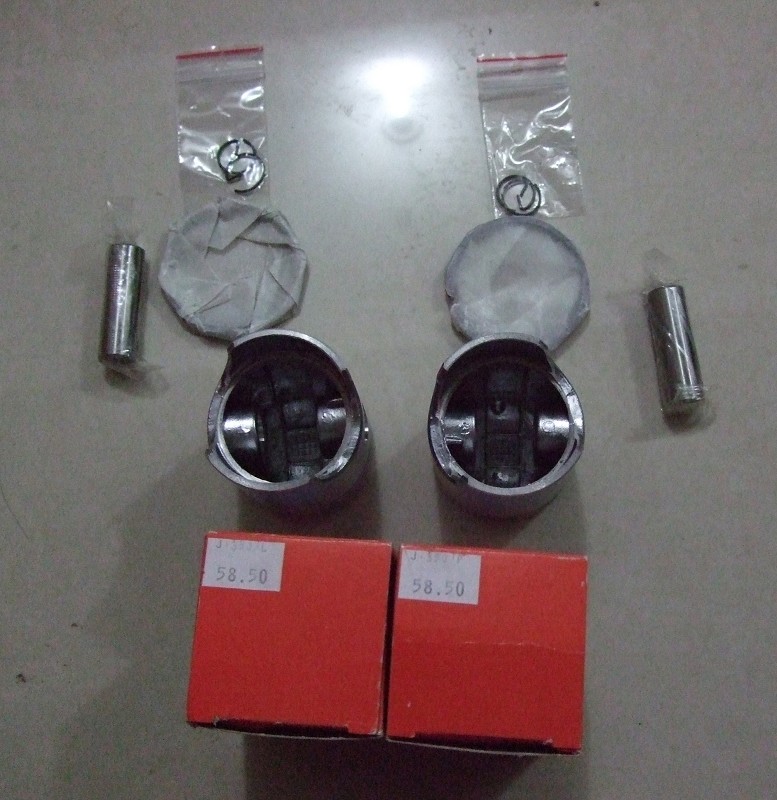
Piston Kit Piston set R+L with rings 58,00 tenon 16mm Pin CZ JAWA 350 638 639 640 Tramp Chopper
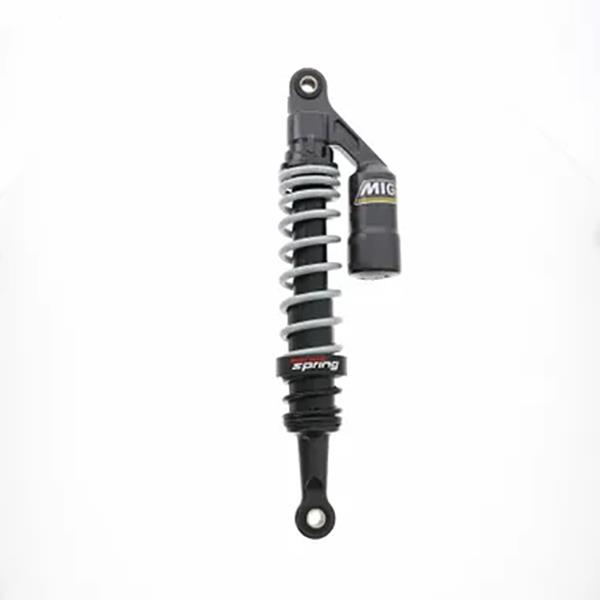
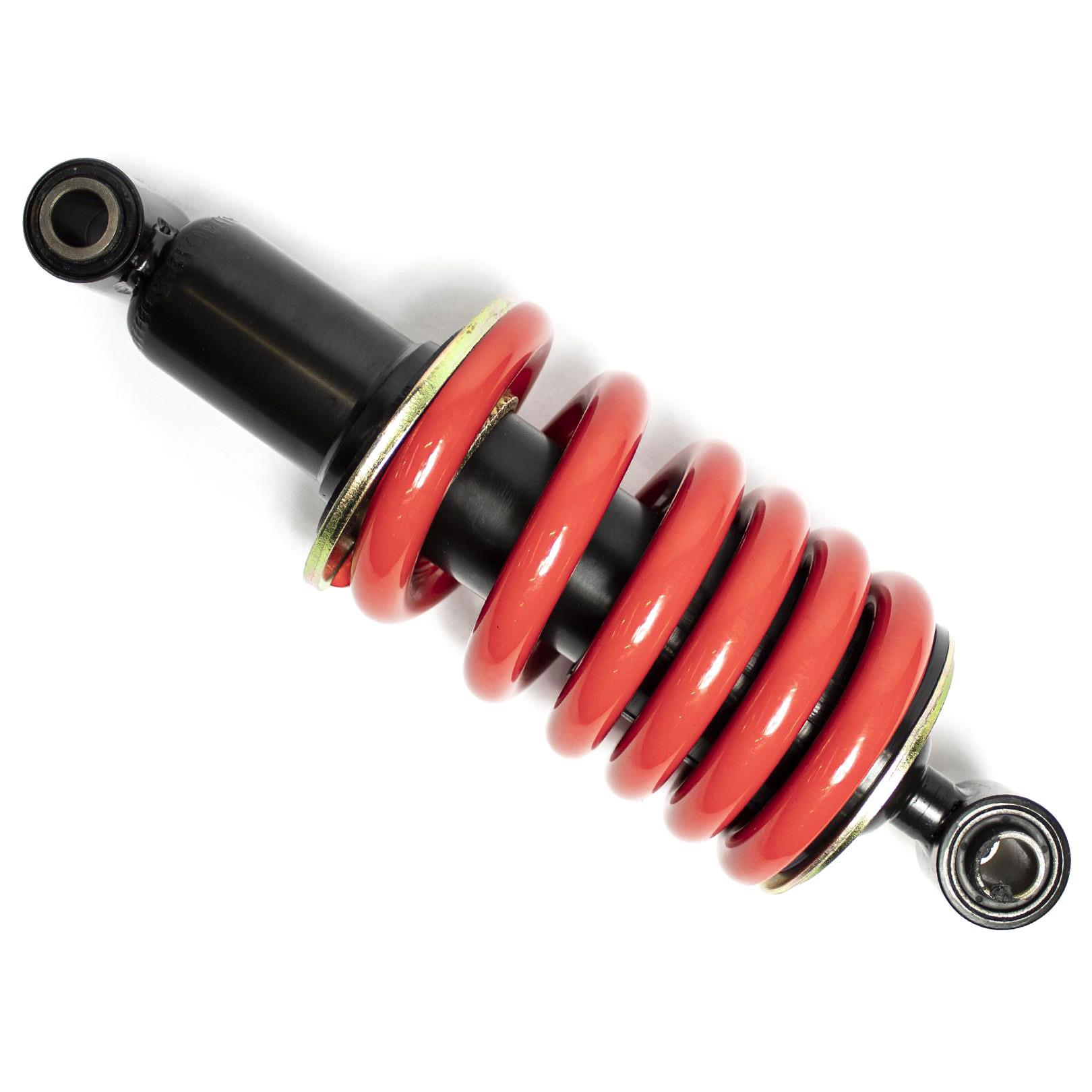
Rear Shock Absorber 280mm F02020070 Rear Suspension Damper fit to Italika RT200 RT200 GP
Headlight Inner VisorMotorcycle Headlight Cover Inner VisorBAJAJ Pulsar 200 NS JL181203 Pulsar150 160
Headlight Inner Visor Motorcycle Headlight Cover Inner Visor BAJAJ Pulsar 200 NS JL181203 Pulsar150 160
Clutch Switch Assy. Bajaj Genuine Parts JZ401403 Clutch Sensor for Discover 100 125 150 Platina 100 Platino 110
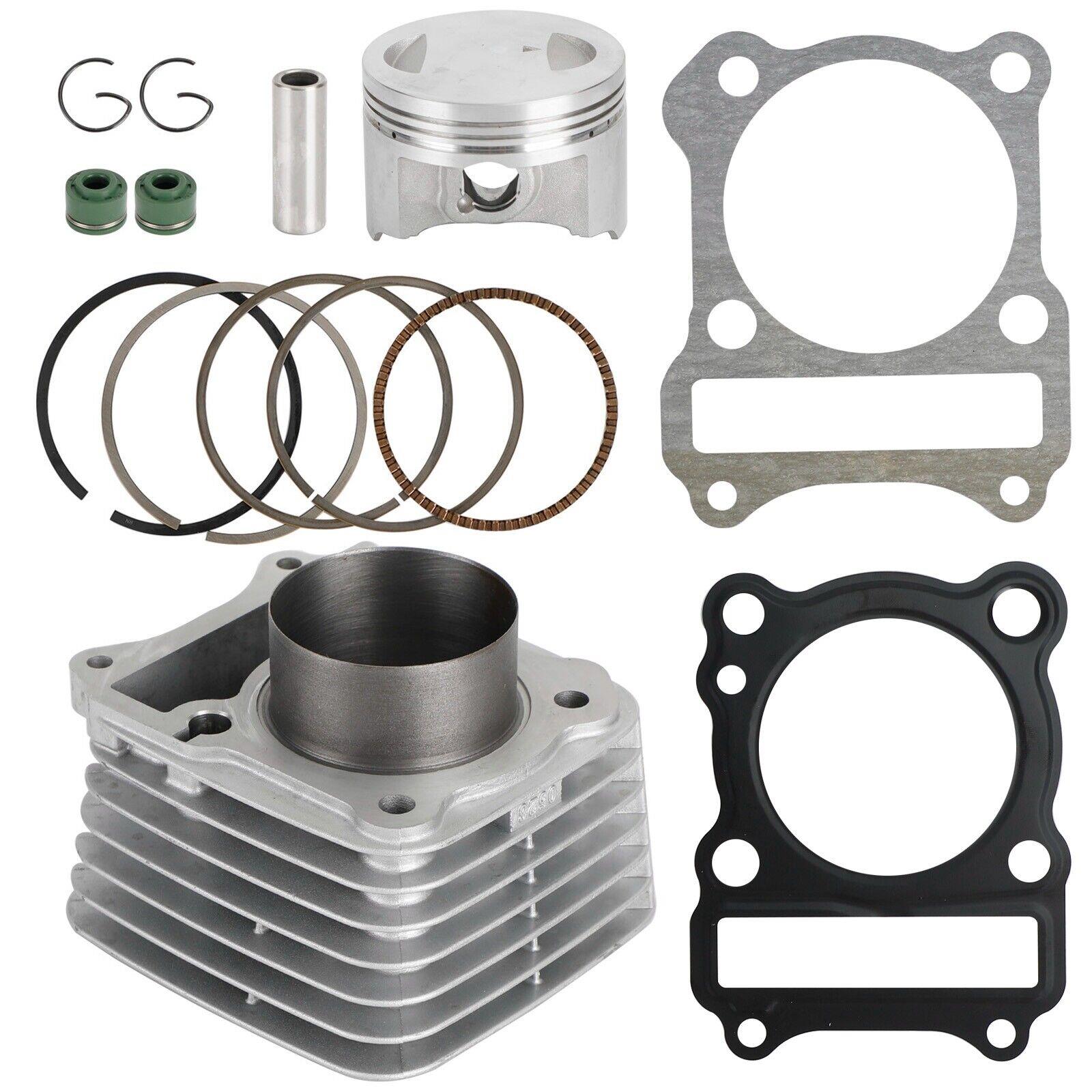
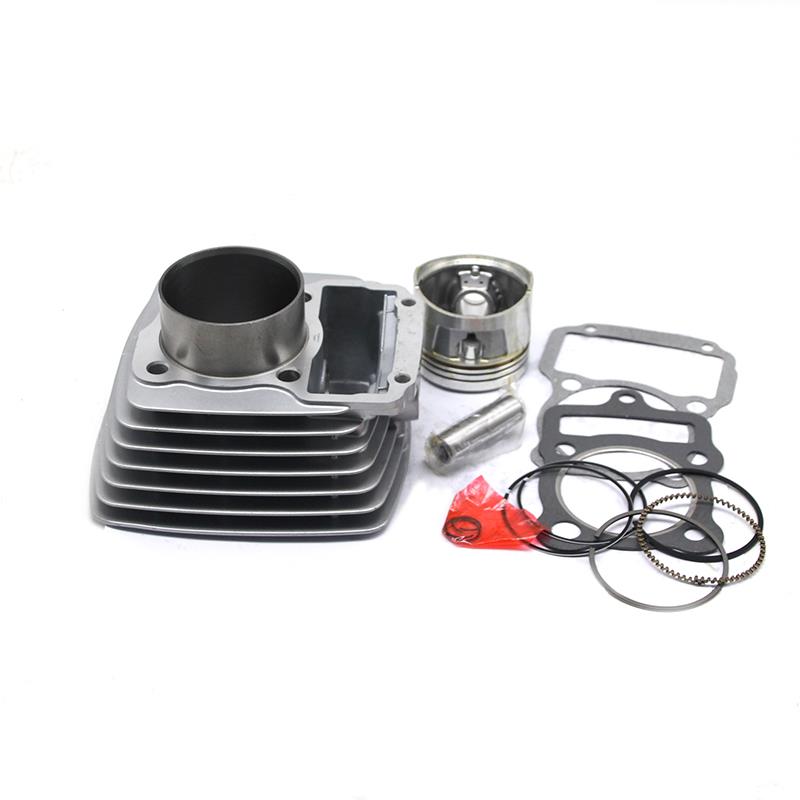
Cylinder Block 125CC Engine Aluminum Cylinder Kit Gasket For SUZUKI EN125HU GN125 DR-Z125 Marauder GZ125
Crankcase Cover Left ABS black chromed protector SUZUKI V125 G Address Left
Crankcase Cover Left ABS black chromed protector SUZUKI V125 G Address Left
Crankcase Cover Left Rear ABS chromed performance protector SUZUKI V125 G Address Left
Engine Assy 49CC 2-Stroke Engine Motor Pull Start for Mini Go Kart Dirt Bike Petrol ATV Pocket Bike
Engine Assy 750 cc Horizontally Opposed Boxer Engine CJ750 12V Type 331 or 52 Reverse Lever
Crankcase Cover Left ABS black chromed protector SUZUKI V125 G Address Left
Handle Switch JF401401(R) JF401400(L) BAJAJ Pulsar 135 LS
Carburetor Jet Needle CR26-33 5 CLIP POSITION Keihin N427-11YXX Genuine Keihin Clip For Needle 0403-802-1000
Headlight Comp. Original Halogen Bulb China Supplier BAJAJ PULSAR NS 150 160 200 JL401012
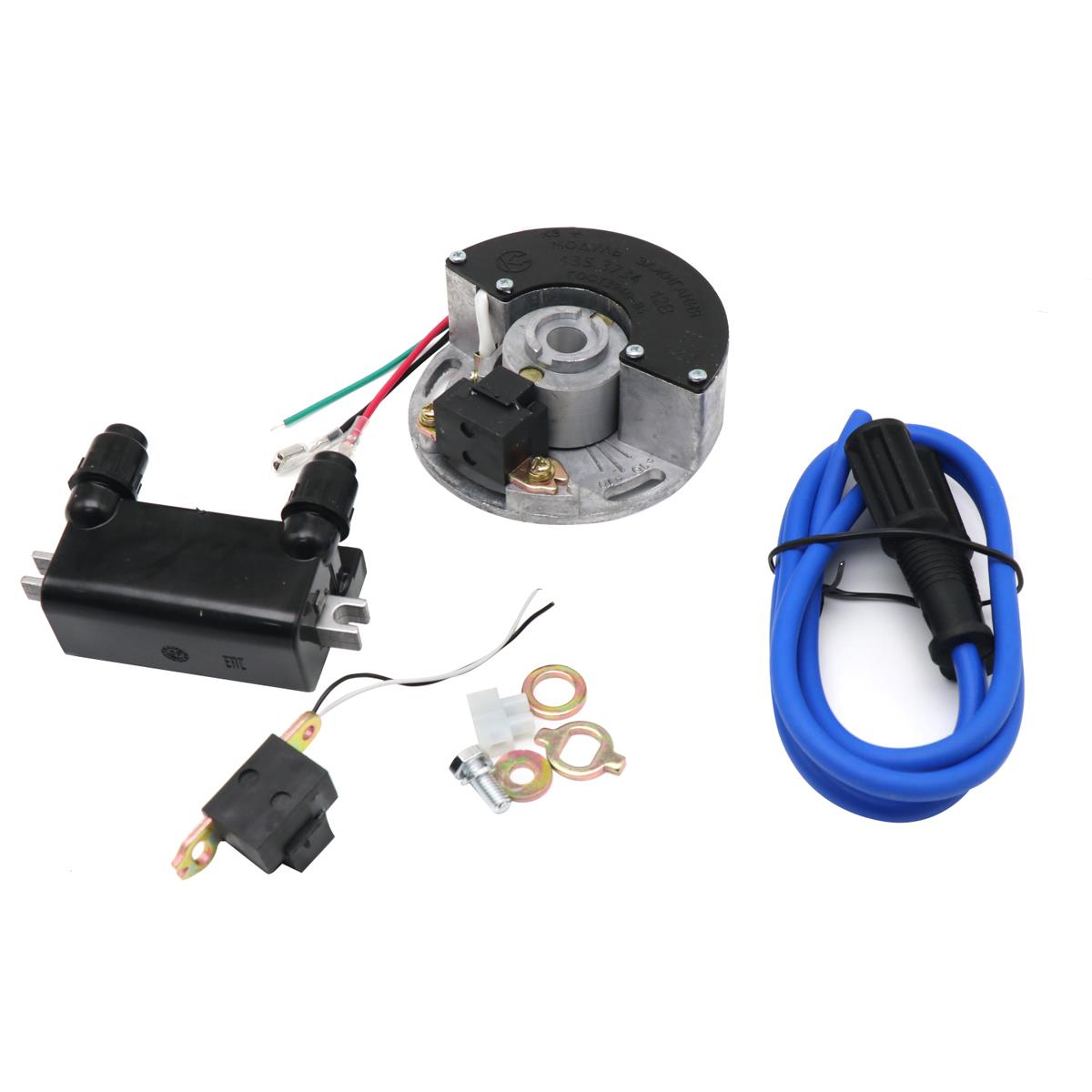
Ignition System Comp. Electronic Contactless System Of Ignition 12V For CJ750 K-750
Rear Fender Genuine Frame Body Plastic Parts Inner Rear Fender India HONDA NAVi 110 CLIQ 110 80107-K74-N00
Rear Fender Genuine Frame Body Plastic Parts Inner Rear Fender India HONDA NAVi 110 CLIQ 110 80107-K74-N00
Oil Level Gauge YAMAHA CY YA YG YV CS50 Jog R KYMCO GY6-125 150 SUZUKI EN GN GS 125
Headlight Inner Visor Motorcycle Headlight Cover Inner Visor BAJAJ Pulsar 200 NS JL181203 Pulsar150 160
Crankshaft Comp. BAJAJ BOXER BM100 Motorcycle Crank Shaft For BOXER BM100 CT100 PLATINO100
Rear Fender Genuine Frame Body Plastic Parts Inner Rear Fender India HONDA NAVi 110 CLIQ 110 80107-K74-N00
Motorcycle Trunk 47L Two Helmets Adventure Tail Box Quick-Release Bottom Plate Soft Backrest
Ignition Coil Assy. Without spark plug cap Italika CS125 DS125 HONDA KYO KCH KGA CG125 Titan Cargo Today
Headlight Comp. India Motorcycle New Streetlight BAJAJ Pulsar 200 NS JL401012 LED New with DRL
Cylinder Block 53mm STD CMX 250 Rebel 250 12100-KBG-671 HONDA CB 250 NIGHTHAWK CB250 Two Fifty
Fuel Tank Cap KEEWAY TX 200 QJ200GY-A 88400J410000 KEEWAY TX 125 QJ125GY-17 QJ150GY-8A
Thermostat Switch Assy Honda 37760-MB4-770 Thermo Switch for VF500 700 1100 Magna Sabre Interceptor
Cylinder Block 57mm Cylinder Kit Gasket Piston Set 11210-05203 for DR-Z125 EN125HU HUZ GN125E GZ125 Marauder
Meter Assy Motorcycle universal modified Mini high-definition adjustable LCD speedometer with oil gauge
Front Fender ABS Mudguard Fender with Stay HONDA KGA CG125 Cargo Fan125 Titan 2000
Front Bracke Cable Comp. Cable Assy Brake Fr. TVS N3170010 Phoenix 125
Fuel Tank Cap KEEWAY TX 200 QJ200GY-A 88400J410000 KEEWAY TX 125 QJ125GY-17 QJ150GY-8A
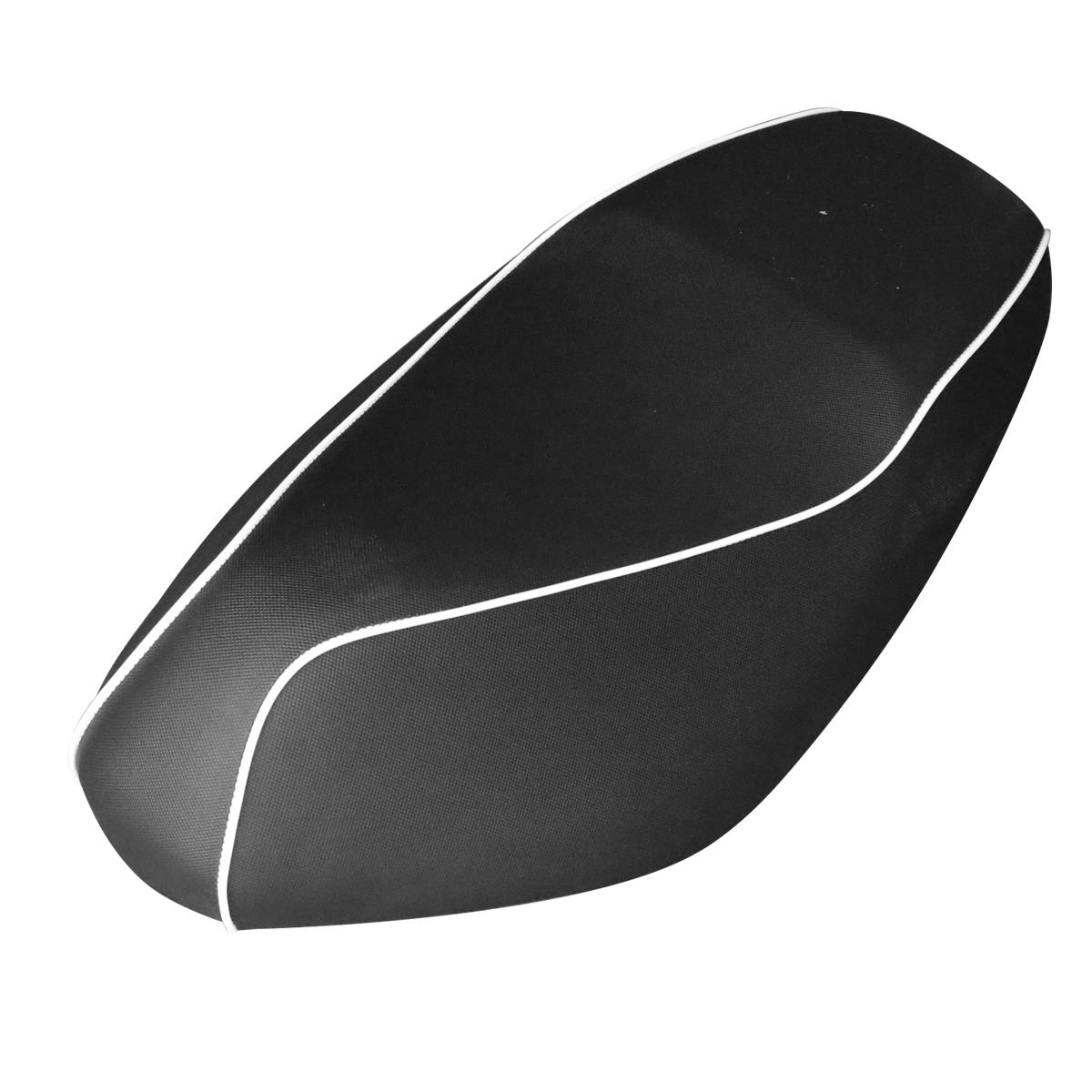
Seat Cover Assy. Motorcycle sunscreen seat cover Prevent bask waterproof Heat insulation Cushion protect
Oil Level Gauge YAMAHA CY YA YG YV CS50 Jog R KYMCO GY6-125 150 SUZUKI EN GN GS 125
Crankcase Cover Left ABS black chromed protector SUZUKI V125 G Address Left
Rear-view Mirror Comp. M8x25 KEEWAY TX 125 QJ125GY-17 QJ150GY-8A TX 200 QJ200GY-A RIVERO GP1
Fuel Tank Cap KEEWAY TX 200 QJ200GY-A 88400J410000 KEEWAY TX 125 QJ125GY-17 QJ150GY-8A
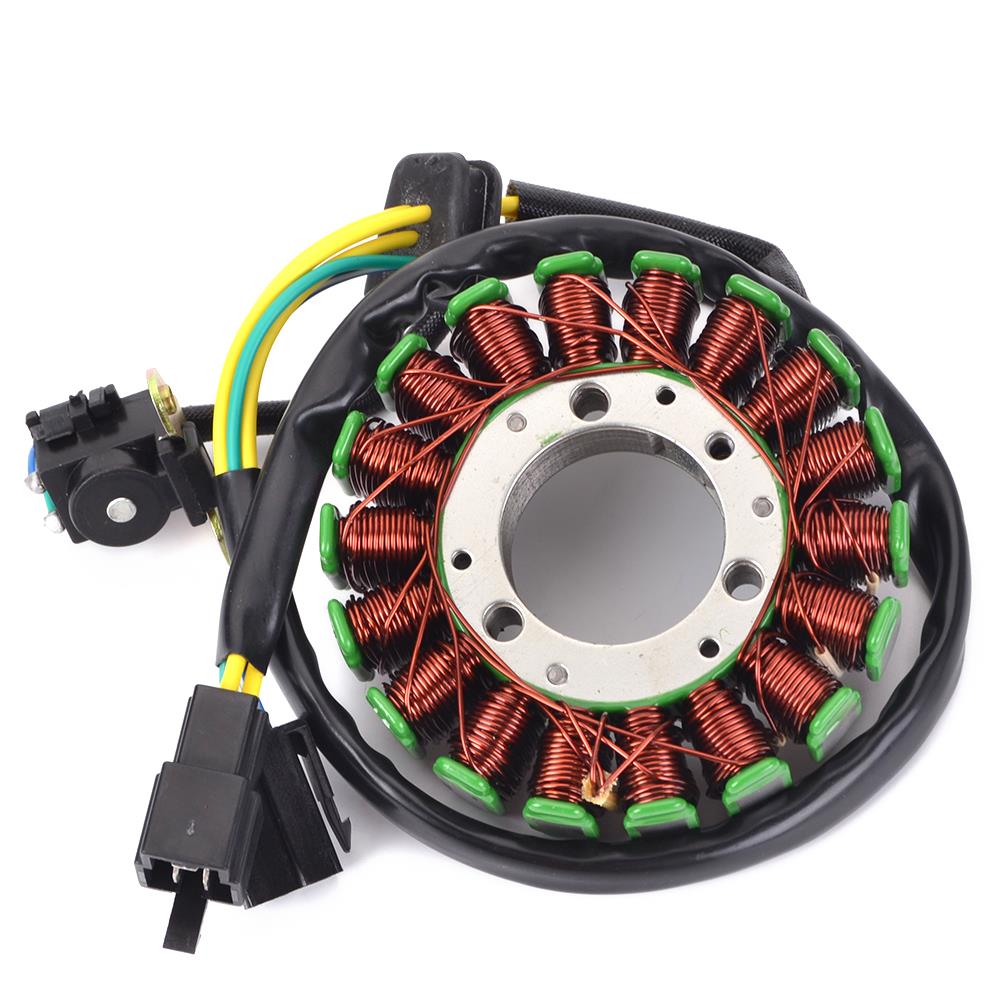
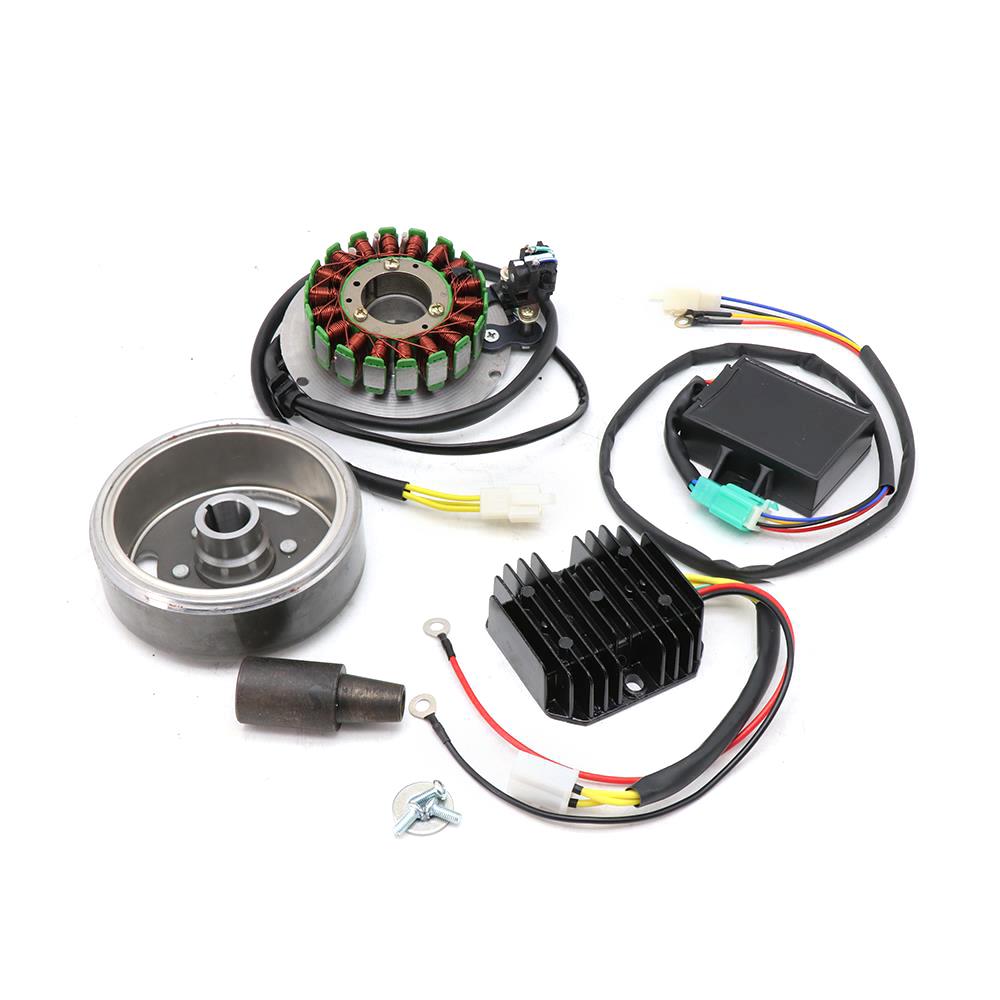
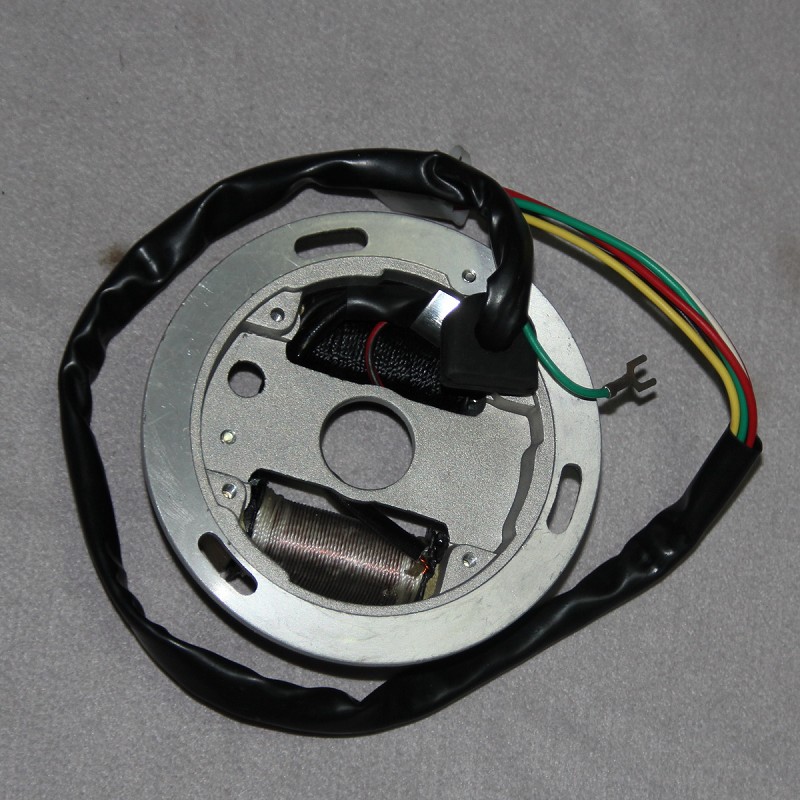
Magneto Stator with plate holder light stator coil SUZUKI AX100 AX115 32101-23410
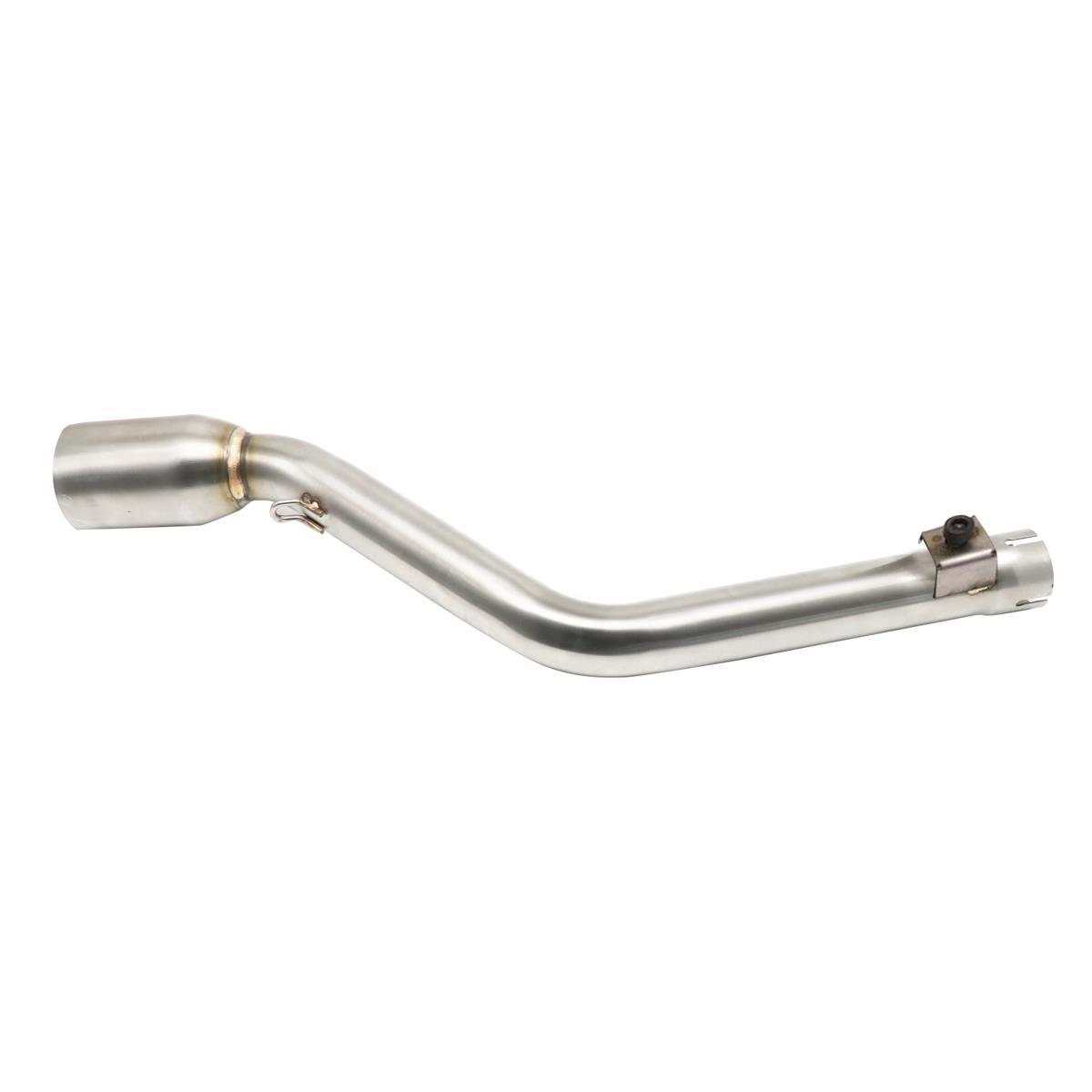
Muffler 51mm Exhaust Pipe Stainless Steel Universal Scooter Sport Bike Street Bike
Exhaust Pipe 50.8mm Stainless Steel Exhaust Middle Pipe for Empire Keeway TX150 QJ150GY
Slow/Pilot Jet Mikuni TM VM TMS TMX carburetors Parts # VM22/210 OEM Kawasaki Suzuki Yamaha 2T 4T models
Slow/Pilot Jet Mikuni N151.067 Pilot Jets size 30-60 for KZ1000 GSF600 Bandit DR650 YFM350 Warrior
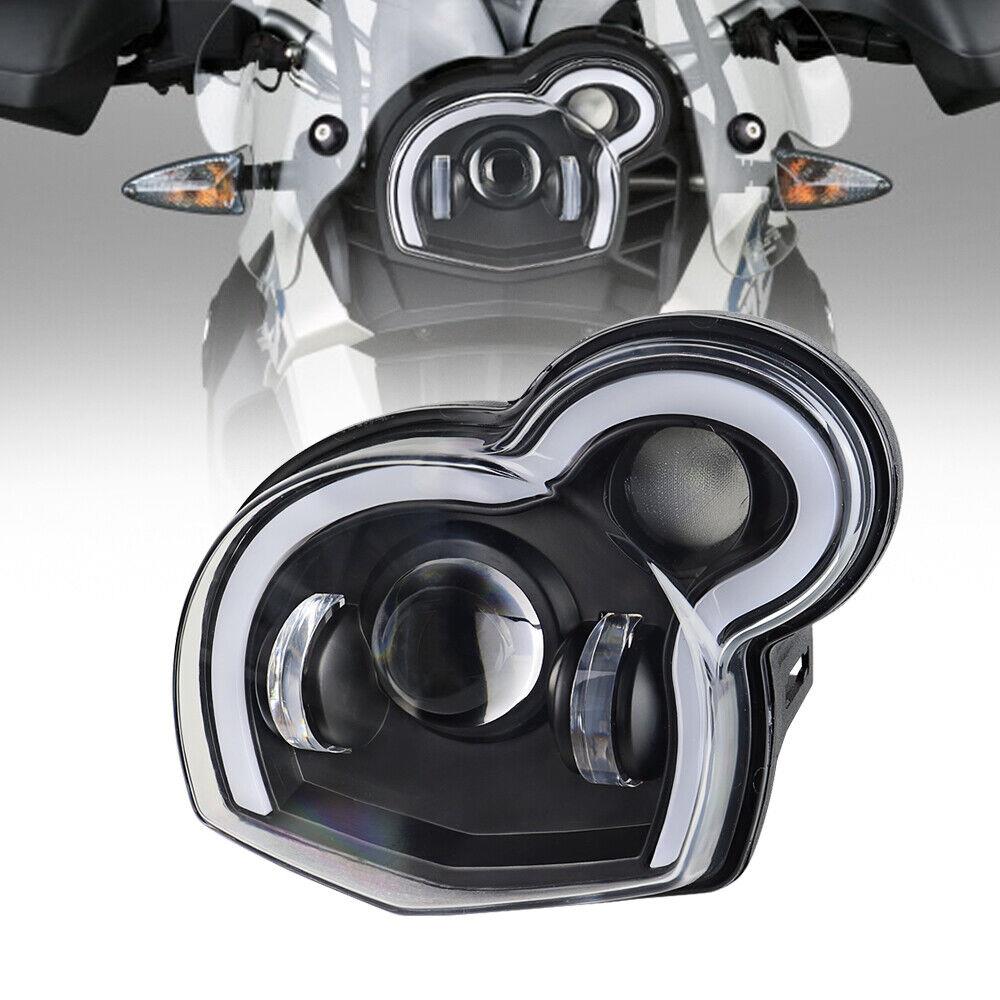
Headlight HP2 Megamoto 63127696880-LED Xmoto BMW-Motorrad G 650 GS Sertão G 650 Xchallenge
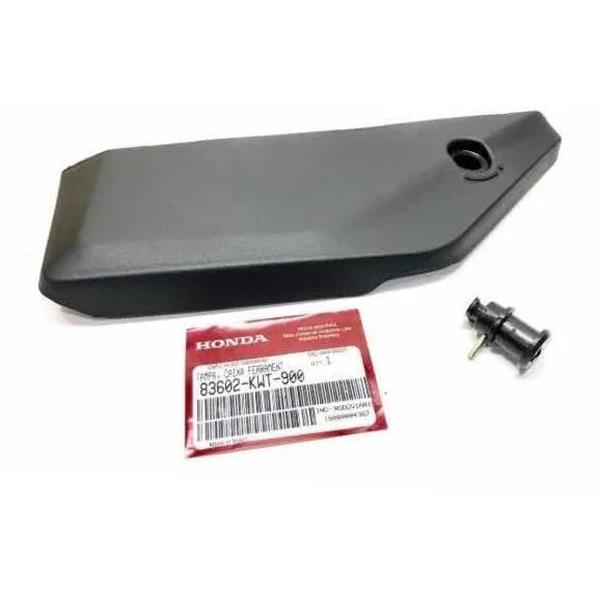
Side Cover Tool Box Lid with Switch Lock 83507-442-000 honda xre300 83602-KWT-900
Headlight Inner Visor Motorcycle Headlight Cover Inner Visor BAJAJ Pulsar 200 NS JL181203 Pulsar150 160
Carburetor Jet Needle CR26-33 5 CLIP POSITION Keihin N427-11YXX Genuine Keihin Clip For Needle 0403-802-1000
Carburetor Jet Needle CR26-33 5 CLIP POSITION Keihin N427-11YXX Genuine Keihin Clip For Needle 0403-802-1000
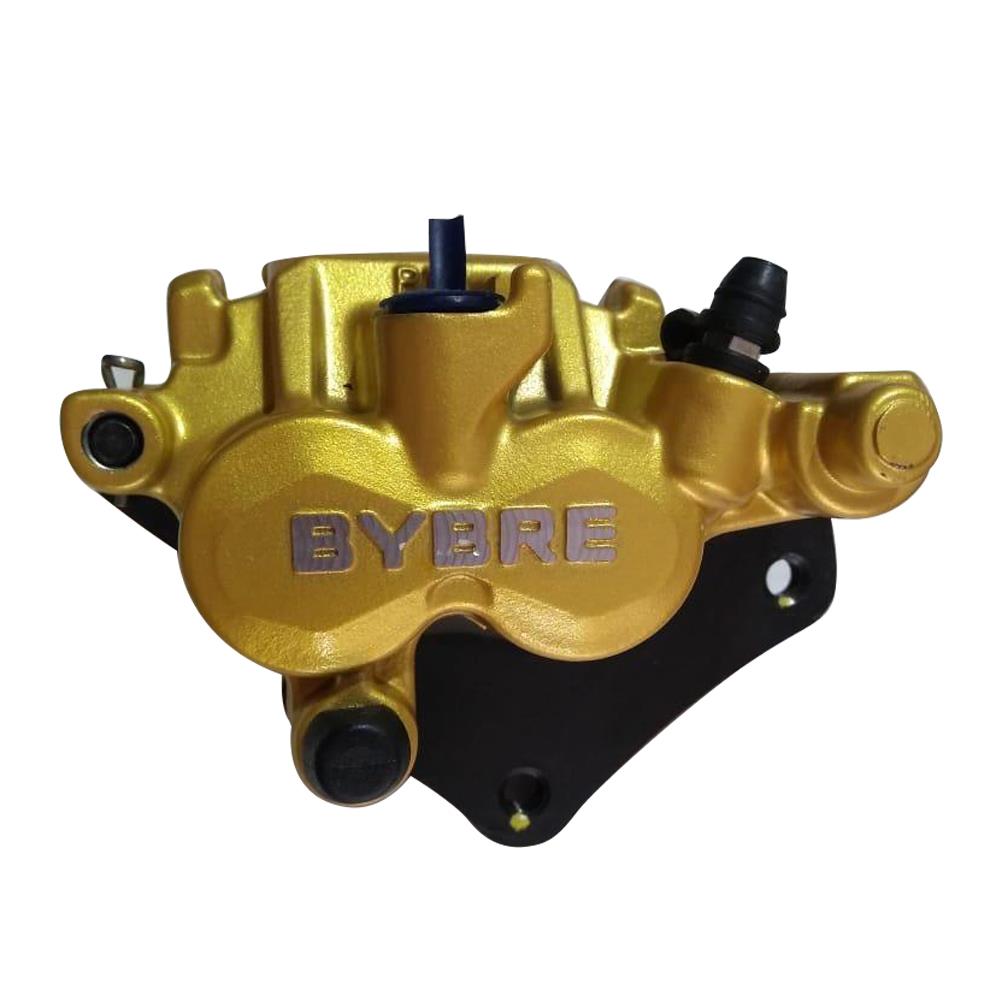
Front Brake Caliper Sub Assy. Front Disc Brake Parts For Suzuki Gixxer 150
Cylinder Block 62mm aluminum cylinder big piston kit ITALIKA FT150 RC150 DT150 Delivery FT150TS
Handle Switch JF401401(R) JF401400(L) BAJAJ Pulsar 135 LS
Handle Switch JF401401(R) JF401400(L) BAJAJ Pulsar 135 LS
Cylinder Block 62mm STD Cilindro Motor Big Piston Kit for CG180 ZONGSHEN ZS180 FT180 TS RT180
Front Fender 53111-34J00 black red ABS high quality SUZUKI GSX150 L5 Gixxer FL6 Gixxer SF
Inlet Pipe Comp. Intake manifold VM16 carburettor for MX50 DT50 RD50 353-13565-00
LED Bulb P15D BA20D H4 P43T COB-3*6W White H/L Beam 9-80V Motorcycle Scooter Headlights Lamp 6500K
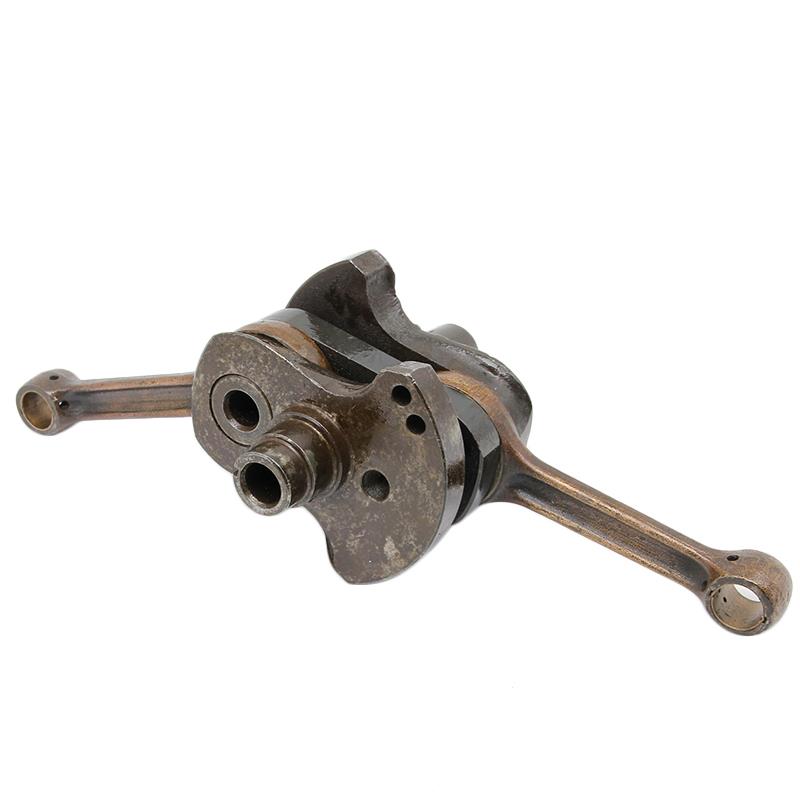
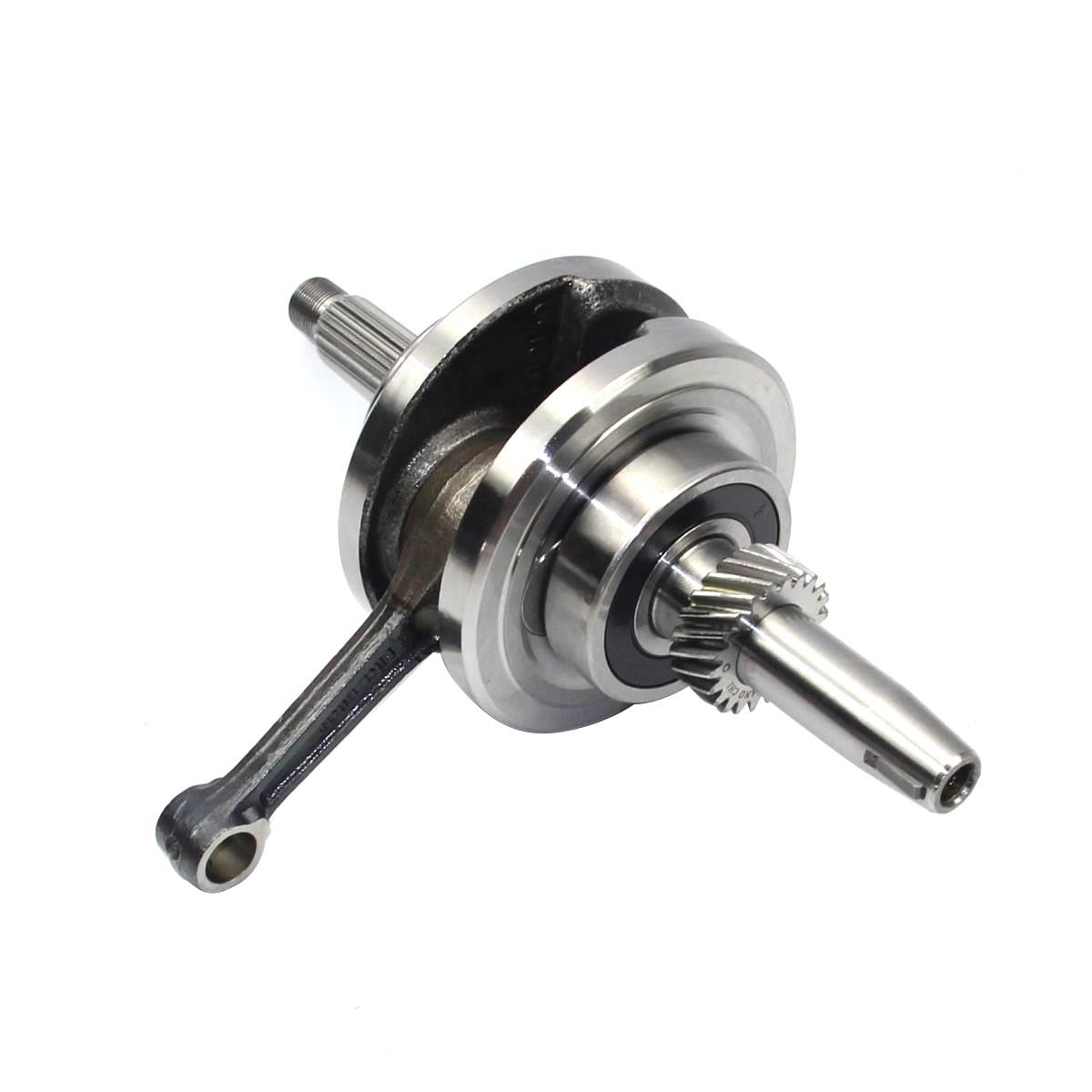
Crankshaft Comp. Balance shaft engine CG 150B HONDA CG150B JAGUAR150 KEEWAY
Inlet Pipe Comp. Intake manifold VM16 carburettor for MX50 DT50 RD50 353-13565-00
Engine Assy 750 cc Horizontally Opposed Boxer Engine CJ750 12V Type 331 or 52 Reverse Lever
Exhaust Muffler Comp. TVS Phoenix 125 Stryker 125 N5050760 Exhaust Guard N5223130 Logo N5225350
Drive Sprocket & Chain Traction kit F0203KS22 for motorcycle Italika 150Z 150SZ RC150 200 Sptfire
Thermostat Switch Assy Honda 37760-MB4-770 Thermo Switch for VF500 700 1100 Magna Sabre Interceptor
Exhaust Muffler Comp. TVS Phoenix 125 Stryker 125 N5050760 Exhaust Guard N5223130 Logo N5225350
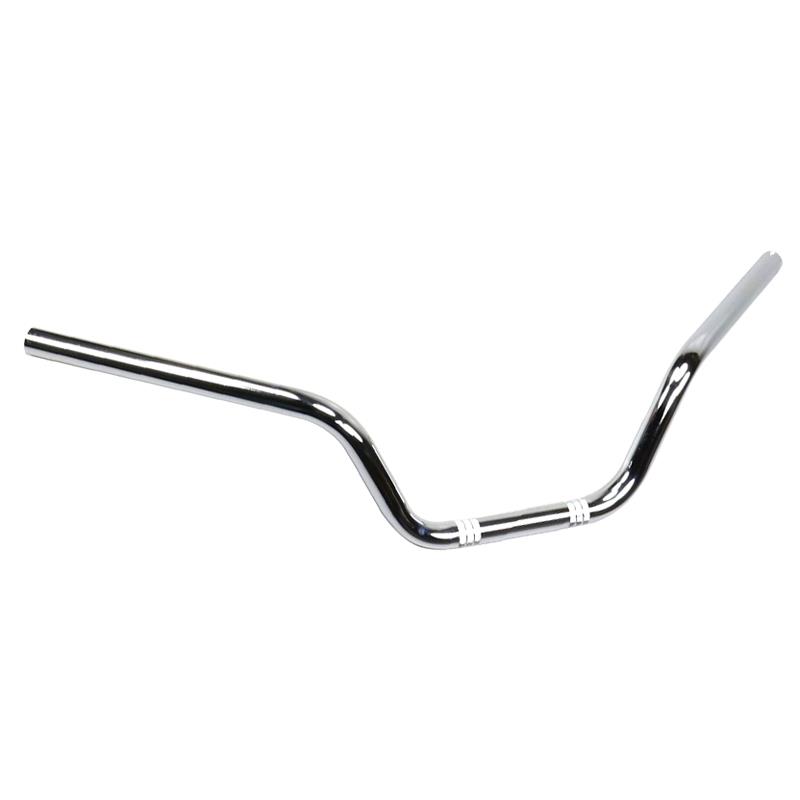
Steering Handle Pipe Chrome Plated Steel Handlebar For Suzuki GN125 56110-05321-000
Carburetor Air Funnel H20 Model 38/42/50/55 Install Size Aluminum CNC Fit to PWK OKO KOSO Racing Carburetor
Carburetor Assy 40B-E4301-00 Double Throttle Cable for YAMAHA T110C Crypton 110 2014-2018
Carburetor Assy Mikuni Round Slide VM Series Carburetor 32mm Bore VM32-33 w Left-Hand Idle Speed Adjuster
Cylinder Stud Bolt QJ164FML Cylinder StudBolt Left KEEWAY Super Light 200 TX200 Flame 200
Regulator Rectifier Assy. 4 Pin Honda Genuine Electirc Parts 31600-KYY-971 for ACE125 CB1 125 CB125
Final Drive Sprocket Rear Sprocket 520H-38T 6 Hole HONDA XR250 Tornado 41201-KPE-900
Oil Level Gauge YAMAHA CY YA YG YV CS50 Jog R KYMCO GY6-125 150 SUZUKI EN GN GS 125
Inlet Pipe Comp. Intake manifold VM16 carburettor for MX50 DT50 RD50 353-13565-00
Under Cowl Lower CTR Cowling 94498-34J00-000 for SUZUKI GSX150F Gixxer SF 2016-2019
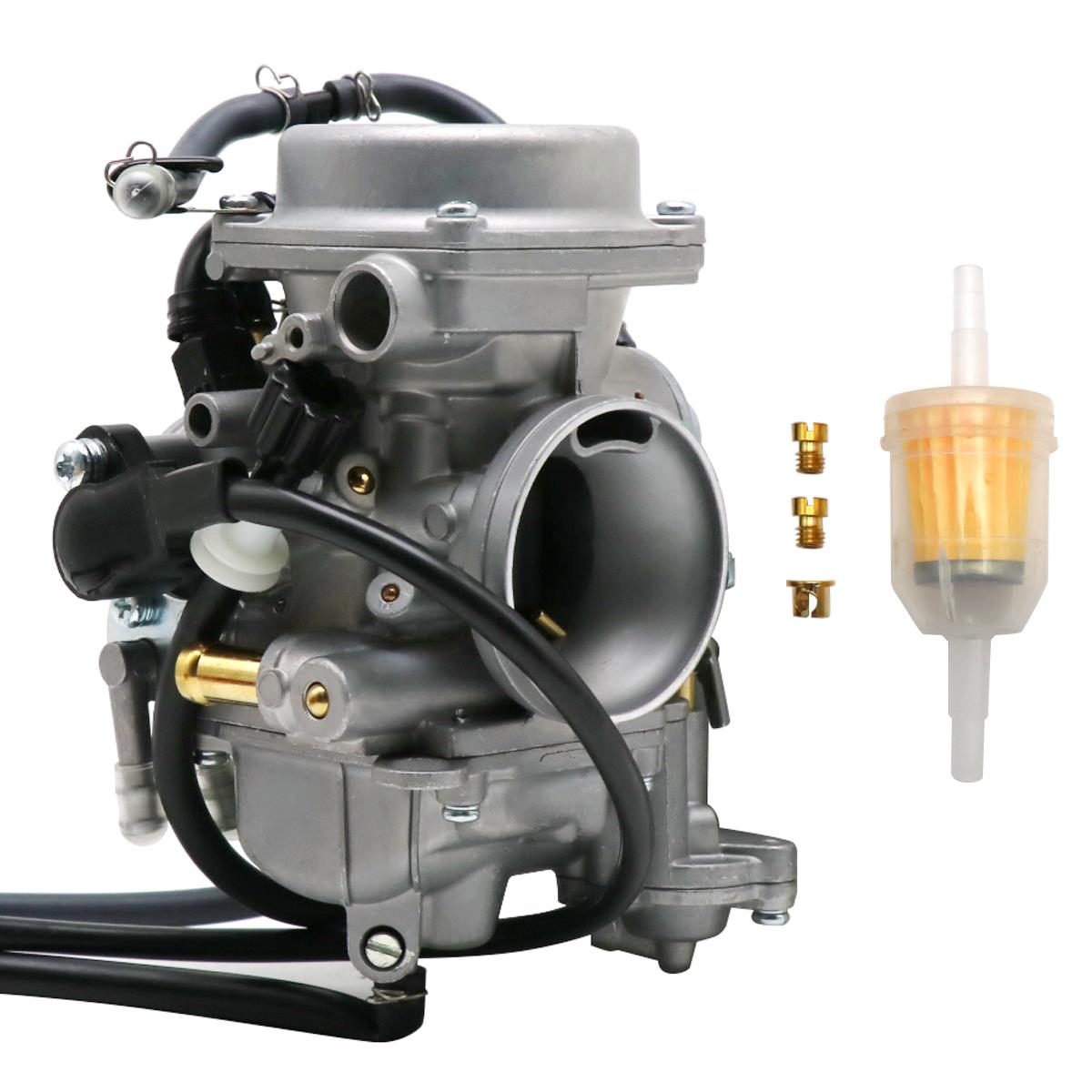
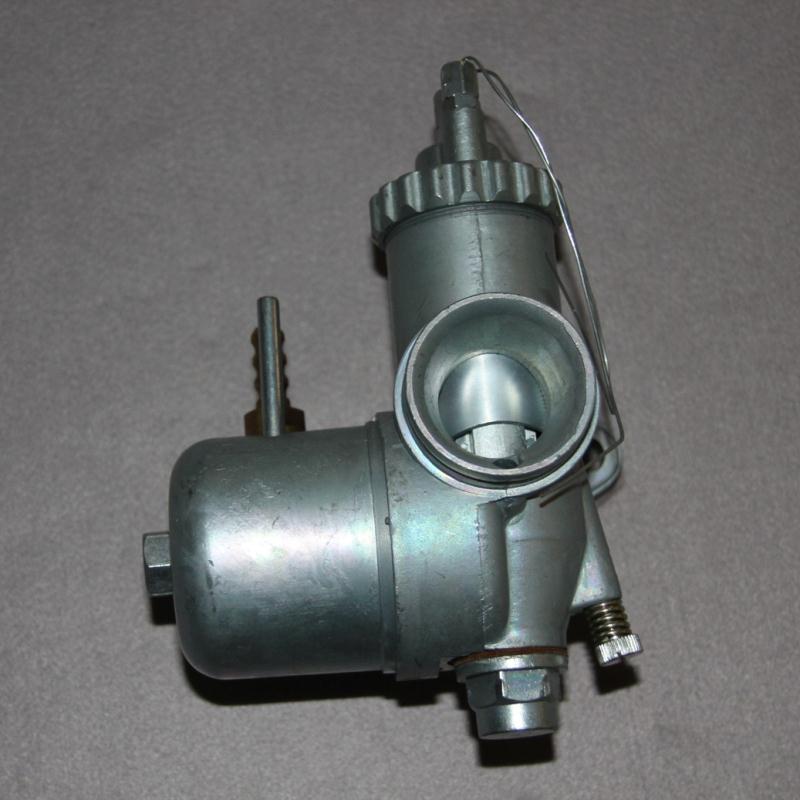
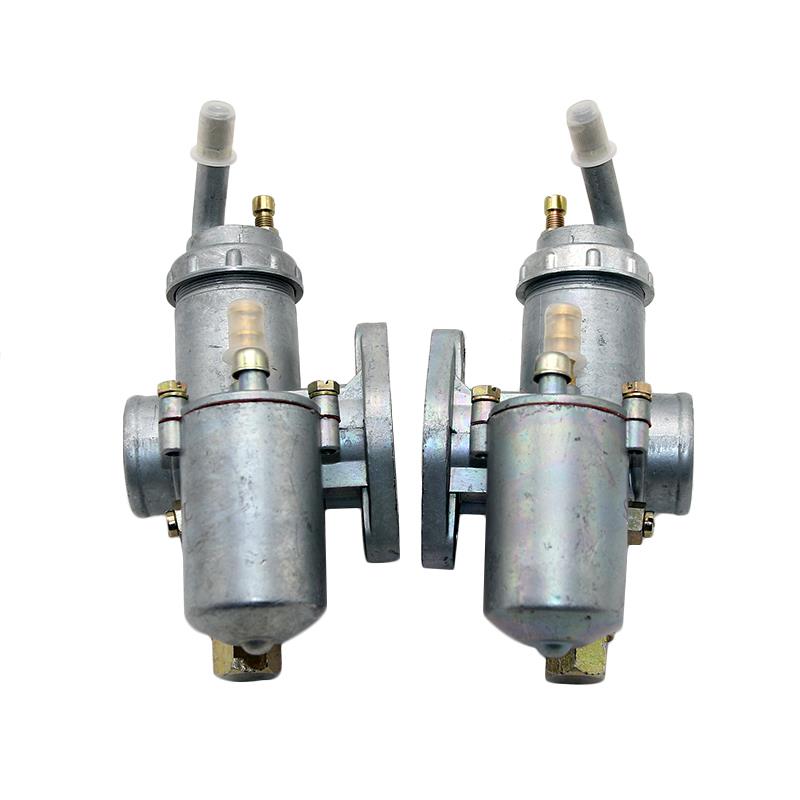
Carburetor Assy Chang Jiang 750 Spare Parts Carburetor Comp. For CJ750 24HP 12V Ural M72 BMW R71
Front Stop Switch Assy. Front Brake Light Switch DJ201100 for Discover 135 Pulsar 200 AS NS XCD125
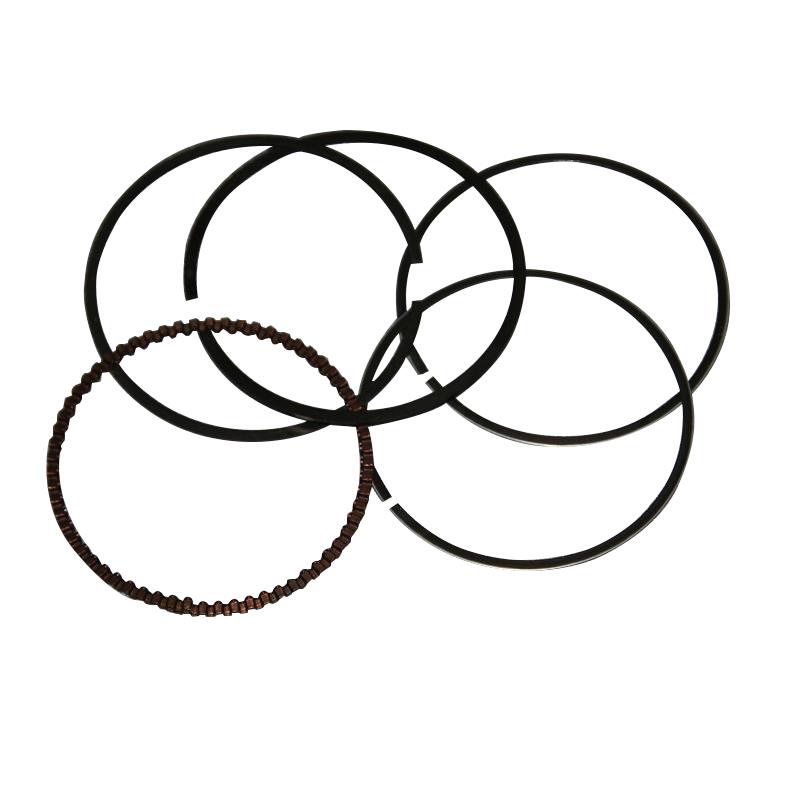
Piston ring Standard Bore Piston Rings fits 57MM STD TVS Star HLX 125 Phoenix 125 Stryker 125 ZT125
Front Brake Caliper Sub Assy. Front Disc Brake Parts For Suzuki Gixxer 150
Front Brake Master Cylinder Brake Lever Set For SUZUKI GSX150 GIXXER SF
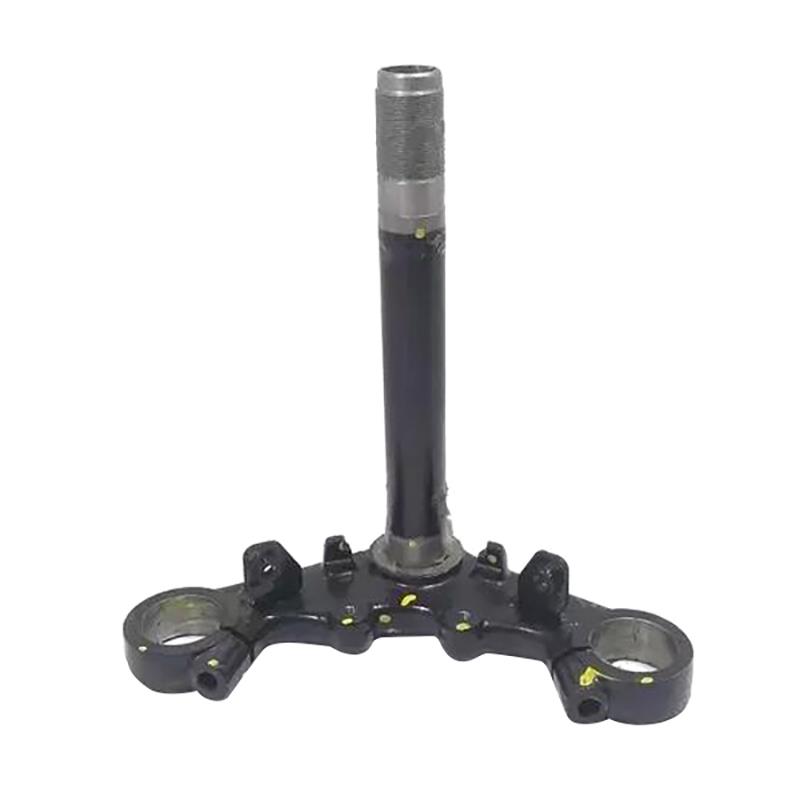
Steering Ball Race Comp. BAJAJ 36JG0011 Kit Steering Head Bearing for Plusar NS150 160 200 AS150 Dominar 250
Starter Relay Bajaj Genuine JN351604 With Grommet for Pulsar 200 RS/NS/AS 135LS 160NS Dominar
Speedometer Gear Box Assy. with Retainer Dust Seal Washer 44800-KRH-901 for Honda XR125LEK XR150LEK
Fork Air Bleeder ValvesCNC Fork Preload Adjusters with Bleedersfor KAWASAKI KLX230 KLX230R 230S 230SM
C.D.I. Unit Genuine CDI igniter ECU 32920-33G00 for Suzuki Address V125 V125G CF46A
Front Brake Caliper Sub Assy.Front Disc Brake PartsFor Suzuki Gixxer 150
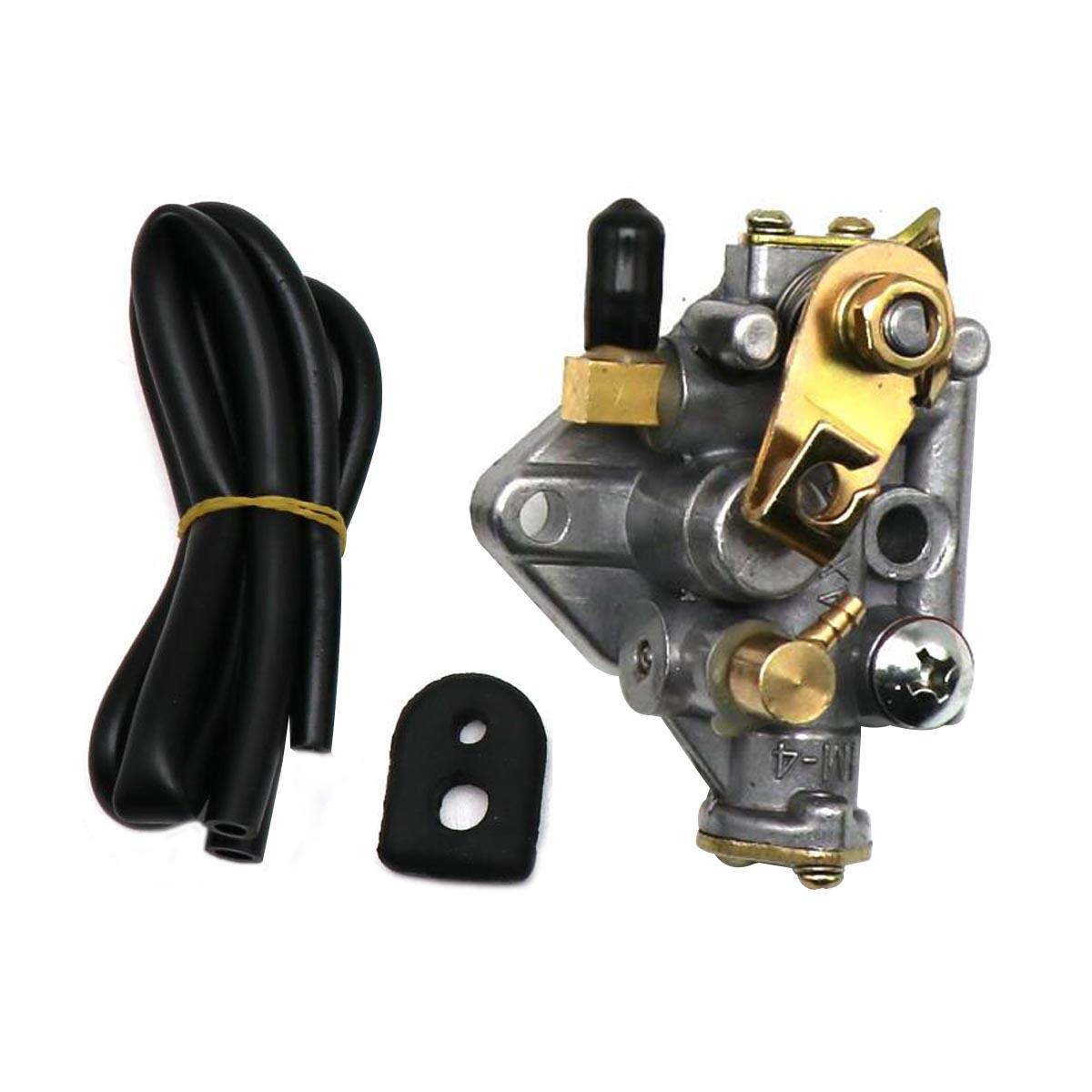
Carburetor Assy Honda PA31M PA31T PA35B PA35D PA35K PA35J PA40B 2T for NE50 SA50 Elite Tact SZ50 Vision Met in SA50
Exhaust Muffler Comp. TVS Phoenix 125 Stryker 125 N5050760 Exhaust Guard N5223130 Logo N5225350
Carburetor Assy Keihin PZ30 Carburador with Cable Choke for CG200 200Z DT 200 Fiera FT180 200 RC RT 180
Headlight Cowl Front Game Deflector for NXR150 Bros ES KS BERA Super DT HAOJIN MD Lechuza Trepador
Carburetor Assy Honda PA31M PA31T PA35B PA35D PA35K PA35J PA40B 2T for NE50 SA50 Elite Tact SZ50 Vision Met in SA50
Rear Brake Disk Front Disc Brake Rotor 55033J410001 for TX200 QJ200GY-A TX125 QJ125GY-17 QJ150GY-8A
Exhaust Muffler Comp. TVS Phoenix 125 Stryker 125 N5050760 Exhaust Guard N5223130 Logo N5225350
Front Bracke Cable Comp. Cable Assy Brake Fr. TVS N3170010 Phoenix 125
CNC Steering Handle Lever Grip L/R Folding Extendable Adjustable Clutch Brake Levers For YAMAHA MT-03 01 07 09 YZF-R1 R25 R3 R6
Front Brake Master Cylinder Brake Lever Set For SUZUKI GSX150 GIXXER SF
Handle Switch JF401401(R) JF401400(L) BAJAJ Pulsar 135 LS
Rear Brake Caliper Sub Assy. OEM No. 69100-34J00-000 Rear Caliper Assy For Suzuki Gixxer 150
Flasher Relay Honda K14 Turn Light Flashing Relay for CB110 CB160 Hornet CBF160 Unicorn Navi 110
C.D.I. Unit Genuine CDI igniter ECU 32920-33G00 for Suzuki Address V125 V125G CF46A
Mark Stripe ABS Chromed Front Fork Cover 51871-05301 with Emblem for EN125-2A EN125-HU GN125 GS125
Throttle Cable Comp. Accelerator Cable 06179-K74-N00 for HONDA Scooter Navi 110
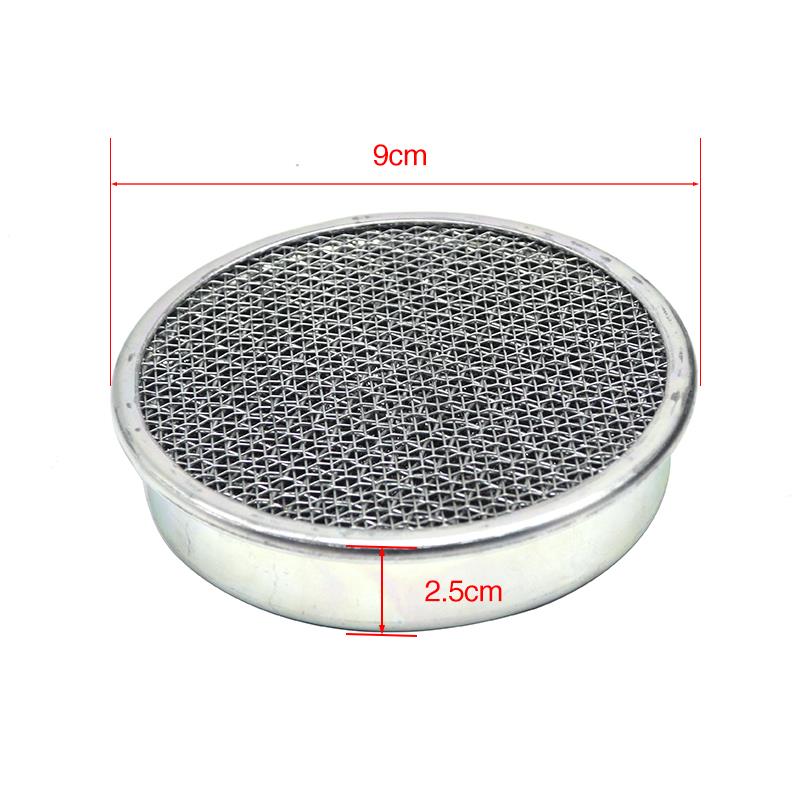
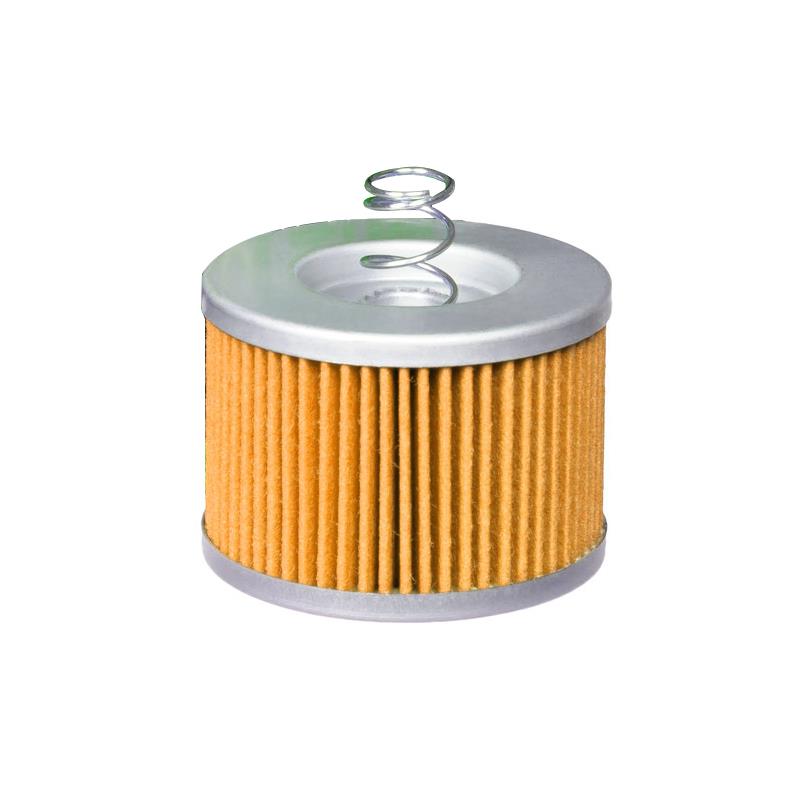
Air Filter Air Filter Cleaner Element 13780-20E00 For Haojue Suzuki AN125 HS125T UA125
Exhaust Muffler Comp. TVS Phoenix 125 Stryker 125 N5050760 Exhaust Guard N5223130 Logo N5225350
Handle Switch JF401401(R) JF401400(L) BAJAJ Pulsar 135 LS
Magneto Stator 12 Poles Original Bajaj Stator For Platina 100 Platino 110 ComforTec DRL
Front Fender ABS Mudguard Fender with Stay HONDA KGA CG125 Cargo Fan125 Titan 2000
Rear Brake Caliper Sub Assy. OEM No. 69100-34J00-000 Rear Caliper Assy For Suzuki Gixxer 150
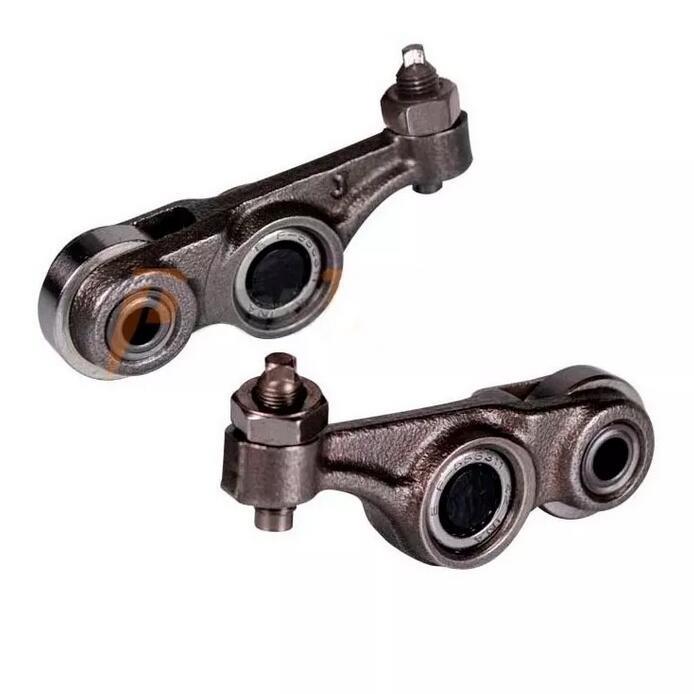
Rocker Arm Comp. Bajaj Engine Parts JA511204 Two-wheeler for Discover 100 DTS-Si BAJAJ XCD 125 135
Ignition System Comp. Electronic Contactless System Of Ignition for URAL DNEPR MT-9 10 11 12 16 K-750 6-12V
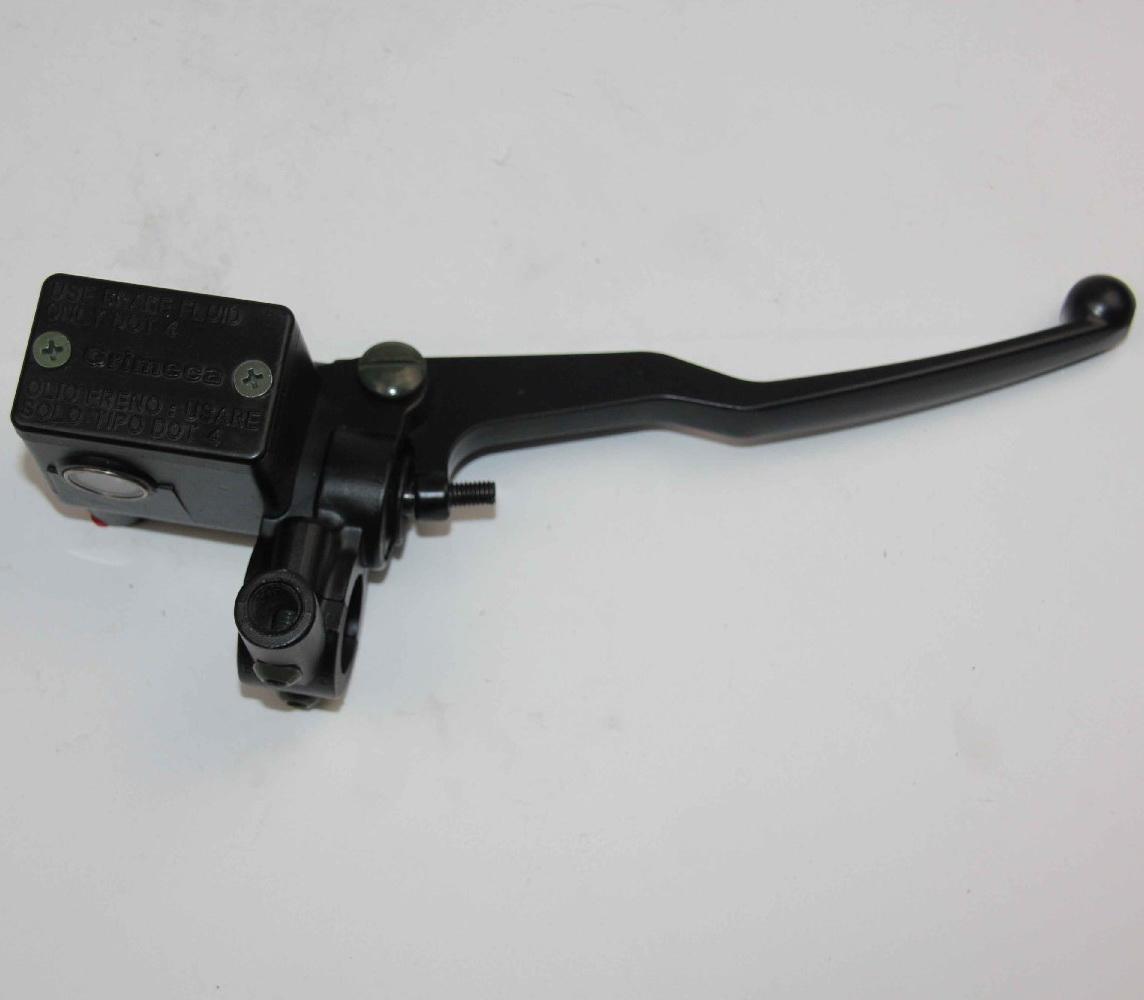
Front Brake Master Cylinder Genuine SYM 45500-A8B-000 Brake Reservoir for Sym Mio 50 Mio 100 HU10W HU05W
Drive Sprocket 428 BAJAJ DH-101117-15T Pulsar 180 UG3 BAJAJ Pulsar 150 DTS-i ES KS Boxer
Exhaust Muffler Comp. TVS Phoenix 125 Stryker 125 N5050760 Exhaust Guard N5223130 Logo N5225350
Fuel Cock Assy Italika OEM F17020035 Motorcycle Fuel Petcock Fit To FT180 FT200 RT180 FT25
Cylinder Block57mm STD N5322130 N5010810TVS Star HLX 125 Phoenix 125 Stryker 125 ZT125
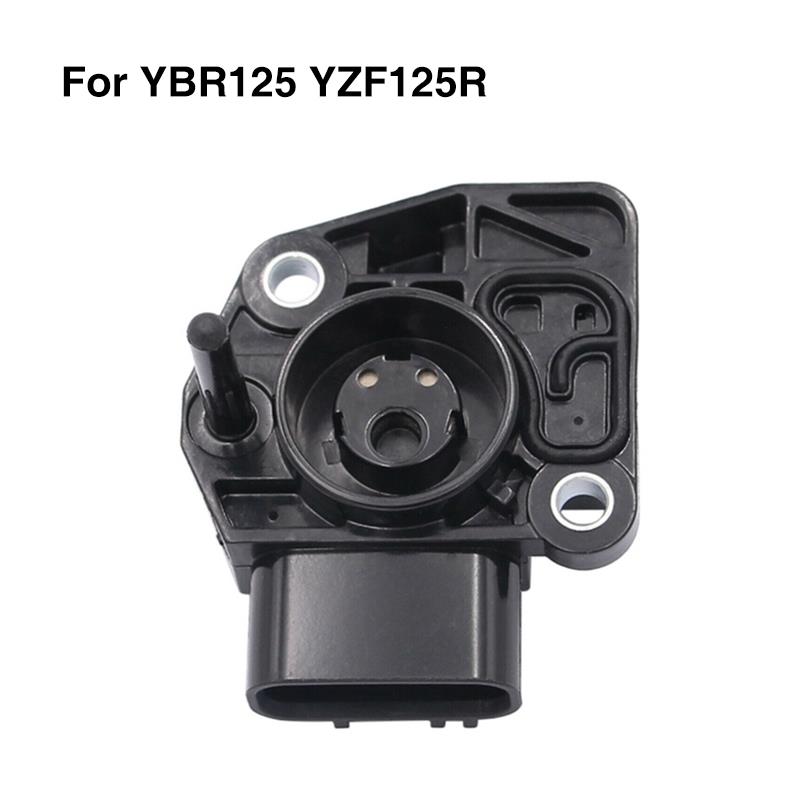
TPS Sensor Set Throttle Position Sensor TPS 5D7-E3750-01 For Yamaha YZF-R125 YS250 Fazer XTZ250
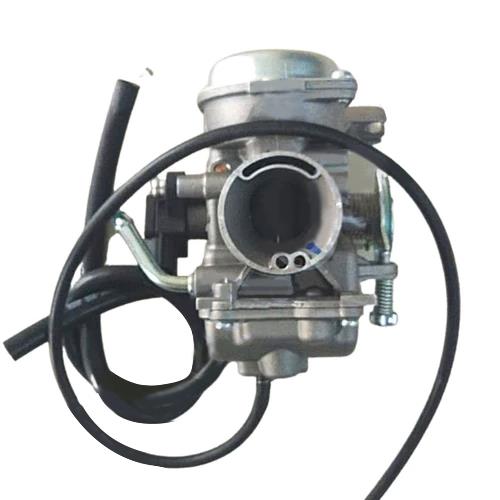
Carburetor Assy 5YY-E4901-02 Carb YBR125 SS125 for YAMAHA GLADIATOR 125 S.Speed YBR125DX
Rear Brake Caliper Sub Assy. OEM No. 69100-34J00-000 Rear Caliper Assy For Suzuki Gixxer 150
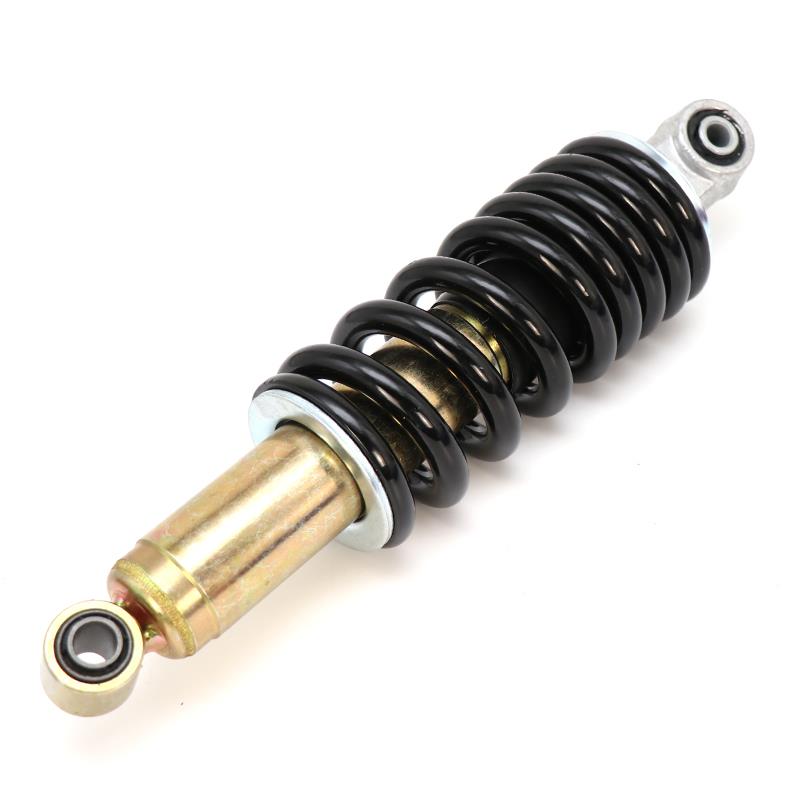
Rear Shock Absorber 305mm 12" Motorcycle Rear Suspension for Honda NXR 125 Bros XLR125 Kick Start
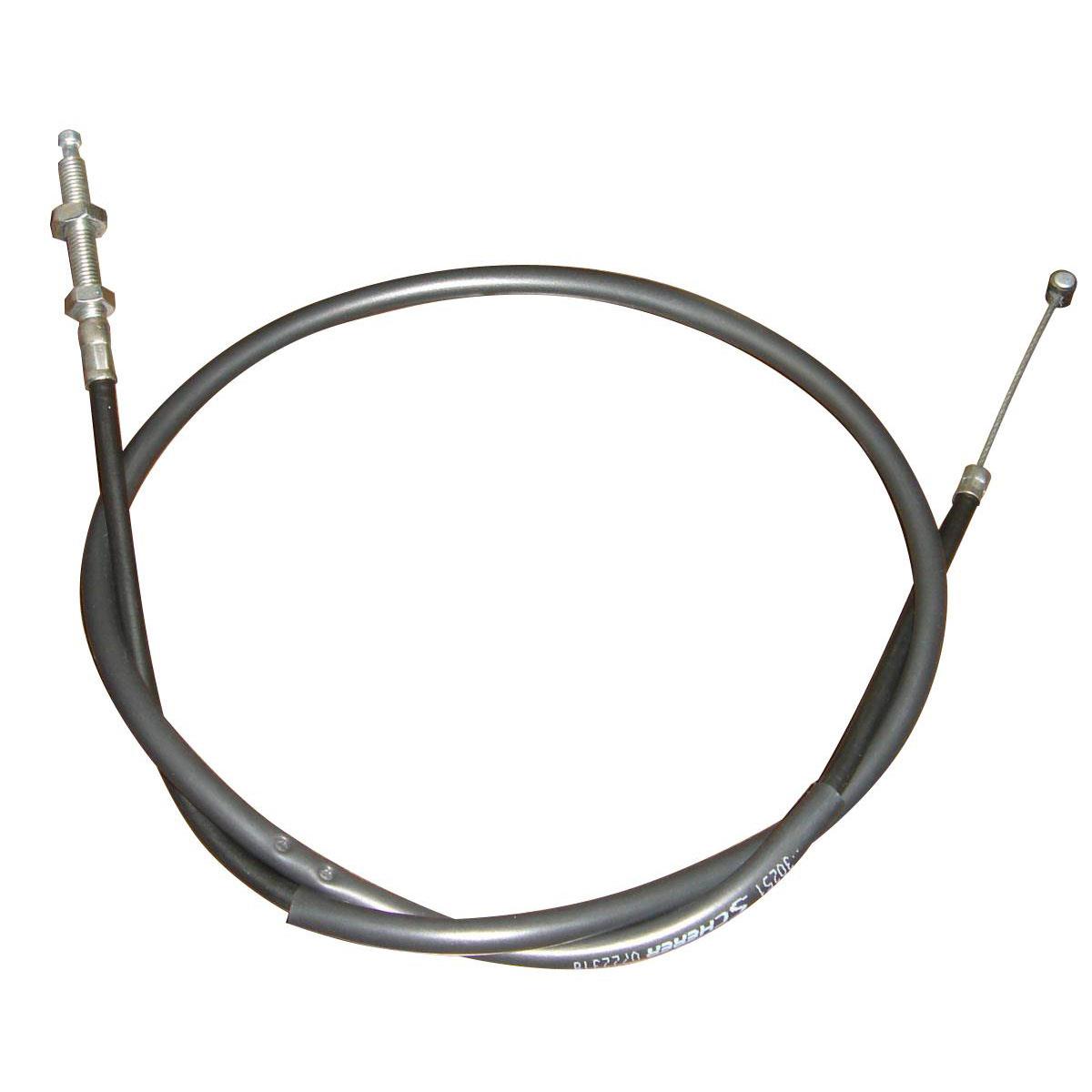
Clutch Cable Comp. 22870-MCG-000 HONDA NX 400 Falcon 2006-2008
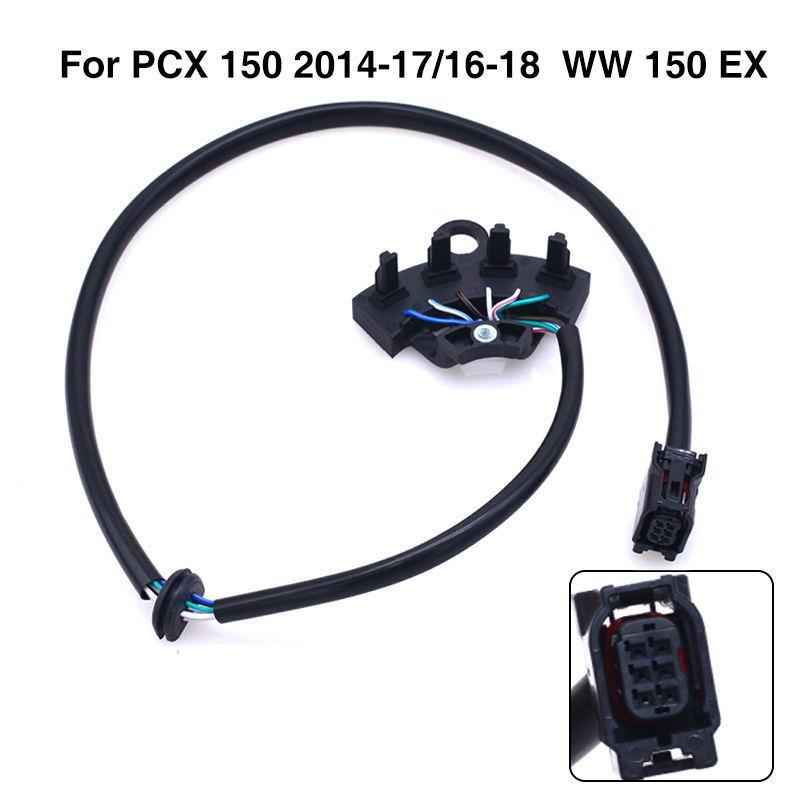
Crankshaft Position Sensor CKP Motorcycle Coil Sensor 31220-K36-T01/J01 For PCX150 WW150 EX 2015-2018
Handle Switch JF401401(R) JF401400(L) BAJAJ Pulsar 135 LS
Handle Switch JF401401(R) JF401400(L) BAJAJ Pulsar 135 LS
Starter Motor Assy. Starter Motor Assy OEM No.31200-KY4-903 HONDA NSR125R NSR125F
Exhaust Muffler Comp. TVS Phoenix 125 Stryker 125 N5050760 Exhaust Guard N5223130 Logo N5225350
Exhaust Muffler Comp. TVS Phoenix 125 Stryker 125 N5050760 Exhaust Guard N5223130 Logo N5225350
Exhaust Muffler Comp. TVS Phoenix 125 Stryker 125 N5050760 Exhaust Guard N5223130 Logo N5225350
Front Brake Disk Motorbike Stainless Steel Front Disc Brake Rotor For YAMAHA FZ16 Byzon 153cc 2010
Exhaust Muffler Comp. TVS Phoenix 125 Stryker 125 N5050760 Exhaust Guard N5223130 Logo N5225350
Carburetor Assy 5UG-14901-10 5UG-14901-00 Replacement Carburetor PD42J-C for YAMAHA Rhino 660 YXR660F 2004-2007
Front Brake Master Cylinder Genuine SYM 45500-A8B-000 Brake Reservoir for Sym Mio 50 Mio 100 HU10W HU05W
Carburetor Float Chamber Hight quality Corrosion resistance Nylon KEIHIN PWK 33/34/35/36/38/40/42MM
Thermostat Switch Assy Honda 37760-MB4-770 Thermo Switch for VF500 700 1100 Magna Sabre Interceptor
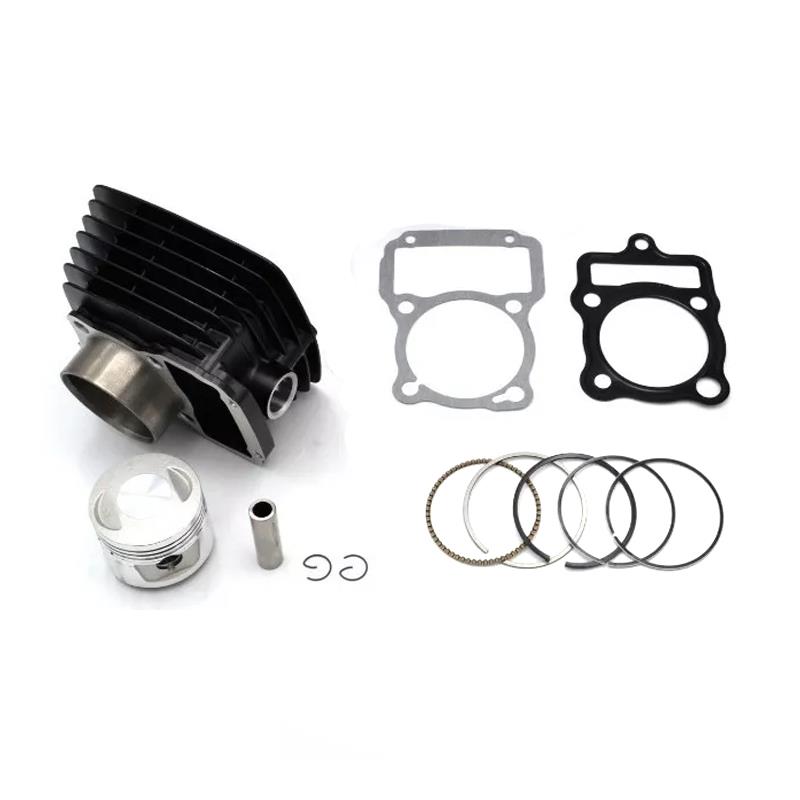
Cylinder Kit Bore: 38mm Cylinder Kit PUCH Maxi 50 K N Rigid Rear NK S Sprung Rear
Mobile Phone BracketMotorcycles Bike Phone HolderFor Motorcycle Scooter Dirt Bike
Exhaust Muffler Comp. TVS Phoenix 125 Stryker 125 N5050760 Exhaust Guard N5223130 Logo N5225350
Steering Handle Pipe Chrome Plated Steel Handlebar For Suzuki GN125 56110-05321-000
Fuel Tank Cowl Set 47012-34J00-19A Fuel Tank Side Cover For SUZUKI GSX150 GIXXER SF
Carburetor Assy 2-Stroke Engine Motorcycle PWK Racing Carburetor For Motorcycle Scooter ATV Quad Dirt Bike
Starter Relay 12V Electromagnetic Device For Yamaha YBR125 YB125 YBR125E XTZ125
Carburetor Assy Chang Jiang 750 Spare Parts Carburetor Comp. For CJ750 24HP 12V Ural M72 BMW R71
Carburetor Jet Needle CR26-33 7 CLIP POSITION Keihin N427-12YXX Genuine Keihin Clip For Needle 0403-802-1000
Fuel Cock Assy Honda Genuine Parts Petrol Fuel Tap for EX5 Dream 100 Super Cub 1000 Wave
Carburetor Assy 4T 24 26 28 30 32 34mm Intake manifold Collector KSR EVO Carburetor Air Funnel
Ignition System Comp. Electronic Contactless System Of Ignition for URAL DNEPR MT-9 10 11 12 16 K-750 6-12V
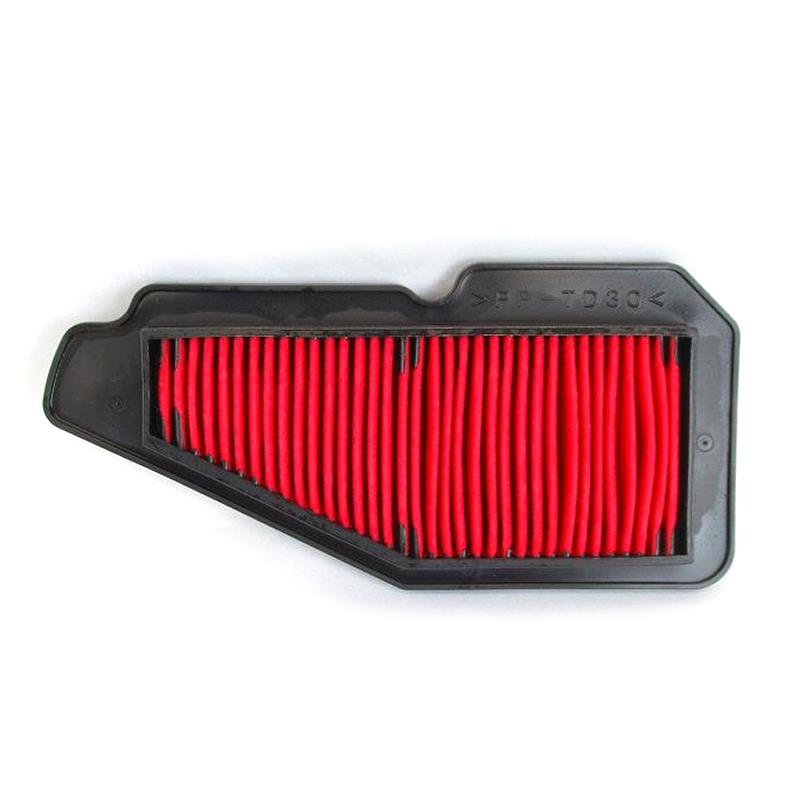
Air Filter Wholesale Motorcycle Air Filter XC115 Cygnus XC115B Ray XC115C Fascino
Rear Fender Genuine Frame Body Plastic Parts Inner Rear Fender India HONDA NAVi 110 CLIQ 110 80107-K74-N00
Drive Sprocket 428 BAJAJ DH-101117-15T Pulsar 180 UG3 BAJAJ Pulsar 150 DTS-i ES KS Boxer
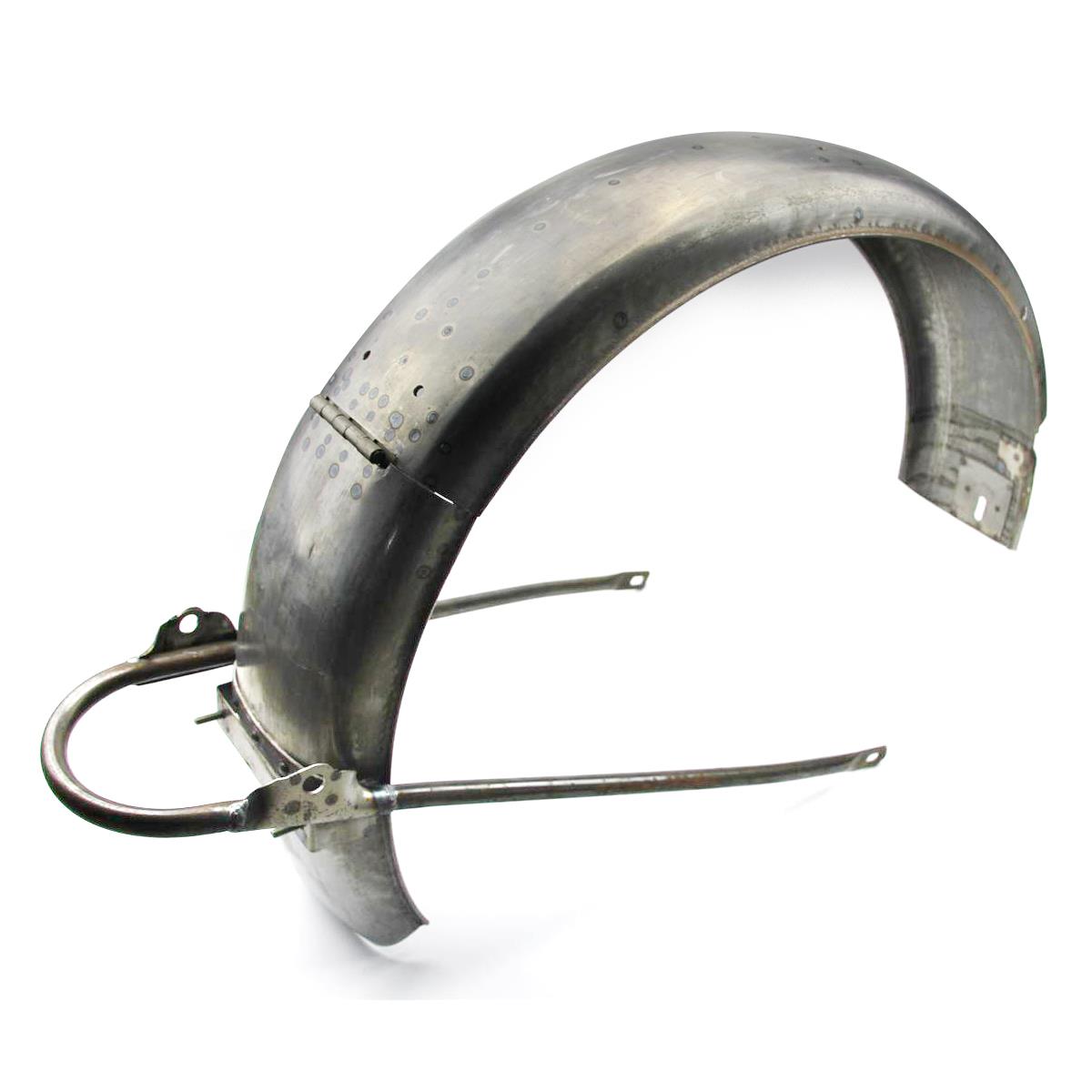
Rear Fender CJ750 Rear Mudguards Folding with Hinge shaft M72 R71 R66 R61 Ural M72 oldtimer Sidecar Parts
Brake pump comp 750cc Motorcycle Rear Brake caliper Disc Brake DIY CJ750 parts BMW R12 R71 Ural K750 M-72
Final Driven Gear Wholesale Rear Final Drive High Speed Gear Assy For M72 CJ750 BMW R71
Exhaust Muffler Comp. TVS Phoenix 125 Stryker 125 N5050760 Exhaust Guard N5223130 Logo N5225350
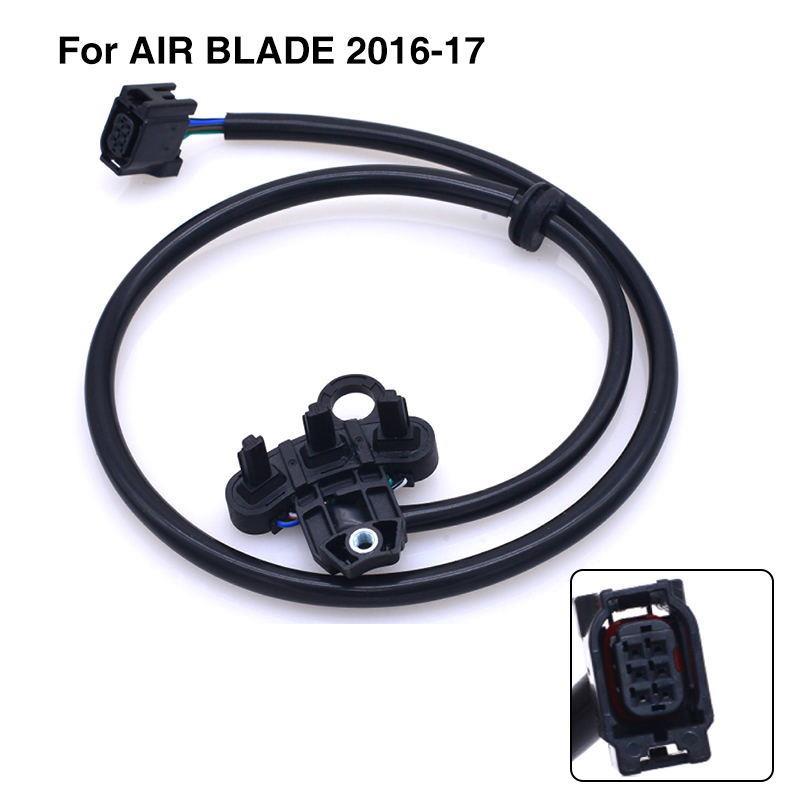
Crankshaft Position Sensor CKP Motorcycle Coil Sensor 31220-K66-V01 For Honda Air Blade 125
Headlight HP2 Megamoto 63127696880-LED Xmoto BMW-Motorrad G 650 GS Sertão G 650 Xchallenge
Starter Motor Assy. Starter Motor Assy OEM No.31200-KY4-903 HONDA NSR125R NSR125F